 DonNTU |
Master's portal of DonNTU |
About author
DonNTU |
Master's portal of DonNTU |
About author


Shevchenko Yuliya
Faculty of ecology and chemical technologies Catalitic methods in cokechemical industries Supervisor: professor of department, associate professor, c.t.s. Panasenko Anatoly
Department of the applied ecology and guard of environment
Speciality "Ecology of chemical enterprises"
as a way of protection of environment
Summary of research and developments
Introduction (Motivation)
A fuel and energy complex is a base of development of economy of any country. Now for the receipt of energy an organic fuel (coal, oil, natural gas of and other) is used in most cases. The special role is played by a coke production, which produces products, which by implication is got from coal raw material, - benzol, coal resin, her chemical foods, pitc hand other.
Cokers are big concerns on which the thermo-chemical processing of raw material is carried out with the purpose of receipt of different types of coke. A coking process is accompanied by formation of matters which in future can be used as raw material for the receipt of commodity foods. Coker in the Avdeevka city is one of the biggest producers in this industry.
There is an enormous amount of methods of processing of raw material and rendering of gas extrass harmless. The choice of method depends on many indexes: chemical composition of raw material or gas, which clears up, presence of mechanical admixtures, to the desirable degree of cleaning of gas or transformation degree of raw material intu a product and others.
Purpose
A purpose hired is research of efficiency of the use of catalytic methods in coke industry.
Tasks
For achievement to the purpose next tasks were put: To consider the mechanism of catalysis and catalytic reactions with participation of different matters;
- To consider existent catalytic processes in the conditions of open corporation "AKHZ";
- To define the lacks of the considered processes and offer the ways of their removal;
- To define possibility possibility of the use of catalytic methods for cleaning of extrass at granulation of electrode pitch.
Actuality
The issue of the day is perfection of setting of wet catalysis. Effective to the methods of increase of degree of conversion of SO2 in SO3 there is a double catalysis and oxidization of SO2 under constraint. The off-gas from the area of granulation and packing of electrode pitch on open corporation "AKHZ" are now taken in an atmosphere without the proper cleaning, therefore building of setting of the т thermocatalitical rendering of gas extrass harmless is a necessity.
1 ANALYTICAL REVIEW of CATALYTIC METHODS[fragments]
1.1 Concept of catalysis
A catalysis matters very much in the wild and modern life : catalytic are almost all biochemical processes, most reactions, which study at a laboratory, and technological processes which are realized in industry.
Classification of catalytic processes can be conducted on a few differences. On phase composition of components catalytic reactions usually attribute to the homogeneous catalysis (if initial matters, foods of reaction and catalysts, are in an only phase) or to the heterogeneous catalysis (reactionary mixture and catalyst are out-of-phase)[1].
As catalysts usually use hard matters and study the systems "Gas- solid " and "liquid - solid" mainly.
A heterogeneously-catalytic reaction shows by itself a difficult process which consists of the next stages (fig. 1),:
diffusion of initial matters from the volume of gas or liquid phase to external and internal to the surfaces
to the catalyst;
- Adsorption of reactive matters on the surface of catalyst;
- Chemical reaction on the surface of catalyst;
- Desorption of foods of reaction;
- Diffusion of foods of reaction from internal and external surfaces of catalyst in a volume.
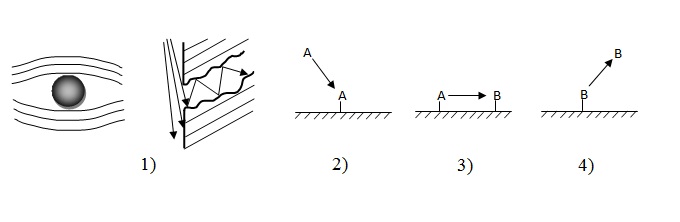
Picture 1 The simplified chart of catalytic process on the surface of hard catalyst
General speed of such difficult process is determined by speed of the most slow stage, which has the name of the limiting stage often[5].
1.2 Catalysts are in industrial processes
In industry catalysts are as a rule, multicomponent systems.
Addition to the catalysts in the two-bipls of matters, which are named промоторами, promotes his activity due to the increase of surface, selectivity and term of action.
Promotor (an activator) is named addition to the catalyst of two-bipl of matter which in itself can be catalytically nonactive in relation to a certain reaction, but very promotes activity actually catalyst.
By Ch. Setterfild classification promotors is divided into two basic classes: texture, which undertake a physical action, and structural, nature of influence of which is chemical.
Catalysts on transmitters are the widespread type of the difficult pin masses. Now synthetic transmitters are widely used what have a row of advantages comparatively with natural materials.
Industrial catalysts use usually in form granules or cylinders by a diameter ~10-3 m, which must have certain mechanical durability, porosity and high values of specific surface[2].
1.3 Choice to the catalyst
A catalyst can be used in an industrial process, only if it answers certain requirements in relation to activity, selectivity and tenure of employment.
Dignities industrial to the catalyst determined by an income which his use can give. For the estimation of it it is necessary to know: the productivity which is expected, to calculate a capital investment on an equipment; selectivity, to find the charges of raw material; thermal effect of catalytic reaction, to conduct the calculation of power expenses or income from a heat which is distinguished; expected term of action of catalyst; cost.
Before to choose a catalyst, it is necessary attentively to consider terms at which he will work in a reactor. At the choice of suitable catalyst it is necessary to take into account undesirable by-reactions which he can accelerate[4].
1.4 Catalytic processes are in cokechemical industry
A production in which one or a few basic chemical reactions will be realized with participation of catalysts is named catalytic. But on volume reactionary space, by sizes and complication of vehicles, amounts of auxiliary personnel and total worth of exploitation actually catalytic processes and vehicles fold insignificant part of such production in most cases.
The typical flowsheet of catalytic production orientation can be presented by the next sequence of operations and processes :
- primary processing of raw material with the receipt of basic reagents for a catalytic process;
- cleaning of reactionary mixture from admixtures which litter (dust) or poisons catalysts;
- festering of gases or transporting of liquid reagents to the reactor;
- heating of reagents to the temperature of catalysis;
- catalysis, which is usually accompanied by taking or tricking into of heat;
- processing of foods of catalysis in having a special purpose foods of production.
Content of these operations differentiates in separate catalytic productions[3].
2 USES OF CATALYTIC METHODS IN THE CONDITIONS OF OPEN CORPORATION "AKHZ"
On coke in the Avdeevka city catalytic methods find a wideuse. In the case of correct selection of catalyst it is possible to get a desirable result at minimum economic charges. Catalysts are used for the receipt of фталевого anhydride the method of steamphase oxidization of naphthalene. A process is carried out on a vanadium-potassium-sulfate catalyst. Ftalievii anhydride is used in the production of alkyd, polyether resins, synthetic varnishes and dyes.
A process passes at a temperature 370-420 °С. Degree of transformation of naphthalene at the use of this method makes 84 %[11].
Also at the absorbing-desorption methods of cleaning of coke gas from the sulphuretted hydrogen get sulphuretted hydrogen gases, which contain the 40-90 %(vol.) sulphuretted hydrogen which is not a commodity product. On the basis of these gases it is possible to get the sulfides of ammonium, sodium, barium and other foods, but greater part them processed in sulphuric acid.
The receipt of sulphuric acid is carried out on the method of wet catalysis. A method consists in the oxidization sulphuretted hydrogen in SO2 and waters by incineration in stoves at a temperature 1100-1300 °C next oxidization of SO2 in SO3 on a catalyst at 450-600 °C and by condensation of sulphuric acid at chilled pin gases to 60-80 °С. Process takes place on the vanadium catalyst[12].
3 TERMCATALYTIC CLEANING OF EXTRASS AT GRANULATION OF ELECTRODE PITCH
Special place as a source of contamination of environment is occupied by a pitchcoke production including fluidizer granulation and packing of electrode pitch. Dast & gas extrass at the production of granular pitch are very toxic.
At the receipt of granular pitch plenty of aerosols and steams of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) is distinguished in an atmosphere, phenol of naphthalene, coke dust and other contaminents. For cleaning of extrass, which appear in this production possibly of the use of thermоcatalytic cleaning on a palladic catalyst.
