The individuals, groups, collectives and organizations activities are beginning to depend on the ability to efficiently use the available information. Finding solutions requires processing large amounts of information that sometimes is not possible without the special technical means.
In the dean office is necessary to store and handle a lot of information, such as:
For effectively management of this information is required an informational system. [2]
The informational system processes the following operations: [1]
Different parts of informational system handle these operations. One of them is user interface.
User interface – the elements and components of the program, which provides the user’s interaction with the software. [1]
For storing the information databases are commonly used.
Database (DB) can be defined as a set of interconnected data used by multiple users.
There are the following basic procedures for processing information: [1]
Thus, the system typically consists of the following components:
According to the method of data processing information systems are divided into systems with centralized and decentralized organization of data.
The centralized system is the simplest implementation. The only database server handles all operations. So, the main advantage of a centralized system is that there is no need to use special means to provide data integrity and relevance of the data. The main drawback is the limitation on the size of the database and the number of handled requests.
In a decentralized organization of information system data base is divided into parts, located at different servers.
There are two basic approaches to organizing detsiontralizovannyh information systems.
In the first case part of the requests can be processed using only local database.
In the second case, each server handles requests from its part of clients.
Anyway, in decentralized systems, there is a need to maintain the relevance of the data in different databases. [1]
Usual information systems uses WIMP user interface [1], provided by the most of modern operating systems, but recently web-based information systems are commonly used. [4]
Web-based information system is a client-server application where the client browser supports, and the server - the web server.
Such an organization has the following advantages: web-browser built into most operating systems, so, the design, installation, upgrade and support of the client parts isn’t system developer’s care. Also, clients aren’t depend on the specific operating system and information system become cross-platform. There’s no need to develop different versions for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, GNU / Linux and other operating systems.
That’s why web applications have become widely popular in the late 1990's - early 2000-ies. [4]
For a web-based applications development on the server side are used following technologies and programming languages:
The development of fifth generation is just beginning. [7]
The choice between commercial and self-made systems is on order. Each of them has own advantages and drawbacks.
the main advantage of serial systems is a large staff of professional developers, debugging and testing on a set of objects, which decreases the chance of errors, updates and technical support is made by the system developer. The main drawbacks are high cost and redundancy of function, leading to an increase in hardware costs. [8][9]
Laboratory of Mathematical Modeling and Information System (MMIS) is an information system «Dean»:
The information system consists of a client application and the database "Dean." To administer the database and access control used by the program «UsersManager».
The program uses an interface tuned to the user's credentials. Users can be allocated by the system administrator security rights to read or change the specified list of departments. [10]
This system uses the South-Russian State University of Economics and Service
Orel State Technical University uses multiple information systems, such as:
The lack of an complex university information system leads to duplication of staff. [11]
The information system is developed as a web-application, server part of which is realized by the LAMP software bundle, which includes:
All components of this package are distributed under free licenses [12], so, the system can operate without using expensive proprietary software.
Web-application realizes services, for the following classes of users (Fig. 1.):
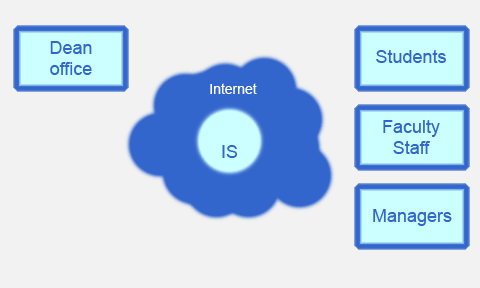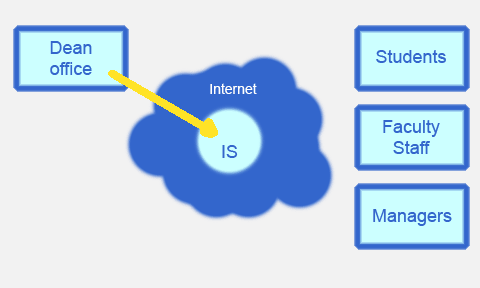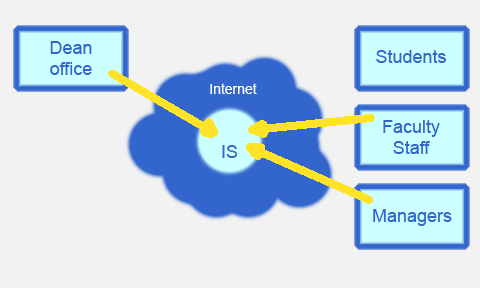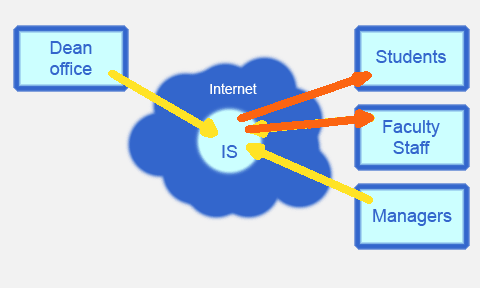
Figure 1. Informational exchange between user groups.
Animation: 5 frames, length 7 sec., loop forever.
The system provides the following output views for printing or hypertext interactive usage: