
Igor Shabalin
Electrotechnical faculty
Chair: Electrical supply of industrial enterprises and cities
Speciality: Electrotechnical systems of electroconsumption
"Automatic systems commercial accounting of electric power at the mine im.Zasyadko"
Supervisor: Victor Oleynik
Resume About myself
Abstract
- Introduction
- The urgency of this development
- The purpose of the work
- The novelty of the result
- Practical value
- Approbation of the work
- General characteristics
- Prospects for research
Introduction
In connection with the transition to a market economy, the need to improve the efficiency of energy management as it meets the economic interests of suppliers and consumers. One of the areas to solve this problem is the precise control and accounting of electricity. This direction should provide a significant portion of the total energy saving potential of more than 1 / 3 of the current level of consumption. New economic relations in the sphere of energy management are manifested in the formation of a single electricity market. Based on the above said, the electricity market should be a multicomponent mechanism of coordinating the economic interests of suppliers and consumers. One of the most important components of the electricity market is its tool support, which is a set of systems, instruments, devices, communication channels, algorithms, etc. to monitor and control the parameters of energy consumption. Base of the formation and development of instrumental support are automated control and accounting of electricity consumption.
The urgency of this development,at present, the share of energy in production costs for many industries ranging from 10-25 to 40%, this is due to the existence of understated tariffs and electricity prices in the Soviet times and faster (2-3 times) growth rate energy prices in 90 years. With projected growth in electricity prices, which for 3 - 5 years probably will reach a level close to the level of Western Europe, the energy companies should be able to control power consumption in order to gradually reduce the share of payments for electricity in the cost of their products. This can only be streamlined commercial and technical accounting of electricity. Modern electricity trade based on the use of automated instrumentation energy accounting to minimize the human involvement in the process of collecting, processing and transmission of information and provides reliable, accurate, fast and flexible, adaptable to different tariff systems of accounting. Creating automated systems for commercial electric power metering (AMR) is a necessary condition for the energy saving mode in an industrial plant. In the presence of modern metering enterprise complete control over the entire process of power and has the ability to harmonize with the energy suppliers flexibility to move to different tariff systems, minimizing their energy consumption. AMR with the technical cost of electricity makes it possible to get a picture of energy consumption of each object in as close to real time and, accordingly, plan connecting its facilities with maximum efficiency. Having AMR, the company has the opportunity to take advantage of differentiated tariffs for electricity costs, and this in turn allows to plan production so as to maximize transfer of energy-intensive operations activities for the duration of preferential tariffs. In these circumstances, an objective need to improve the scientific approach to the construction of AMR.
The purpose of the work - the analysis of the nature and purpose of automated systems for commercial electric power accounting, investigation of the characteristics of modern metering system on the market of Ukraine, to build a model AMR and evaluating the effectiveness of its functioning.
The novelty of the result - scientific novelty of my research is to develop a model of an automated system of commercial electric power accounting and justification of methods to assess the effectiveness of its introduction into production. A comparative analysis of the automated systems of firms operating on the Ukrainian market of AMR.
Practical value - Analysis of the situation on the Ukrainian market of AMR may be useful to potential customers of such systems, as well as companies that develop systems of this class. Currently, there is a problem assessing the effectiveness of the introduction of AMR and the results obtained in the course of the study can be used for such evaluations.
Approbation of the work - basic theoretical position and results of the thesis were reported, discussed and approved at the conference, Department of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science DonNTU dedicated day.

Basic rules for development and implementation of AMR:
• Measurement based on digital methods of processing processes.
• Digital transmission interfaces of the measured parameters.
• Deep archive basic measurements in the counter.
• Control accuracy and completeness of the data at all levels.
• Diagnose system uptime.
• Redundant communications channels.
• Parallel Synchronous and Asynchronous Processing.
• constructing a hierarchical system.
• Ability to distributed computing.
• Protection of information at all system levels.
• Use of proven and standard components and tools.
• Parallel data collection
• Scalability and extensibility
• Management-availability system design phase.
The composition of AMR systems include:
• Microprocessor-based electricity meters
• Device data collection and communication (RTU) RTU-325 series, RTU-327, cupboards NKU ASKUE.Programmnoe software for all levels of systems
• Communications equipment (telephone, high-frequency and radio modems, modem pools, fiber optic converters, cables, etc.)
• Workstations (AWS), computer hardware (communications servers, database servers, workstations, UPS, hubs for organizing the local network, etc.).
Principles for creating a modern AMR
Approach to the creation of AMR is based on a synthesis of standard solutions and work with the customer in choosing the optimal (according to price and functional performance) option in each case.
In the concept of a metering system conveys two basic principles: a recognized reliability of digital technologies for collecting and transmitting data and an open architecture that allows to its further development.
Flexible adjustment to any object, scalability, use of digital and pulse counter in the same system, operational control and monitoring in real time

