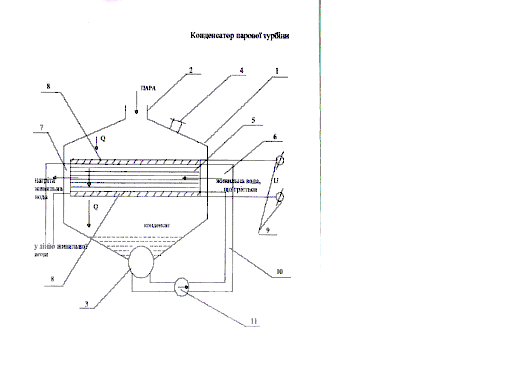
The aspiration to increase results efficiency of thermal electroinstallations to that now raise temperature of a heater up to a maximum and use the refrigerators, capable to take away probably a lot of heat at T.Chto's minimally possible temperature is characterized by expression All energy of falling water and burning fuel finally dissipates as heat. The most appreciable pollution is created by power stations as they make superfluous heat. The efficiency equal, represents that part of allocated heat which has gone on development of the electric power; the rest should be removed in available nearby nizkotemperatyrnuy the tank. Now the maximal working temperature of metals at which metal parts of the steam boiler can function, is close to 880 K.Temperatura Т at which heat is allocated, makes about 300К. Having substituted these values in the equation, we shall receive efficiency about 66 %. Efficiency real modern ТES - less than 40 %. Means, in an environment dissipates about 60 % of heat. The problem of protection of natural water objects from thermal pollution has arisen as a result of use of the rivers, lakes and water basins for cooling circulating water of power stations. The concept « thermal pollution » includes set of hydrochemical and hydrobiological processes which occur in the water environment under action of heat acting from condensers of power units. That influence of waste heat did not break экосистемы a reservoir, the maximum permissible temperature should not exceed more than on 3? With natural temperature of the hottest month of year for last 10 years. For an establishment of maximum permissible temperature it is possible to use value of temperature of the hottest month with the account перегрева. In figure 1 dependence среднемноголетней natural temperature of water of the hottest month from breadth of a place is shown. She it can be applied to an establishment of maximum permissible temperature of a reservoir. These norms can be sustained in the event that specific thermal loading on a reservoir does not exceed 12-17. With the purpose of decrease in thermal pollution on power stations the condenser of the steam turbine which provides decrease reduction in thermal losses as cooling water comes back in the circuit of work of the condenser with the pump established in itthrough a branch pipe of a supply of cooling water is offered, instead of is dumped in a reservoir. Thus reduction a current consumption as submission of cooling water is made not from a rate - cooler, and from конденсатосборника is reached, that demands the pump of low power. As the heated up water is not dumped in a reservoir, and directly acts in a line of a feedwater, decrease in environmental contamination is reached. In figure 1 the circuit of the offered condenser of the steam turbine is represented.
Figure 1 - The circuit of the condenser of the steam turbine 1-case;2-mouth; 3-condensatosbornik; 4-branch pipe отсоса air; 5-tubes; 6-branch pipe of a supply of cooling water; 7-branch pipe of tap of cooling water; 8-casing; 9-source of electrosupply; 10-pipeline; 11-pump. |