

Faculty:
Geotechnology and Management of Production
Speciality:
Labour Protection
Theme of master's work:
"Research of the deformation process of the bolted rock massif with the help of modelling by the end elements
method"
Leader of work:
docent Novikov Aleksandr OlegovichEmail:shishko_d@mail.ru
Abstract
1.Topicality.
2. Analysis of the present models of the rock mass condition around workings.
3. Analysis of the opinions on the mechanism of anchor bolting interaction.
4. Conclusions.
5. Library.
Topicality
To increase the operating efficiency it is first of all necessary to solve the problem of rational timbering and firm workings support. The presently used shaft lining despite materials consumption do not meet mining and geological conditions they are used in. That is why at present to ensure the overhaul workings maintenance new methods of shaft lining are developed and implemented. They are characterized by higher bearing power and less steel intensity. Anchoring (bolting) belong to this type of lining.
One of the technological progress directions is developing mine workings with the use of anchor bolting with the steel arch support.
Use of this lining type has shown that anchors lessen roof rock displacement and load on framework structures. However the absence of the admitted method of anchor bolting parameters calculation as well as absence of simple and efficient constructions of yielding anchor lining do not allow to ground the area of its rational use.
Aims and tasks of the research.
The aim of the research is to examine the mechanism of bolted retaining rock deformation with the help of finite element method (FEM) modeling and to ground anchor bolting parameters and rational area of its use.
Scientific novelty and practical value
Experience of anchor bolting use has shown that this type of lining can be used in a wide range of rocks varying in competence and structure alone and together with supporting lining.
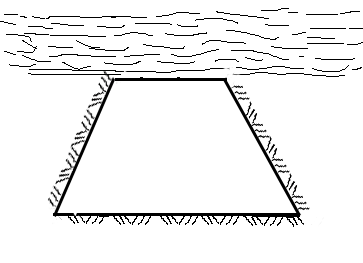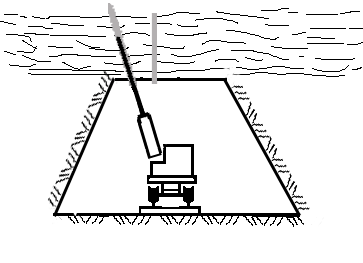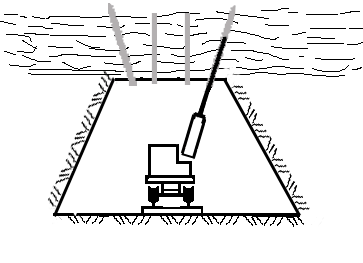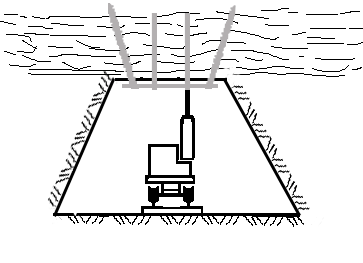
Animation 1. The bolted rock massif
Depending on roof rock structure there are the following main conditions of the shaft use:
- weakly stable stratiform rock of direct or indirect roof are bolted by anchors to the main roof;
- various rock layers tied by anchors compose a beam preventing roof from collapsing;
- around each anchor the parts of fractured reservoir are squeezed to each other creating a steady block. Along the parameter of such workings there is a circle of such blocks supporting each other like in a stone arch.
Analysis of the present models of the rock mass condition around workings
Mining damages the balance of rocks and leads to re-distribution of tension in the surrounding massif. Increased tensions along the outline of a working result in appearing of a zone of inelastic deformations around workings. Zone structure and rock deformation character depends on the depth of the extraction, rock types and their physical, mechanical, rheological characteristics, shaft size, type and characteristic of the support.
According to Chernyak I.L. there are 3 types of deformations:
1. In the rock around the shaft there appears the zone of inelastic tight deformations less than long-term strength.
2. The second type of deformations appears at tension along the outline more than long-term strength but less than instantaneous rock steadiness.
3. The third type of deformation around the shaft appears when the tension along the outline is more than instantaneous rock steadiness.
Analysis of the opinions on the mechanism of anchor bolting interaction
Opening strength means its ability to keep the definite parameters and cross-section form during the given lifetime.
To achieve the strength of the opening it is necessary to increase the rock bearing capacity by any type of support. The most efficient way is to increase flexural and tensile strength affecting the rock. It is necessary to strengthen the rock against tensile stress. It is achieved by bolting steel and polymeric rods - anchors.
In contrast to framework anchor bolting is constructed being pre-stressed, that is why immediately after the construction the cohesion between the rock layers or gullets.
The mechanism of anchor bolting and supported rock interaction is described in the theory by A.T.Talpakorev. He shows that anchor bolting due to its yielding cannot completely prevent the process of inflexible roof rock displacement - it can only limit its speed and under certain conditions to stop.
During displacement the stress condition of the rock decreases and anchors ability to react a load increases.
This process will continue developing until there appears balance in the system "bolting - rock". If anchor bolting is constructed behind the basset definite stress is created then rock strata will be linked in natural connection and their stratification will be prevented.
This also increases rock bearing capacity. Due to anchor bolting layers slips is decreased.
Opening can be supported with anchor bolting when the roof is not flat, but arch, caved are characterized by different ways of layers attitude.
In arched workings anchors are bolted in the rock where there is no equilibrium stress condition and tension does not exceed elastic limit.
To resist tensile stress anchors have to be bolted to levels of incipient cracks.
In rock strata with different bed attitudes anchors have to be fan-shaped taking into account attitude.
At present there are more than 600 different anchors types - steel, reinforced concrete, plastic, bamboo, rope, which have been systematized for the first time.
Conclusions:
1. The use of anchor bolting allows to exclude expensive steel arch support during seam developing in Donbas. Anchor bolts with steel plate and net installed at the angle of 60-70 on epoxy (instead of vertical bolts) increase the bearing system of the system "anchor - working" by 30%.
2. Analysis of the rock condition change around workings shows that in the conditions of deep mines the formation and development of inelastic deformation zone take place. Its size is about 2-6 m.
3. At present there is no common opinion on the mechanism of anchor bolting and surrounding rock interaction.
Library.
1. Заславский Ю.З., Дружко Е.Б. Новые виды крепи горных выработок. М.: Недра.1989.- 256с.
2. Лисичкин В.Г., Зислин Ю.А., Берлявский Г.П. Анализ тенденции в применении металлических арочных крепей на угольных шахтах // Шахтное строительство. - 1984.- № 1.-С.8-9.
3. Розенберг Ф.Я., Елагин Л.И. О совершенствовании крепей для подготовительных выработок// Шахтное строительство. - 1980.- С.19-23.
4. Широков А.П. Теория и практика применения анкерной крепи. - М.: Недра. 1981.- 381с.
5. Байкенжин М.А. Разработка способа поддержания пластовых подготовительных выработок глубоких горизонтов шахт податливой рамно - анкерной крепью: Дисс. канд. Техн. Наук.- Караганда.- 1987.- 156 с.
6. Клюев А.П. Опыт применения комбинированной анкерно - арочной крепи.- Донецк, ЦБНТИ Минуглепрома СССР.- 1989.- 4с.