Shevchenko Julija Vladimirovna
Abstract of dissertation in the theme of master's work: Study of influence of non-polar reagents during flotation of coal
Introduction Coal is one of important thermal and electric energy sources, technical raw material for major types of production. The necessity in coal as fuel and technological raw material in ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy production of artificial abrasives materials and chemical processing increases.
Application of narrow-cut technique of mining in Donbass is accompanied by the increase of output of shallow classes. At coals enriching factories, as a result of growth of ash level, the ash level unconcentrated sifting out and coarse-grained mud of raw material increases. In this connection its enriching acquires the special importance. Foamy flotation can be one of methods providing the increase of efficiency of enriching of coarse-grained mud.
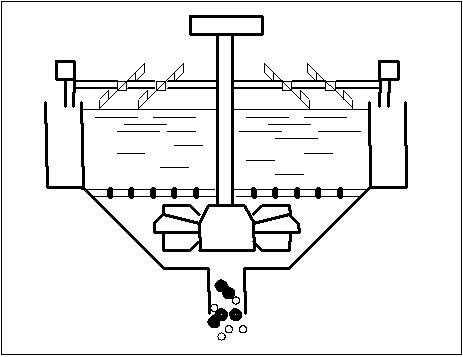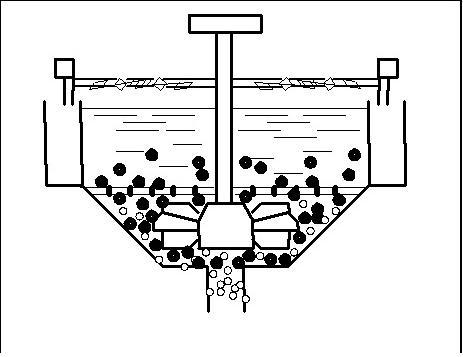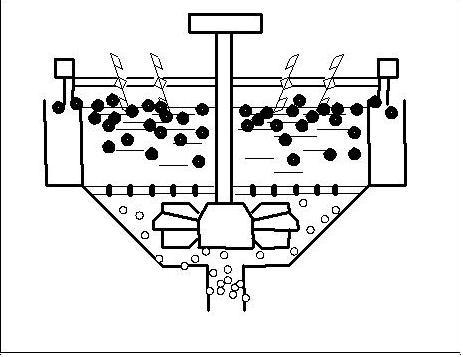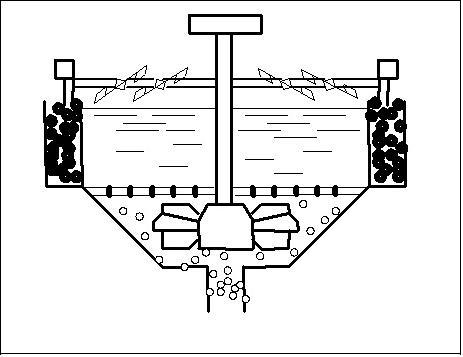
Picture 1 - The foamy flotation.
The purpose of this work is research of process of foamy flotation, determination and verification of applicability of separate methods, for estimation of reagents at enriching of coal. For realization of this purpose such problems are set: • research of physical and chemical properties of biphasic bubble column as an environment where the division of mineral corns takes place; • review of the applied methods; • development of reagents estimation method; • determination of surface-tension; • research of properties of foaming.
1. Reagents – frothers The purpose of coal flotation reagents is to create stable bubbles, to alter the natural or induced hydrophobicity of coal, pyrite, or ash forming minerals, or to alter the flotation operating conditions, through, e.g., dispersion, flocculation, acidity control, etc. Not infrequently, a reagent may influence more than one of these functions, and its effect may differ markedly depending on the concentration used. The primary function of a frother is to produce a copious supply of bubbles of the proper size and at modest cost. The bubbles produced should have sufficient toughness and persistence to provide the transport of coal particles from the slurry to the froth, but they should not be so tough and persistent as to prevent their destruction by water sprays in the froth launder or to interfere with the subsequent pumpability of the froth concentrate. The frother should have no collecting power for any particle other than the particle to be floated. Since one of the major goals of coal flotation is to achieve selectivity between coal and gangue particles, there are many subtle properties of the frother which can either enhance or restrict its ability to selectively float only the desired particles. The frother should also be readily dispersible in water. The most commonly used frothers for coal flotation have been cresol, pine oil, alcohols (e.g., MIBC), and the polypropylene glycol ethers (e.g., Dowfroth 250). Historically, the first coal flotation frother used was probably an impure cresol, a byproduct of coke making. There are several problems with the use of this frother: 1) it absorbs strongly onto coal, so reducing the frother concentration in solution as to require relatively large amounts of this reagent; 2) commercial grades used for frothing are relatively impure and have a substantial, but highly variable, collecting power for coal (ostensibly due to its variable benzoid compound content); 3) it may pose environmental and health problems. For these reasons it is rarely used as a frother today. Pine oils, whose principal constituent is terpineol, have also been popular frothers for coal. They have suffered from the defect of composition variability due to the source of the conifer used for their production. They also are known to have a significant, but variable, collecting power.