General characteristics
• The system provides reliable and complete measurements and calculations made based on them in accordance with a flexible, customizable timing diagram of
• The system provides reliable and complete measurements and calculations made based on them in accordance with a flexible, customizable timing diagram of
• The system has high reliability
• System maximum is invariant to changing requirements
• The system runs on the basis of uniform, used standard solutions
• The system has a high rate: the functionality / cost, reliability / cost.
Requirements, optimality criterion and the objective function AMR
The use of different technological solutions to create AMR should be considered in the context of compliance with the generalized optimality criterion, which refers to the minimum cost of implementation and operation of the AMR:
where ZASKUE – energosbyt company's costs for the implementation and operation of AMR.
Comparison of existing solutions on this basis will identify areas of their rational (irrational) use and offer a functional solution that satisfies the optimality criterion (1) and realizing the objective function metering as a condition of the complex to minimize commercial losses of electricity (2):
where PNED – losses due to deficiencies in energy sales activities;
POPL – losses at reclaiming payment;
PHISCH – losses from theft of electricity;
POGR – losses due to limitations in power consumption "from above";
PKACH – losses due to violations of the quality of electricity;
PDOLG – loss on debt collecting.
It should be noted that the term PDOLG is dependent on the terms PNED, swam and PHISCH. Therefore, the minimization of the latter leads to the minimization of PDOLG.
Reaching the global minimum objective function is possible with a complex condition (3):
As for the condition (1), the additional reduction in the size ZASKUE can be obtained by competent phased implementation of AMR.
PNED-—> min
POPL—> min
PHISCH—> min
POGR—> min
PKACH—> min (3)
In particular, total automation of energy accounting "exemplary taxpayers" will not help to reduce the value of Pople and PHISCH. However, the implementation of priority metering, satisfying the conditions (1) and (2), for "forgetful" subscribers and "malicious defaulters" can improve their payment discipline and reduce the amount of unauthorized (bezuchetnogo) electricity consumption.
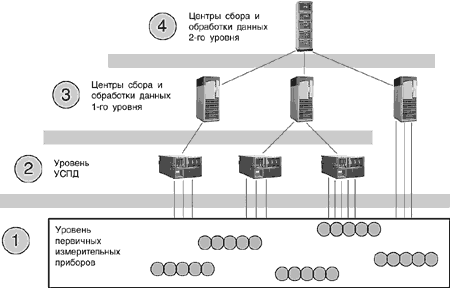

Prospects for research - currently the market of automated systems for commercial electric power accounting is booming. Development of new principles of building automation systems, introducing new technology. Increasing focus on evidence-based information systems, developing methods for evaluating the effectiveness of their implementation. This work may serve as a basis for further research in the field of AMR.
References
- Сапронов А.А. Концептуальный подход к организации и управлению предприятиями коммунального хозяйства // Проблемы экономики и организации производственных и социальных систем: сб. научн. трудов. – Вып.4. – Новочеркасск: ЮРГТУ, 2001.
- Типовой договор энергоснабжения для одноставочных и прочих потребителей электроэнергии ОАО «Ростовэнерго». Ростов-на-Дону. 2006.
- Методические рекомендации по регулированию отношений между энергоснабжающей организацией и потребителями. / Под. общ. ред. Б.П. Варнавского. – М.: РАО «ЕЭС», 2002.
- Конституция РФ. – М.: Изд-во ЭЛИТ, 2005.
- Гражданский кодекс РФ. – М.: ТК Велби, Изд-во Проспект, 2005.
- Правила предоставления коммунальных услуг. Утверждены Постановлением Правительства РФ от 26.09.1994 г. № 1099 (в ред. Постановлений Правительства РФ от 24.02.95 N 182, от 10.02.97 N 155, от 13.10.97 N 1303, от 01.02.2005 N 49).
- Системы коммерческого учета потребления электроэнергии на базе PLC-технологий с передачей данных по сети GSM. Техническое описание. –М.: Группа компаний ТЭСС, 2004.
- Медведев Д.В. Методика построения моделей автоматизированных систем управления технологическими процессами // Изв. вузов Сев.-Кавк. регион. Техн. науки. – Новочеркасск, 2004. – Приложение №6.
- Российская Федерация. Законы. Об энергосбережении: федер. закон. от 03.04.1996 №28-ФЗ.
- ГОСТ Р 51541-99. Энергосбережение. Энергетическая эффективность. Состав показателей. – М.: Изд-во стандартов, 2000.
- Бренерман Ю.Б., Рубичев Н.А. Показатели качества многовходовых систем // «Измерительная техника». – 1985. – №7.
- ГОСТ 24.701-86. ЕСС АСУ. Надежность автоматизированных систем управления. Основные положения. – М.: Изд-во стандартов, 1986.
- А.А. Сапронов. Анализ структуры коммерческих потерь электроэнергии в распределительных электрических сетях // Энергосбережение и водоподготовка. № 4(42). 2006.
Resume About myself