
Relevance of the topic.
It is known that in connection with the separation of a single grid Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) on the combined system of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the structure of power does not correspond to sets of modes, as planned those used previously. Thus, major changes have occurred in the circulation of power in the system. In such way it is difficult to solve the problem of optimal configuration of the electrical system, and therefore premature to analyze the load lines reactive and active power in advance to assess the capacity of a transmission line (ETL) and on the basis of this analysis to identify lines with low margin of stability of parallel operation. In such conditions increases the possibility of severe accidental processes due to the presence of "weak links between the separate parts of the electrical system. And, as we know, it is namely in them may cause an asynchronous transfer because of the appearance of large power imbalance in the individual subsystems.
There is a need for rapid detection of conditions that allow short-term asynchronous mode and ensuring the resulting stability in the systems containing weak intersystem communication (WIC), which confirms the relevance of the topic. The USSR had some experience using asynchronous mode (AM) as an effective means of improving the reliability and survivability of the electric power system (EPS). The experience of exploitation, resistance EPS in some cases restored without disable WIC, that is going on successfully resynchronization. In the case of AM recovery subsystems, or perhaps by turning off power links with further timing (in this case there is a need for automatic frequency discharge (AFD) and disabling some of consumers in deficit area EPS and disable a number of generators in excess of the system) or by its resynchronization. In the latter case can the relatively long AM, admissibility of which, the conditions of parallel operation of generators in the middle of each subsystem should be tested. Ensure resynchronization, to restore synchronous EPS probably within a few seconds, in that time to be precise synchronization EPS, one must sometimes more than 10 minutes. Assuming short-AM via WIC is important to know the mean values of operational parameters in each of the subsystems. However, the permissibility of AR via WIC may be limited by the stability conditions responsible load nodes found near the center of the electric oscillations. It is necessary to ensure that the synchronously operating sub-system containing WIC, there is no mutual fluctuations, which may be due to the phenomenon of electromechanical resonance in the weak damping oscillations. Thus, intermittent AM suppose the power grid if the following conditions: there is no danger of damage to the asynchronously operating generators as a result of automation possible resynchronization; disturbances arising as a result of AM in the power system does not lead to the further development of the accident.
Aim is to develop analytical methods for determining average values of operational parameters during the steady progress of asynchronous weak interconnections, as well as evaluation of critical parameters for large fluctuations, causing a secondary violation of stability.
Testingof Some methods for solving this problem were discussed at the XV All-Ukrainian student's Scientific and Technical Conference "Electrical and electromechanical systems" (Sebastopol, SevNTU - 2010).
Problem
In a number of foreign and domestic scientists noted that a fundamental change in energy associated with structural adjustment and the introduction of the energy market, violating the hierarchical relationship of the existing management system, which used to cover a single EPS. As a consequence, there is a significant increase in the number of technological problems in the management of electric power facilities, their diversity and integration through a dynamic situation, which must be analyzed. The introduction of microprocessor technology in various management and development of new telecommunications technologies creates the conditions for building integrated (automated and automatic) control systems of power objects on a common information base. Thus, 34 Committee SEAGRY proposed functions of the integrated substation control system and certain standards of reliability for the implementation of these functions.
To ensure the required reliability of electricity supply systems requires the establishment of a management information systems for local electric power utilities, taking into account the particular technological challenges managing local objects and elements, and facilitate the solution of diverse problems in specific situations, and automatic control systems based on digital devices, emergency automation (EA).
The level of use of intelligent methods in the construction of modern devices, emergency automation allows to realize the work of the past, as adaptive devices. Generalized functional model of the device includes EA launchers bodies, tripping, etc. The software of digital devices EA implements mathematical models launchers bodies. It is clear that the effectiveness of digital devices, the EA, especially to ensure adaptability to the current status and coping with the transition progresses over time, largely dependent on implementing a method for assessing the situation (of the regime and state) [1].
Current status of automatic control systems in electric power systems of Ukraine can be characterized by ambiguous: on the one hand creates and implements digital device, EA, on the other hand uses outdated mathematical models and methods of estimating transition regimes that do not provide opportunities to adapt to the current state of the device, which reduces the effectiveness of management. Analysis of the use of microprocessor devices for the implementation of management control during shows that those methods and models used to assess the current status and treatment are based on several assumptions. A corollary of this is to reduce the effectiveness of the device, and in some cases is not ensured to work correctly, because the model does not take into account peculiarities of the situation that arose.