2. Research of physical and chemical properties of biphasic bubble column as an environment where the division of mineral corns takes place To basic properties of biphasic bubble column, having substantial significance for technology of foamy flotation belong: stability, speed of destruction, height of froth, coalescence of air bubbles, dispersion, density and viscosity of froth. The basic parameters of foamy layer are related to chemical properties structure of superficially-active matters. Biphasic froth depending on the type and concentration of superficially-active matters contains the different amount of interfilm liquid phase expiration of which in a greater or less degree changes the density of foamy layer. Along with a density its viscosity is major description of biphasic foamy layer. The presence in the biphasic foamy layer of thinly-dispersions air bubbles results in difficult character of resistance of internal friction during deformation of such system.
3. Study of influence of non-polar reagents during flotation. Adsorption of reagents on a solid surface of the pulp is of particular interest because flotation efficiency depends greatly on the intensity of reagent adsorption on a solid surface of the pulp. Study with an adhesiometer has shown that non-polar reagents adsorb mainly on vitrinite {a pure coal particle). Adsorption of reagents is stated to be proportional to vitrinite content. It changes with the reflectance of vitrinite (Ro). The emulsion method has been used to study reagent adsorption on the surface of coal particles of different size fractions, petrographic composition and degree of metarnorphism. Depending on granulometric composition non-polar reagent adsorption is linear in nature. Adsorption rate of non-polar reagent by coal particles is high for a fine size fraction and low for a coarse size fraction. To the present day the problem of selection and research of flotation reagents has not been practically solved yet. Products of oil refineries, such as domestic fuel, gas oil of catalytic cracking and coking, arc used as a non-polar collector today. Studies carried out in the institute's laboratory and at coal preparation plants have resulted in the suggestion that heteropolar substances such as define oxides and cubic residues of caprolactam can be added for increasing flotation activity of non-polar reagents. Consumption of non-polar reagents at coal preparation plants varies from 2 to 5 (6) kg/t depending on the degree of metamorphism.
Conclusions During the studies with adhesiometer, vitrinite has been proved to have the best adsorption capacity relative to the non-polar reagent. It has been revealed that sorption capacity of fine coal depends on vitrinite content for different metamorphosed coals. The higher the vitrinite content the better the sorption capacity. Use of non-polar reagent, activized with rnicroadmixtures, makes it possible to increase notation process efficiency. Flotation process efficiency depends on the quality of the blend under preparation.
LIST OF THE USED LITERATURE 1. ANT1PENKO, L.A. Development of physico-technical methods of coal pulp conditioning during flotation. Author's abstract for a doctor's degree, Kemerovo, 1998. 2. PLESKACHEVSKAYA, A.A., KHARITONOVA, ZH. D., and BARANOV, L.A. Usage of the emulsion method for determination of kerosene in flotation tailings of coal preparation plants. Preparation and utilization of coal. Scientific proceedings. Scientific and research institute 'Kuzniiugleobogashcheniye'. Prokopyevsk, 1976. Issue IX, pp. 118-124. 3. IVANOV, G.V., TYURNIKOVA, V.I., and ANTIPENKO, L.A. Influence of ethylene oxide on collective properties of kerosene during coal slime flotation. Preparation and utilization of coal. Scientific and research institute 'Kuzniiugleobogashcheniye'. Prokopyevsk, 1976. Issue IX, pp. 93-103. 4. Coal Preparation 5th Edition. Editor Joseph W. Leonard, III. Published by socienty for mining, metallurgy and exploration, inc. Littleton, Colorado 1991. pp 458-459. 5. В.К. Тихомиров. Пены. Теория и практика их получения и разрушения. М.: Химия. – 1975. – 264с.
RUS | UKR | DonNTU | Master's portal | Biography | Library | Links | Search report| Individual task