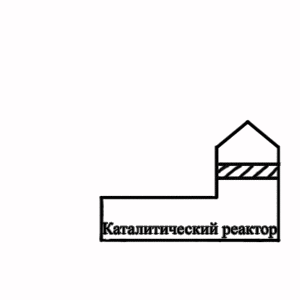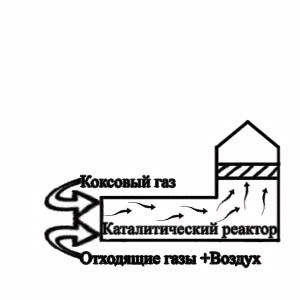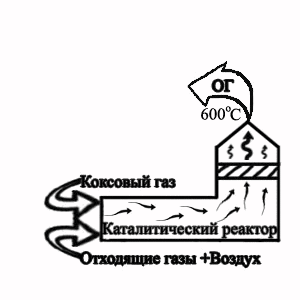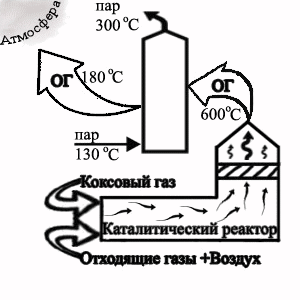
Picture 2 — Flowsheet of the termcatalytic cleaning of extrass at granulation of electrode pitch
Animation: shots — 7, cycles of reiterations — 7, size — 30,5 кB
Literature
- Байрамов В.М. Основы химической кинетики и катализа: Учеб. пособие для студ. высш. учеб. заведений/В.М. Байрамов. — М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2003. — 256с.
- Дж. Андерсон Структура металлических катализаторов/ Перевод с английкого к.х.н. Э.Э. Рачковского, под ред. академика Г.К. Борескова. — М.: «Мир», 1978. — 485с.
- Технология катализаторов/ И.П.Мухленов, Е.И.Добкина, В.И.Дерюжкина, В.Е.Сороко; под ред. проф. И.П.Мухленова. 3-е изд., перераб. — Л.: Химия, 1989 — 272с.
- Катализ в промышленности: в 2х т. Т.1. Пер. с англ./ Под ред. Б. Лига. — М.: Мир, 1986. — 324с.
- Катализ в промышленности: в 2х т. Т.2. Пер. с англ./ Под ред. Б. Лига. — М.: Мир, 1986. — 291с.
- Улавливание химических продуктов коксования: учебное пособие для вузов: в 2ч./ А.Ф. Гребенюк, В.И. Коробчанский, Г.А. Власов, С.И. Кауфман. — Донецк: Восточный изд. дом, 2002.
- Попова Н.М. Катализаторы очистки газовых выбросов промышленных производств. — М.:Химия, 1991. — 176с.
- Платонов О.И. Промышленный опыт и перспективы развития технологии каталитического разложения коксохимического аммиака // Журнал «Кокс и химия», 2008. — Вып. 1. — сс.22-27.
- Платонов О.И. Особенности промышленной технологии каталитического разложения коксохимического аммиака/Платонов О.И., Егоров В.Н., Лутохин Н.Н., Мельников И.И., Чистяков Н.П., Егоров М.А., Криницын Е.Н., Щукина Р.И.// Журнал «Кокс и химия», 2005. — Вып. 5. — сс.37-41.
- А.с. 1324681 СССР, кл. В 01 37/02. Способ очистки отходящих газов от оксида азота/ В.Е. Майзлиш, А.В. Величко, Ф.П. Снегирева, Н.Л. Мочалова, Г.П. Шапошников, Р.П. Смирнов, В.Л. Ивасенко. — №4464169/31-26; Заявлено 20.07.88. Опубл. 07.12.90. Бюл. №45. — 3с.
- Гуревич Д.А. Фталевый ангидрид. — М.: Химия, 1968 — 232с.
- Амелин А.Г., Яшке Е.В. Производство серной кислоты: Учебник для проф.-техн. учеб. заведений. — 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. — М.: Высш. школа, 1980 — 245с.
 DonNTU |
Master's portal of DonNTU |
About author
DonNTU |
Master's portal of DonNTU |
About author
