RUS| UKR | ENG
DonNTU >
Master's portal DonNTU

Konko Sergey
Speciality: Mine and underground excavations
Theme of master's work:
Substantiation of parametres of concrete fastening of vertical shafts on border of cold joints
Materials on the theme of master's work:
About author
The abstract on a theme of master's work
Introduction
Now for a constant fasten vertical mine trunks basically it is used monolithic concrete fasten (MCF) which possesses sufficient for usual mountain-geological and mining conditions bearing ability and reliability. Thanks to it MCF it is applied practically in all conditions, including and not always prove in difficult mountain-geological and mining conditions - in areas of interfaces, in zones of influence of clearing works, at crossing of soft rocks and manufactures spaces, in the presence of aggressive waters and at high residual water inflows.
Thus negative qualities MCF, insignificant in usual conditions, in more severe conditions become causes of infringement fasten. To such lacks it is necessary to carry the limited durability of concrete (as a rule В15), extreme sensitivity to non-uniformity of loading, presence of "cold" seams between zahodkami on concreting, low water penetration. From alternative MCF kinds fasten the most preferable is the national team fasten from ferro-concrete tubings. Other kinds fasten - pig-iron tubings, monolithic ferro-concrete, national teams fasten from piece elements (a brick, concreter) repeatedly lose owing to considerable cost and labour input of erection.
Ferroconcrete tubing fasten (FTF) combines high load capacity with relatively low cost of labor and construction. Main advantages FTF due to manufacture tubing in factory conditions, allowing for high strength, water resistance and corrosion resistance tubing [1, с. 298].
Actual subject
Since the most complex, costly and dangerous process in the overall package works on the construction of mining enterprises should be considered a penetration of vertical shafts in complex mining-geological conditions of the special ways, including freezing of rocks, the vertical shafts require constant searching and developing effective solutions to intensify their bezremontnoy construction and operation, which in turn is relevant scientific and technical task of development of the coal industry in Ukraine.
The purpose and tasks of operation
The purpose of master’s work is the definition of parameters of interaction of a concrete mix and rock mass in conditions of negative temperatures and increase of waterproofing properties of a support.
In the course of the following objectives need to be:
1. To analyse forces of bond of a concrete support and rock mass at negative temperatures.
2. Laboratory researches of water tightness of a monolithic concrete support of shafts.
3. To lead(carry out) researches of the engineering specifications on construction of shafts with the help of a way of freezing on the data State open joint-stock company "Trust Донецкшахтопроходка ".
4. To develop computer model of system " a support - frozen rock mass " for a substantiation of operation of parameters of a support setting of shafts.
Main results
The best technical and economic indices achieved with the mounting shaft monolithic concrete after podviganiem face [2]. However, this technology does not ensure the security of reference works and a reliable seal joints between zahodkami roof.
Many researchers, particularly those involved in the construction of vertical shafts, a proper scientific and technical base, real progress in the design, construction and maintenance of shafts and partially solve the identified problem. However, in a complex of these studies are not sufficiently studied the interaction wetted rock mass with the lining and, in particular, are not studied this form of rock pressure as vyvaloobrazovanie with light water inflow; insufficiently studied issues of quality management and the properties of the concrete roof, using modern high-performance building impurities; not fully take into account the identified factors that make the specifics of the development of technological regulations installations trunks, there is no complete picture for a holistic understanding of the interaction of elements of «technology penetration - lining the trunk - wetted rock massif».
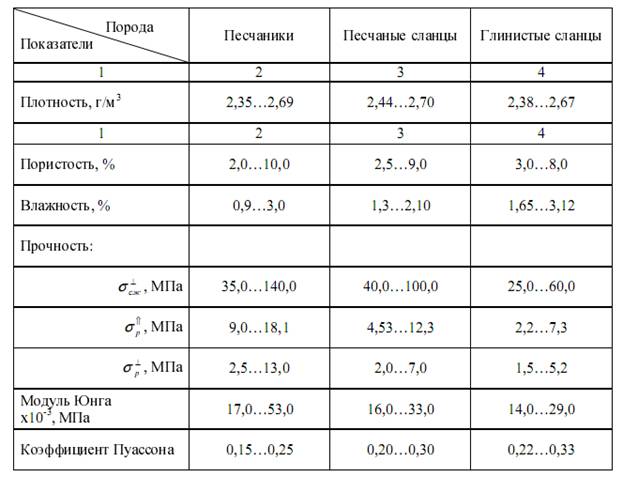
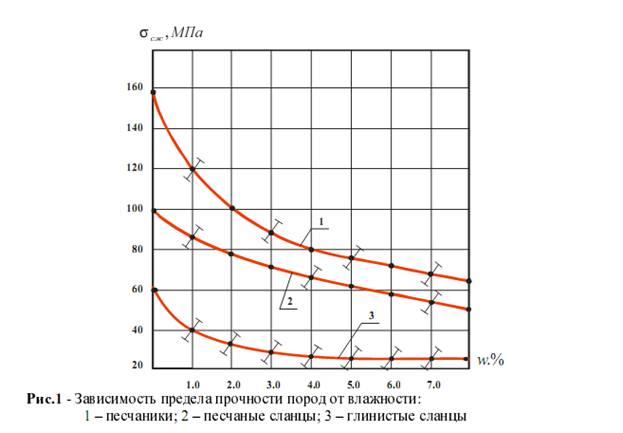
