A.M.LARIN, Boudraa MOHAMED
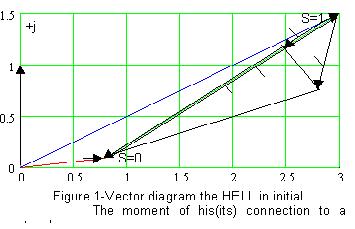
The method of definition frequency characteristics of conductivity is offered on the part of a winding stator electric machines of an alternating current with a symmetric design of the rotor, based on given the measurements of currents and pressure(voltage) at their start-up from a motionless condition. A Fig. 5, pag. 6. Introduction. Rational designing of systems with the asynchronous electric drive probably only on the basis of the complex physical phenomen given deep studying determining behaviour of asynchronous machines in all variety of operational and abnormal modes, is especial predetermination of the transients connected to occurrence of currents and the electromagnetic moments, essentially exceeding rating values. Calculations spent for it should be based on the specified description of electromagnetic properties of the asynchronous engines caused by replacement of a current in cores of a rotor and saturation of ways of magnetic streams. Influence of replacement of a current may be equivalent is reflected with the help of multiplanimetric equivalent circuits. Necessary for synthesis of such circuits set of electromagnetic parameters in the form frequency characteristics may be precisely enough received by experimental methods [1-3]. In the present work the way of definition frequency characteristics of conductivity the HELL with a short-circuited rotor is considered(examined) according to experiences of inclusion in a network breiking machines. Choice of mathematical model. The way is based on established in [4] communications(connections) between making a transitive current s˛Ó˛ţr at inclusion of the rotating or motionless machine in a network with frequency characteristics or diagrams. Under frequency characteristics dependence of complex values of conductivity here is understood on the part of a winding stator From sliding or frequency of a current in a rotor. If the characteristic is known frequency , That according to [4] current of inclusion The motionless electric machine with a symmetric rotor Value of the established current At the initial moment of time corresponds to sliding of a rotor s = 1 under the characteristic : (2) └preidic making a transitive current At the moment t = 0 it is determined on a point of the characteristic At : (3) Initial value so named a transitive periodic current Pays off from a condition . (4) Hence, . (5) On rice 1 the vector diagram at the initial moment of time of connection to a network of the motionless asynchronous engine with two contours on a rotor is shown. If after inclusion of the machine in a network speed of her rotation will not change, (the engine remains motionless), in synchronously rotating axes a vector of the established current It will be motionless. └periodic component Rotates clockwise with synchronous angular speed, fading with a constant of time . Periodic component of a current , Displaying change of the free currents arising in rotory contours, also will rotate with synchronous speed clockwise since the rotor of the electric machine is motionless. At presence on rotor N of symmetric windings a current Represents sum and exponotial in the components having different initial values And constants of time . Thus, the law of change of representing transitive current stator in time under condition of a constancy of sliding will be such , (6) Where - The module and argument of a vector of a current At the initial moment of time: - The module and argument of a vector At the initial moment of time: - Initial values and constants of time exponontial components of a current ; - Argument of a vector At the initial moment of time. . Values exponotial components of a current Are determined by parameters of the equivalent circuit representing parallel inclusion of synchronous inductive resistance and equivalent resistance of contours. The equivalent circuit of such kind is shown on rice 2. Parameters of the specified equivalent circuits correspond frequency to characteristics Also determine initial values and factors of attenuation exponotial making a free periodic current stator in a transitive mode and a short-circuited condition of a winding stator at sudden change of a pressure on his conclusions: