 Ferrous metallurgy is priority branch of economic development in Donetsk region. It takes one of the leading places in melting cast iron and steel in Ukraine. One of the most important directions of the development for ferrous metallurgy is improvement of quality. Requirement for metals increase every day. Export is a big part in iron industry. Further enlargement of metallurgy production is important part of ukranian economic growing. Ferrous metallurgy is priority branch of economic development in Donetsk region. It takes one of the leading places in melting cast iron and steel in Ukraine. One of the most important directions of the development for ferrous metallurgy is improvement of quality. Requirement for metals increase every day. Export is a big part in iron industry. Further enlargement of metallurgy production is important part of ukranian economic growing.
The requirements to me metal quality are very high. It is necessary to build up complex sytem of quality control. Production of metallurgy passes through the complex testing in scientific laboratory.
Metallography takes especial attention as a science about crystal structure of metals and the alloys, visible with the eye and with the help of a microscope. It gives most of information and define if it is necessary to do the further production control.
Technical progress has big influence on all the human activity on the past few years. The resolution of the mocrosope increase. Now it is possible to combine microscope with computerand to build up an interesting and useful complex.
The analysis of different laboratories work has shown that computer is not used competely there. Most of them are used for simplification of microimages taking with microscope. Digital image processing and analysis with the help of computer is not used in metallographic laboratories nowadays in full way.
Present-day methods of steel and alooy production has no opprtunities to get completely pure metal without any non-metallic inclusions. More or less inclusions are presented in any steel in order with it mixture and conditiond of production. Usually amount of non-metallic inclusions in steel is not higher than 0,1%. However, number of inclusions in metal is very high because of it extremely small size.
Non-metallic inclusions in steel are foreign substance. It break homogenety of structure, so its influence to the mechanical and other properties could be considerable. During deformation which occure in the process of flatting, forging and stamping non-metallic inclusions can lead to crack and to fatigue failure of steel.
While investigate influence of non-metallic inclusions to the quality of stell the great importance is its properties: size, shape, chemical and physical characteristics. All this properties depend on chemical content of steel, method of smelting and for certain steel grade. It can change in wide limits even for one and the same mode of production.
Different methods for non-metallic inclusions analysis are developed and used now. It allows to determine content, structure and amount of non-metallic inclusions in steel and alloies with high exactness.
In metallurgy it is very important to avoid presence of non-metallic inclusions in metal. For metallography it is important to develope various methods of recognition and characterisation of non-metallic inclusions.
In this scientific work the main problem is to execute detailed studying of non-metallic inclusions in steel and automation of stell quality assurance.
The most popular method for inclusions classification which is commonly used in Ukraine is comparison microimages from the microscope with standart microimages where the most common inclusions of different shape, character and size. All this microimages are gathered in standart scale. Nowadays standart scale GOST 1778-70 is widely used in metallographic laboratories. It contents three types of inclusions which are oxides, sulphides and silicates. Oxides are gatherd in the first group, sulphides and silicates in the second group (as its are very similar and have the same influence to steel) and nitrides are in the third group. Each group of inclusions has five number^ the first number are the smallest inclusions and the fifth number are the biggest. Changing from one number to another is accordance to the area of inclusions and is two times bigger with every number.
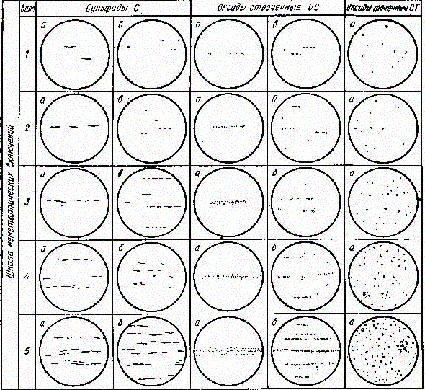
Research of metal samples is entirely reduced to the analysis and interpretation of their images in the automated system of digital microimages processing. Reliability and objectivity of the stell control and technological processes management depends on perfection of detection and methods which are used in the automated microimages analysis.
However results of laboratory researches have big influence from the person who is working with this. At this stage of the microscope analysis automatic registration of microimages with this specially created hardware-software complexes, described below, is already achieved. Thus the analysis of the received image occurs without attraction of computer technics. After introduction of results of the given work in laboratory it will be possible to reduce essentially time of the analysis of each sample and to increase accuracy of target results.
|