As a result of data analysis GOAO «Trust Donetskshahtoprohodka» revealed that water inflow over 15 m3/hour reduce speed by 20-25%. If we consider vyvaloobrazovanie, it not only causes deterioration of working conditions, but greatly affects the performance drilling: increasing the issuance of rocks on the surface and the volume of concrete works. To design engineering activities to strengthen the broken water prikonturnoy explosive work zones need to know its characteristics. To this end, has been selected 6 plots in the trunks of mine «Krasnoarmeyskaya West № 1», «Trudovskaya» and AP «mine them. AF Zasyadko »and made a set of field studies with the shaft of geophysics [2,3]. The most informative method for allocating vlagonasyschennyh zones in rock masses is an electric [4-6]. According to the results of research in water-bearing rocks of their strength characteristics greatly reduced [2]. The intersection of the barrel zones with high water entails vyvaloobrazovanie for non prizaboynom station. For the computer simulation [2] and perform calculations when determining the parameters CREPY trunks performed laboratory measurement of indicators of physical and mechanical properties of rocks surrounding the surveyed trunks. The results are given in Table 1. In particular, these are indicators of strength ranges: for the sandstone - 35 ... 140 MPa; sandy shale - 40 ... 100 MPa; clay shales (mudstones, siltstones) - 25 ... 60 MPa. Given the task, testing the samples in a moistening. Fig. 1 shows the graphic function [сигма]сж. Processing of test data are analytical expressions for determining the strength of rocks according to their moisture.
Table1. The results of determining the physical and mechanical properties of rocks surrounding the trunks of surveyed Donbass
Dependence 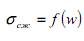 sandstone is given to hyperbole:
sandstone is given to hyperbole:
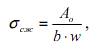 (1)
(1)
where 1,27<А0<1,62; 0,9>b>0,003; w - air humidity
For sand and shale glinichtyh indicated dependence has the form of direct
sandy shale - 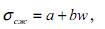 (2)
(2)
where а=96; b=-6; w - moisture breeds.
clay shale - 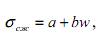 (3)
(3)
where а=49; b=-4.
Thus, the term will then appear:
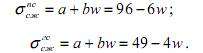 (4)
(4)
The obtained dependence (1-4) may be taken as the boundary conditions in the computer computing ekspiriments.
Conclusion
The analysis of literary sources to determine the purpose and objectives of the Master's work. The dependencies as boundary conditions for the computer Computer ekspiriments.
Animated
figure (13 frames, 103 Kb, 8 repetition)
Bibliographic list
- Прогрессивные технологии строительства, реконструкции, реструктуризации и безопасности в капитальном строительстве предприятий угольной промышленности: материалы региональной научно-практической школы – семинара. – Донецк: Норд-Пресс, 2008. – 336 с.
- Борщевский С. В., Плешко М. С., Лиманский Д. В. Лабораторные и компьютерные исследования водостойкости и прочности бетонной крепи. Науковий вісник Національного гірничого університету, 2007. – №5, С. 41-45.
- Булат А. Ф., Усаченко Б. М., Яланский А. А., Паламарчук Т. А., Борщевский С. В. и др. Методическое пособие по комплексной геофизической диагностике породного массива и подземных геотехнических систем – Днепропетровск: ИГТМ им. Н. С. Полякова НАН Украины, 2004. – 75 с.
- Тарасов Б.Г., Дырдин В.В., Иванов В.В.. Геоэлектрический контроль состояния массива.–М.: Недра, 1983. – 215 с.
- Паламарчук Т.А., Земба В.А., Сергиенко В.Н., Слащева Е.А. Электрометрический контроль пространственно-временной изменчивости литосферы вблизи геомеханических объектов. Сб. научн. тр. – Днепропетровск: НГАУ. - Вып. 3. Т. 5. – 1998. – С. 168 – 171.
- Глушко В.Т., Ямщиков В.С., Яланский А.А. Геофизический контроль в шахтах и тоннелях. - М.: Недра, 1987. - 278 с.
- Конспект лекций по дисциплине "Технология сооружения горных выработок в сложных горно-геологическизх условиях (специальные способы строительстьва)", ООО Лебедь Донецк-2007. Пшеничный Ю.А., Левит В.В.
- Федюкин В.А. Проходка стволов шахт способом замораживания. Изд-во "Недра", 1968. Стр. 1-350.

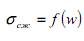 sandstone is given to hyperbole:
sandstone is given to hyperbole: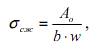 (1)
(1)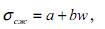 (2)
(2)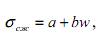 (3)
(3)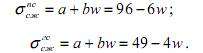 (4)
(4)