
"Multiagent systems for studing of students at cathedral level"
Abstract*
The main difference of modern intellectual systems is their distribution, maintenance of processing and application of the distributed knowledge. The accent of development of artificial intelligence techniques becomes on transition from the isolated systems of an artificial intellect, from individual systems to the distributed intellectual analysis of the information and working out of multiagent intellectual systems (MAS).
On the basis of the multiagent systems using artificial agents, the virtual organisations which represent one of the most promising areas of development of an artificial intellect are created. Are besides, integrated with modern network WWW-technologies, and artificial intelligence techniques, including big a database (knowledge) and systems of object-oriented programming.
Today the basic directions in working out МАС are the distributed artificial intellect and an artificial life. The kernel of distributed AI is made by researches of interaction and cooperation of a small number of intellectual agents, for example, the classical intellectual systems including the knowledge bases and решатели. The main problem in distributed AI is working out of intellectual groups and the organisations, capable to solve a problem by the reasonings connected with processing of symbols. Differently, here the collective intellectual behaviour is formed on the basis of individual intellectual поведений. It assumes the coordination of the purposes, interests and strategy of various agents, coordination of actions, the resolution of conflicts by negotiations; the theoretical base is made here by the results received in psychology of small groups and sociology of the organisations.
Important section distributed AI is the co-operative distributed decision of problems. It is a question of a network poorly connected among themselves решателей which in common work with a view of the decision of problems which is beyond individual possibilities. Various knots of a similar network, as a rule, have unequal experience (knowledge, the points of view) and different resources. Each knot should be capable to modify the behaviour depending on circumstances, and also to plan the strategy of communications and cooperation with other knots. Here indicators of level of cooperation are: character of distribution of problems, association of the various points of view and, of course, possibility of the decision of the general problem during set time.
The second direction — an artificial life — is connected with treatment of intellectual behaviour in a context of a survival, adaptation and self-organising in the dynamical, hostile environment. In the tideway of ИЖ the global intellectual behaviour of all system is considered as result of local interactions of the big number of simple and unessentially intellectual agents.
For construction of training system for students it is necessary to solve following problems:
- Creation of model of knowledge of the teacher.
- Creation of model of a studied subject.
- Creation of model of the student.
Here there are following problems:
- How to reach such representation that knowledge was not static, but dynamic?
- How to receive such model that knowledge has been formalized on the one hand, and are easily accessible with another?
- How to receive an automatic conclusion of new knowledge?
- How to receive an estimation of knowledge of students on the basis of accessible knowledge?
- How to provide the maximum adaptation to each trainee. Such systems at a choice of the next educational influence should consider all picture of knowledge of the pupil in a studied subject, and even its personal features.
The given questions are actively discussed by many scientists of the world, however the program system solving in full given questions does not exist yet.
Now the question on what computer program should be qualified as the agent or multiagent system, is in a stage of intensive discussion [2]. It is accepted to distinguish two definitions of the intellectual agent — "weak" and "strong".
As the intellectual agent in weak sense it is understood software or hardware realised system which possesses such properties as: autonomy, public behaviour, reactance, activity [1,2,3].
Strong definition of the agent includes use of some additional properties. In particular, the main thing from them is presence at the agent at least some subset so-called "mental properties" which knowledge concerns, belief, intentions, the purposes.
The idea of multiancy assumes cooperation of agents at the collective decision of problems. In multiagent system aгент which is not capable to solve some problem independently, can address to other agents. Other variant when cooperation is necessary is use of collective of agents for the decision of one general difficult problem. Thus agents can plan actions, being based not only on the possibilities but also to consider plans and intentions of other agents. It is known, that collectives even the elementary automatic machines in which each of them pursues only the primitive aims, as a whole are capable to solve very much challenges. For example, a beehive or an artificial neural network.
For an exchange with each other the information agents carry on negotiations. The scheme on which such negotiations are carried on, defines the report of interaction of agents (drawing see more low). There is a number of schemes of negotiations [1,2].
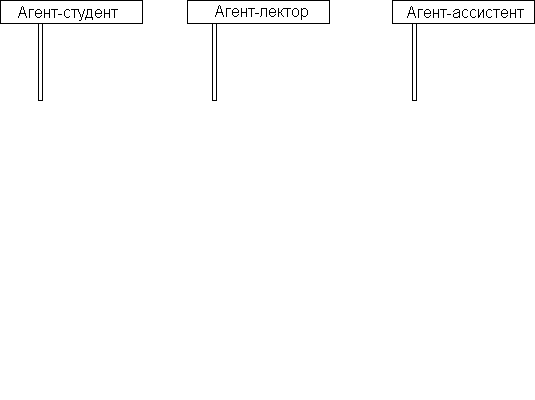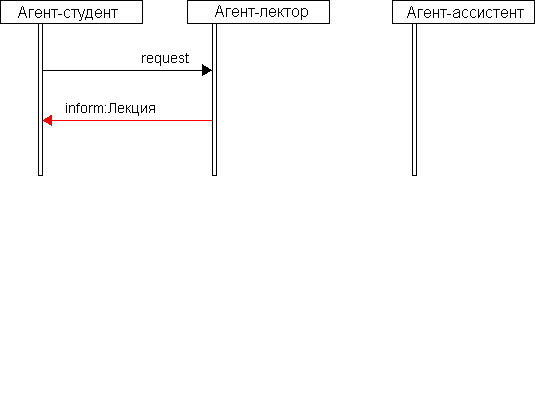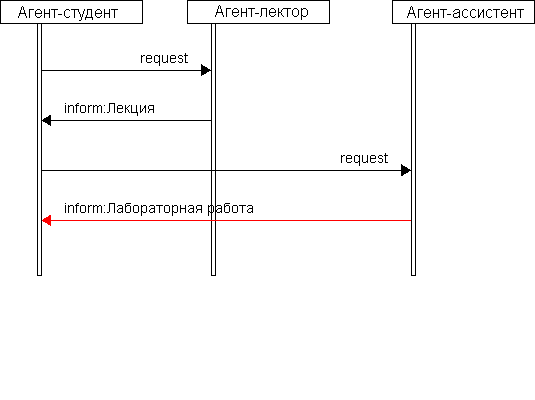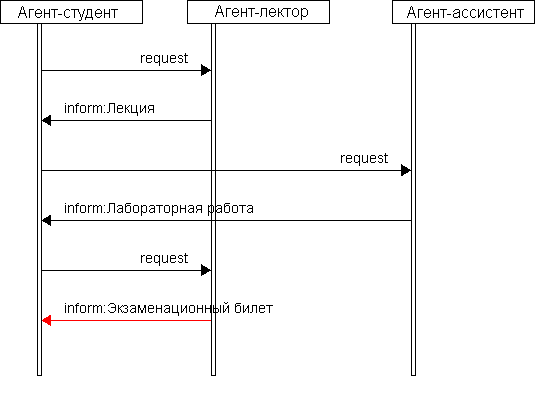
Message exchange between agents (7 frames, duration of frames is 1s., 535х400 pixels, 27.9 Kb, made with MP Gif Animator)
Typical representation of tool systems of creation MAS, system Bee-gent is. It is intended for designing and realisation MAS. In it the special MAS-LIBRARY realised in language Java, and technology is used, is based on methodology of the specification of behaviour of agents of the distributed system. Thus in system Bee-gent some types of agents are used: packers (agent wrappers) and intermediaries (mediation agents) [4].
The behaviour of all system directed on achievement of definite purposes, is based on the specification of "conversations" (message exchanges), in which basis exchange XML/ACL of messages through interaction reports (interaction protocols).
In Bee-gent the special language ACL developed on the basis of KQML is used. The logic structure of ACL-expressions is represented in the form of XML. Therefore language of an exchange of messages of agents in Bee-gent is called XML/ACL.
Agency library of Toshiba is enough developed and meets the basic requirements to components of the software of the given class. Перформативы XML/ACL higher, in comparison with KQML, level. For the specification of reports of interaction it is offered to use the programming language, instead of representations of knowledge.
References- Городецкий В.И., Грушинский М.С., Хабалов А.В. Многоагентные системы (обзор) // Новости искусственного интеллекта, №2, 1998. c.64-117.
- Клышинский Э.С. Некоторые аспекты построения агентных систем. Портал "Программирование магических игр" URL: http://pmg.org.ru/ai/agent.htm
- Писарев А.С. Применение подхода многоагентных интеллектуальных систем и высокопроизводительных баз знаний для задач дистанционного обучения. Портал "Информационно-коммуникационные технологии в образовании" URL: http://www.ict.edu.ru/vconf/files/tm99_120.doc
- Toshiba Bee-gent, http://www.toshiba.co.jp.
* — At a writing of the author's abstract, the working on degree project is in progress.