It should be emphasized that informatization is a promising and less expensive way to improve performance management systems EPS.
Thus, current is the development of improved methods and mathematical models, primarily for the launch of digital devices bodies EA.
Analysis of existing approaches and methods to assess modes of electrical systems
Analysis of a large number of papers shows that the methods of analysis of dynamic stability in the EPS can be divided into the following groups:
- numerical methods for assessing the stability in time domain based on the solution of systems of equations describing the transient processes;
- Direct methods for the type of Lyapunov.
- rapid tests;
- methods based on pattern recognition theory.
Computational methods for evaluating sustainability in the time domain
These methods allow you to: get information on changes in the profile, to formulate any scenario analysis of stability. However, these methods do not allow:
- determine the region of regimes that need to be analyzed (no recommendations for cutoff perturbation in terms of sustainability);
- directly assess the sustainability of stocks;
- get summarizing recommendations for resistance management;
- require multiple solutions of control systems for evaluation of boundary conditions of stability.
The main advantage of direct methods of assessing sustainability is the direct calculation of the limits of dynamic stability (without re-computing), a convenient definition of stock sustainability. However, the application of these methods is limited due to the adoption of significant assumptions in the implementation of methods that are based on the theory of Lyapunov. But the assumptions do not provide reliable information about how to modify the regime, and thus realize the optimal control of a particular regime [2-7].
Direct methods for the type of the Lyapunov
A considerable amount of work has been directed at developing a pseudo-Lyapunov approach to the tasks of the analysis of dynamic stability, so that was quite flexible in terms of modeling power, with a precision that is comparable analysis in the time domain, and effectively in regard to the calculations. These studies have allowed to formulate the following conclusions:
- problem of assessing the stability region can be solved by considering dvuhmashinny or equivalent single-multimachine power systems;
- modeling problem can be solved by integrating the direct method, taking into account the processes in the time domain.
Subsequent work focused on the development of hybrid methods, among which we can identify those that deal with the Lyapunov function for multimachine system when performing the calculation of past trajectory, and those that deal with single-equivalent in multimachine power systems. In the second case to the test - a method for simplifying the problem area and the method of SIME. Both methods use the classical simplified model of synchronous machines, but SIME method takes into account the change in the profile over time, as assessed by the program analysis of the processes in the time domain. Thus, the method is a hybridization method SIME area with information about the process in time domain. On the basis of the area defined by the stability of stock cars, which are responsible for the loss of synchronism. Depending on how the obtained information about the parameters of the regime over time - from the program for calculating the transition process or by means of measuring the profile of the real system at a pace of implementation of differentiated hybrid applications in the form of a preventive anti-damage SIME. The method of preventive SIME in this fit in with industry software and tested on many models of power systems (SIME EUROSTAG - Belgian version; EDF, France; SIME ETMSP - American test systems EPRI; SIME ST600 - Hudro-Quebec power grid in Brazil and Canada). We use the classical model of synchronous generator. The most complete model takes into account the physical processes in the generator rotor with one damper circuit in axes d and q.
Methods based on pattern recognition
In complex electrical systems (ES) detection of emergency operation performs relay protection.
In practice, in some cases, emergency ES regime on the parameters (attributes) are similar to normal-operating. For example, short-circuit can be considered similar to an outline mode asynchronous load, sync generators in parallel operation, etc. In these cases, the existing methods and tools for operational management of the ES regime are not always the best way to deal with the problem of classification of emergency conditions. To create an automated control system for the ES, it is necessary to solve several important problems, including the task of error-free detection of emergency situations in the ES. Because this task requires processing of large volume of statistical data to identify specific specific qualities that belong to the class of modes, and a decision on the status of the ES in the face of uncertainty, it is advisable to implement its methods of statistical pattern recognition theory.
