Alla Sheptulia
Faculty:
Computer Sciences and Technologies
Speciality:
"Information Control Systems and Technologies" (ICS)
Department:
Automated Control Systems (ACS)
Theme of Master's Work:
Decision Support System of Enterprise's Price Politics Formation and Regulation
Scientific Supervisor:
Ph.D. (in Engineering), Associate Professor of the ACS department Aleksandr Sekirin
Introduction
The process of enterprise management is a continuous development of management decisions and their application in practice. From the development effectiveness of these decisions largely depends on the success of business. And before you start any business, must define the purpose of their actions. During production, the enterprise managers are often faced with critical challenges, and on whether the number of optimal decision will depend on the final financial results of companies.
The need for decision arises only when there is a problem, which is in general characterized by two states - given (desired) and actual (projected), and it is forecast to be the starting point in making managerial decisions. The mismatch between these states determines the need to develop - the management decisions and monitor of its implementation.
The successful functioning of the production environment is a decision making that comply with the conditions in which objects are functioning. Decision support systems, which are concentrated powerful methods of mathematical modeling, management science, computer science, is a tool designed to assist managers in their work in an increasingly complex dynamic world [1,2].
1. Topical issue
For companies the issue of forming and regulating the price policy plays an important role. The enterprise`s profits are depends on how being pricing at it. In addition, price has become a significant factor in the competition in existing now a market economy.
2. Communication of work with scientific programs, plans, theme.
Master's qualification work is executed during 2009-2010 agrees with a scientific direction of the department “Computer Engineering” of Donetsk National Technical University.
3. Aims and objectives
The aim is to create a system of decision support system of enterprise`s price politics formation and regulation, namely the achievement of maximizing profits by setting the highest possible price for maximum sales of products in the enterprise.
The main tasks are:
- - analysis of the literature of decision support systems;
- - analysis of the literature of methods for forecasting and optimization;
- - choice and justification of forming and regulating enterprise`s price policy methods.
The objects of investigation are existing methods and models used for the automated creation and management of price policy.
4. Scientific novelty
Proposed scientific novelty are:
- - application of the method of analysis and forecasting of time series for the automated creation and management of enterprise pricing;
- - achieve the maximization of profits by setting the highest possible price for maximum sales of products in the company with the regulation of mark-ups.
5. The practical value of the work
The practical significance of the results is the high demand for this kind of systems in business at the national level and throughout the world.
6. Approbation
Approbation of the results was obtained in a performance at the I International scientific conference of students, graduates and young scientists "Information control systems and computer monitors - 2010", which took place in Donetsk natsionaltom Technical University, with report named "Decision support system of enterprise's price politics formation and regulation"
7. A review of existing development and topic research
Review of existing methods. Today, scientists have developed a variety of forecasting techniques, which are combined in different ways within one or another approach. So the methods of forecasting sales include: methods of expert estimates and casual methods. A point forecast of sales volume, which refers to methods of peer review, contains the smallest amount of information, so it can be misleading. The complexity of causal methods is that the application of multivariate prediction requires the solution of complex problems of choicing the factors that can not be solved purely statistical way, but connected with the necessity of the economic substance of the phenomenon or process deep study. To solve this problem is invited to choose the method of analyzing and forecasting time series.
The mathematical formulation of the problem. Our challenge is to maximize profits. To construct its formal scheme (model), we introduce the general notation.
The letter N denote the set of all decision makers (DM). Let N=1. Assume that the set of pricing strategies maker previously studied and described mathematically. Denote them X1 , X2 ,..., Xn. After this decision process by all the DM comes down to the next formal act: the DM selects a specific element of its allowable set of solutions 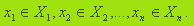 The result is a set of х =(x1 ,..., xn) selected solutions, which we call the situation.
The result is a set of х =(x1 ,..., xn) selected solutions, which we call the situation.
To assess the situation x in terms of choice of the best pricing strategies to maximize profits construct functionsf1 ,..., fn, that relate to each situation x numeric ratings f1(x) ,..., fn(x) – earnings of the company in a situation х. Then the goal of DM is formalized as follows: choose its decision 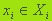 , to a situation х =(х1 ,...,хn) number fi(х) was the largest as possible. Let the fact that we were able to describe mathematically all those conditions under which the decision were making(describe the linkages between the managed and unmanaged variables, a description of influence of stochastic factors, accounting dynamic characteristics etc.). The combination of all these conditions, for simplicity, denoted by one symbol
, to a situation х =(х1 ,...,хn) number fi(х) was the largest as possible. Let the fact that we were able to describe mathematically all those conditions under which the decision were making(describe the linkages between the managed and unmanaged variables, a description of influence of stochastic factors, accounting dynamic characteristics etc.). The combination of all these conditions, for simplicity, denoted by one symbol 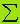 .