In solving problems of recognition, the analyzed mode, which is described by m parameters (features), is represented as a vector (object) in the m-dimensional space of observations. Pattern recognition - a decision establishes a new identity earlier in the process of studying the object, was not addressed to this class of objects (an image) by comparing the properties of this object is already known and understood. The entire set of parameters (features) describing the emergency situation in the EPS, is divided into three groups:
- Quantitative characters, if the value of attributes can be expressed in numerical form (eg, mode settings, the duration of the accident, the resistance elements of EPS, etc.);
- Qualitative (rank) symptoms, if the value attribute is not expressed in numbers, but varying degrees of manifestation of the properties of objects, resulting in possible ranking of traits (eg, types of short circuits, controllers, and a strong violation of the proportional action, etc.);
- Classification (nominal) features, when the characteristic value are not the numbers, and are not affiliated natural ordering. This type of sign can be the solution of problems of recognition of situations in the EPS in the form of logical variables taking the value zero or one. The latter group includes the direction of flow characteristics of power lines, the presence or absence of APV on the submarine, the condition of power lines and standby generators in the EPS (enabled or disabled), etc.
For the mathematical description of the recognition procedure is used: deterministic methods; probable methods and statistical methods [8,9].
Application of a rapid assessment of modes of electrical systems
One of the main tasks of management regimes of electrical systems is the management of transition processes occurring at large perturbations. Managed in a variety of devices emergency automatics, most of which embody the principle of the program. Disadvantages of Automation of this type are well known. It is therefore very promising is the creation of Automation Power Supply, which is adapting to changes in system parameters and the regime changes its control law, the values of setpoints, etc. The implementation of this management principle implies the creation of devices that identify the nature of the transition process in its current pace. Therefore, the methods of determining the stability, which are implemented in such devices, imposed stringent requirements not only to the accuracy of the calculation, but also to the speed of obtaining results. The use for this purpose numerical methods for calculating the resistance is irrational, because they require the fulfillment of more settlements and various background information, which is obtained from the pace of the transition process is difficult. Promising paths in this direction are:
- obtaining solutions of differential equations of the transition process in an analytical form that allows the initial conditions to determine the parameters of the system for a given point in time;
- Develop a method of qualitative analysis of stability that allows you to modify the mode set with some ahead of time the state of the system.
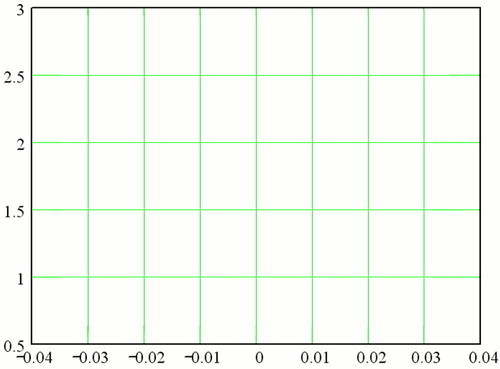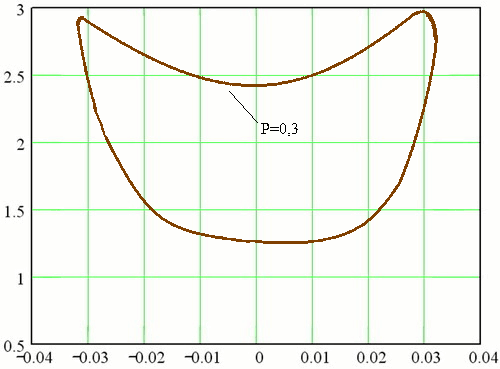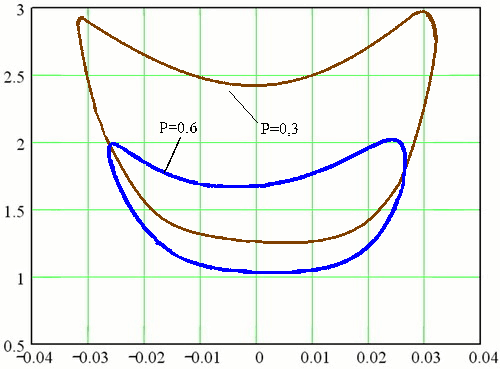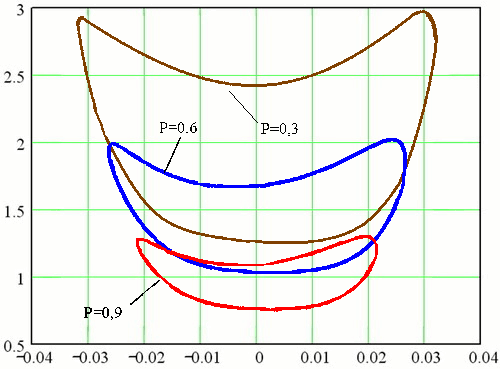
The real transition may differ significantly from the current, so we must correct the calculation of control actions. This correction is expedient to perform on the basis of a rapid assessment of the stability of EPS in the pace of the transition process. For rapid assessment of the stability of EPS should be used methods to determine the state of the system in the transition process, with some lead-time. To assess the stability of a simple system proposed according to Δ (t), a1 (t) and A0 (t), which are nonlinear functions of the derivatives of the angle δ between the vector emf station and the stress vector EPS reception. They are available in advance for a specific EPS and then use for decision-making (Fig. 1). With the same functions you can perform a rapid assessment of stability in the presence of automatic excitation regulators on generators and implementation of an automatic emergency discharge turbine. Note that in these cases the stability of EPS is also estimated with some advance, but the presence of adjustment is different. In particular, the definition of stability EPS only in the first cycle of oscillations is not enough, because its violation is possible and in the next cycle fluctuations. Given this assessment of the stability of EPS by the nature of changes in the functions Δ (t), a1 (t) and A0 (t) should be carried out in each polufaze swings.
In writing this essay master's work was not completed. The final work can be obtained from the author or supervisor after December 2010.

The findings can be installed setpoint emergency automation to disable short-circuit. Based on the stability of surfaces defined limiting angle eliminate accidents, in which the system remains stable [10].
Findings
We studied the following methods of evaluation of dynamic stability: methods for rapid assessment, methods of pattern recognition theory, methods of the theory of Lyapunov. The methods used to assess the admissibility of failure mode and asynchronous mode. One such method is the method of rapid assessment of the admissibility of AM on weak intersystem lines, which can be attributed to the methods of rapid assessment. Currently, relevant is the growing number of weak interconnections, in connection with the separation of a unified energy system of the USSR in the combined system of the CIS countries.
1. Коган Ф.Л. Анормальные режимы мощных турбогенераторов./Ф.Л. Коган//М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1988. — 192с.
2. Венников В.А. Переходные электромеханические процессы в электрических системах./В.А. Венников//М.: Высшая школа, 1986. — 398с.
3. Литкенс И.В. Коллебательные свойства электрических систем./И.В. Литкенс, В.И. Пуго//М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1988. — 208с.
4. Хачатуров А. А. Несинхронное включение и ресинхронизация в энергосистемах./А.А. Хачатуров//М.: Энергия, 1969. — 192с.
5. Веников В.А. Управление переходными режимами электроэнергетических систем./В.А. Венников//М.: Высш. шк , 1982.
6. Портной М. Г. Управление энергосистемами для обеспечения устойчивости./М.Г. Портной, Р.С. Рабинович//М.: Энергия, 1978.
7. Беркович М. А. Автоматика энергосистем./М.А. Беркович, В.А. Гладышев, В.А. Семенов//М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1985. — 240с.
8. Веников В.А. Экспресс-оценка устойчивости процесса по его начальной стадии/В.А. Веников, С.Н. Асамбаев//Изв. АН СССР. Энергетика и транспорт. N3. — 1986. — С. 22-25.
9. Веников В.А. Опережающее определение изменений параметров режима при управлении переходным процессом/В.А. Веников, С.Н. Асамбаев//Электричество. N2. — 1981. — с.5-8.
10. Асамбаев С.Н. Нелинейные зависимости для экспресс-оценки динамической устойчивости ЭЭС/С.Н. Асамбаев//Изв. Высш. Учеб. Заведений. Энергетика. N4. — 1989.— с.45-47.
Coment
By using a rapid assessment of the admissibility of asynchronous modes of weak intersystem lines of communication can estimate the admissibility of AM in the system.