.
Thus, the general scheme of a decision problem may look like:
 (1)
(1)Specifying the elements of the model, defining their characteristics and properties, we can obtain a particular class of models of decision making. With this scheme we can write the extremal problem of the two types:
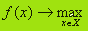 - Profit maximization. (2)
- Profit maximization. (2)
In an extreme problem explicitly take into account the time factor, so it is called the optimal control problem.
In the case of the profit maximization model elements (1) depend explicitly on time, so the decision making process is a multi-discrete or continuous time process, so the problem is called dynamic. Also, elements of the model (1) does not contain random variables and probability events, so the problem is called deterministic.
Optimization. We will described the "problem of enterprise`s price politics formation and regulation".
Suppose that a company can spend available capital K in the next quarter for the purchase of goods N species, is required to determine the appropriate share of costs.
May xj, j= 1,N – the amount of capital spent on the product j-th species. Then the variables to the following restrictions:
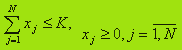
Assume that the firm has statistics on the profitability of sales rj(t), j= 1,N, t= 1,T, for each type of goods for T periods, beginning with t0. Profitability rj(t) is defined as income for the period t to one monetary unit cost of goods j. Magnitude rj(t) can be determined from the ratio
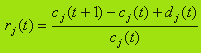
с j(t) - price of commodity j-th type at the beginning of period t;
d j(t) - total profits earned during the period t.
Values rj(t) are volatile and may fluctuate greatly from period to period. These values can be of any sign or be zero. To assess whether the cost of purchasing goods j-th species is necessary to calculate the average or expected return Mj from the commodity type j.
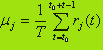
The average or expected profit E(x) of goods is defined as follows:
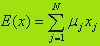
Along with the average (expected) income of the most important characteristic is the risk associated with the cost of goods. As a measure of investment risk can be considered the deviation of return on its average value over the past T periods. Then the evaluation of investment risk for the product type j is the dispersion, which is calculated by the formula
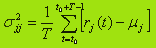
In addition, some courses are securities subject to joint oscillations (examples of such securities are shares of oil and auto companies). Assessment of the investment risk for a couple of types of securities belonging to the interrelated areas of the economy, is the covariance, which is calculated by the formula
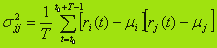
Note that i=j this value is reduced to the dispersion of market type j.
Therefore, as a measure of investment risk for procurement of goods may be value:
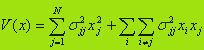
Based on the described characteristics - expected return E(x) and the investment risk V(x) - look at several models, optimizing task.
Model 1. Maximizing the expected profit under the constraint on the total cost of goods.
The model has the form:
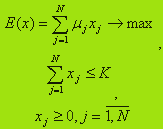
This model is a model of linear programming (LP). Optimal solution x*={x*j}, j= 1,N, E*=(E*j) can be found by the simplex method.
Purchased products can be formed taking into account various constraints associated with the policy of the company.
Model 2. Minimization of the procurement risk at a given average income.
The owners bought the goods may be interested in obtaining a given expected return R with minimal risk. Optimization model in this case has:
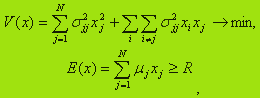
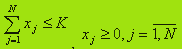
This model is a model of quadratic programming as a quadratic objective function and constraints are linear. Optimal solution x*={x*j}, j= 1,N, E*=(E*j) can be found by quadratic programming.
The topology of neural networks and time series. As the main task is chosen to maximize profits by setting the highest possible price for maximum sales [8,11].
To implement the task will use the following scheme:
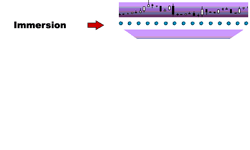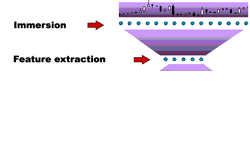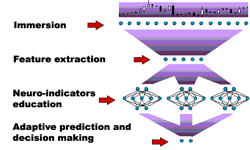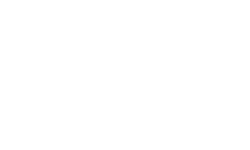
Figure 7.1 - Scheme of the technological cycle of the market time series predictions
Animation: volume - 29.0 KB; size - 250x150; number of shots - 5; delay between shots - 250 ms;
delay between the last and first shots - 100 ms; number of repetition cycles - infinity)
Consider the immersion method. Takens`s theorem was prove for dynamical systems : if the time series generated by a dynamical system, ie values Xt is an arbitrary function of the state of the system, there is a deep dive d (approximately equal to the effective number of degrees of freedom of the dynamical system), which provides an unambiguous prediction of the next value of the time series. Thus, by choosing a sufficiently large d , can guarantee the unique relationship the future value of some of his d the previous values: Xt = f(Xt - d), ie prediction of time series is reduced to an interpolation function of many variables. Neural networks can be used for further reconstruction of the unknown function on a set of examples, given the history of this time series [3,5].
Formation of the input feature space. Img. 7.1 that the increase in window width dive series leads, eventually, to lower predictability - when increasing the dimension of inputs is not compensated by an increase in their information.
Consider the structure of free retail price.
Table 1. The structure of free retail price
| Free retail price | ||
| Free selling price | Mark-up | VAT trade |
Free retail price of goods sold, taking into account broker (commercial or wholesale supply and marketing organizations), includes a free selling price without VAT, allowances mediator (wholesale mark-up) and VAT mediator (purchase price) and trading allowances [6,7,10].
The input feature space is formed as follows:
- 1. Average rate of profit
- 2. Demand for products
- 3. Expenses
- 4. Price competition
- 5. The average consumer's wealth
- 6. Dollar exchange rate
- 7. Seasonality
- 8. Cyclic recurrence
- 9. Free selling price
To train the neural network is not enough to form a training set of inputs-outputs. It is also necessary to determine the prediction error network. RMS error, the default in most neural network applications, has a large "financial sense" for the market series.
When training a neural network data are divided into three samples: training, validation and test. The first is used for training, the second - to select the optimal network architecture and / or to choose when to stop learning. Finally, the third, which is generally not used in training, is used to monitor the quality of the forecast trained neural network. As a training set using the values of input attributes [6].
8. Description and future results
At this point was analyzed the literature on decision support systems, forecasting and optimizational methods, has been chosen method of implementing the development, described the mathematical formulation of the problem, as well as its optimization. As a basic scheme for implementation of the development scheme was chosen technological cycle of the predictions of market time series. Based on the study of literature has been described the topology of a neural network. In the future there will be implementation of decision support system f enterprise`s price politics formation and regulation.
Conclusions
There was chosen the main task of price politics formation and regulation adopted by the company to maximize profits by setting maximum prices for maximum sales. The result of work is analysis of the literature of decision support systems, methods of forecasting and optimization. It was formulated in a mathematical formulation of the problem, its optimization, selected circuit implementation problem, the topology of a neural network. IIn the future there will be implementation of the development.
Literature
1. Гайдрик К.В. Системы поддержки принятия решений: эволюция концепции и некоторые перспективы. / К.В. Гайдрик - Кишинев, Молдова. Институт математики АН РМ, 1988. - 6 с.
2. Система поддержки принятия решений [Electronic resource] – Access mode to article: http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Система_поддержки_принятия_решений.html
3. Предсказание финансовых временных рядов. AB Forex. [Electronic resource] – Access mode to article: http://www.abforex.ru/download/vremya_ab%20forex.rar
4. Новиков Д.А. Активный прогноз. / Д.А. Новиков, А.Г. Чхартишвили – М.: ИПУ РАН, 2002. – 101 с.
5. Сергей Шумский. Предсказание финансовых временных рядов [Electronic resource] – Access mode to article: http://articles.mql4.com/ru/542
6. Прогнозирование цен с помощью нейросетей [Electronic resource] – Access mode to article: http://articles.mql4.com/461
7. Есипова В.Е. Цены и ценообразование. / В.Е. Есипова. – СПб: Питер, 2001. - 464 с.
8. Харчистов Б.Ф. Методы оптимизации: Учебное пособие. / Б.Ф. Харчистов – г. Таганрог: Изд-во ТРТУ, 2004. – 140 с.
9. Новиков Д.А. Механизмы функционирования многоуровневых организационных систем. / Д.А. Новиков – М.: Фонд "Проблемы управления", 1999. – 161 с.
10. Салимжанов И.К. Ценообразование: учебник. / И.К. Салимжанов. – М. : КНОРУС, 2007. – 304 с.
11. Бурков В.Н. Экономико-математические модели управления развитием отраслевого производства. / В.Н. Бурков, Г.С. Джавахадзе - М.: ИПУ РАН, 1997. – 64 с.
12. Лушин С.И. Ценность. Цена. Стоимость. / С.И. Лушин - М.: Юрист, 2001. - 80 с.
13. Корнеев С.В. Системы поддержки принятия решений в бизнесе. Журнал "Сети & Бизнес" (№6, 2005) [Electronic resource] – Access mode to article: http://www.sib.com.ua/arhiv_2005/...
Remark of material significance
The abstract of the Master's work is not complete yet . The final completion in 1st December 2010. Full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after that date.
