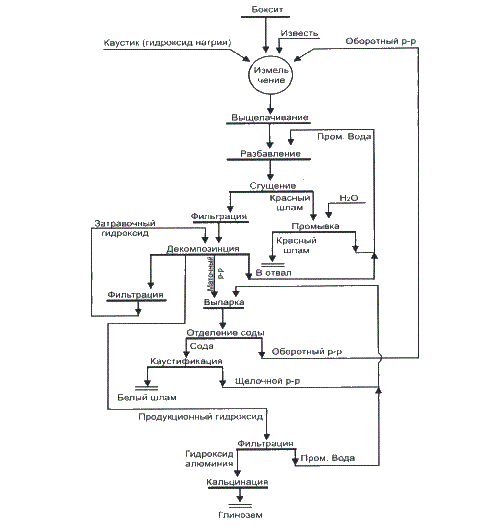
The process consists of the following technological process stages: milling, leaching, sedimentation of red mud; expansion aluminate solution, filtering the hydrate of aluminum oxide, drying and calcining aluminum hydroxide to produce alumina residue other solutions and to obtain solids. The main stage production of alumina from bauxite ore is ripped out of her aluminum hydroxide. It is based on the following chemical property of aluminum oxide hydrate: crystalline aluminum hydroxide, which is part of bauxite, is highly soluble at high temperature in a solution of sodium hydroxide (caustic lye, NaOH), high concentration and with decreasing temperature and concentration of the solution re-crystallizes. Useless to produce aluminum materials that are part of bauxite (the so-called ballast) is not transferred at the same time in a soluble form or recrystallized, and precipitated before the crystallization of aluminum hydroxide is produced. Therefore, after the dissolution of aluminum hydroxide ballast can be separated and removed in a dump. Purified from impurities in the aluminum hydroxide solution of alkali (representing mainly a solution of sodium aluminates NaAlO2 undergoes crystallization. To this end, the concentration of alkali and the solution temperature is reduced to certain values that are optimal for obtaining crystalline aluminum hydroxide. Crystallization substantially accelerated if the solution already presents crystals of aluminum hydroxide of sufficient size (embryos). Therefore, at this stage in a solution specially introduced a certain amount of fine-crystalline aluminum hydroxide, which is called a seed. After a sufficient degree of crystallization is separation from the solid hydroxide solution. Alumina (Al2O3) is obtained from aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) calcinations in furnaces last (calcinations) to remove bound water of the hydrate, leaching autoclave used scheme. The purpose of further this research is the development of tubular leaching cheaper for hardware design. HIGH TUBULAR leaching. Leaching at temperatures above 280 ° C, commonly called high temperature. High-temperature autoclave leaching has not found distribution of the high cost of autoclaves operating at a pressure of 60-100 atm. High leaching began to spread only after the development of Installation of tubular leaching, in which leaching occurs when moving slurry in the pipe long (1 km). Pipe length is determined by performance and holding time. Heating is provided by heat exchange on a "pipe-in-tube" (the main pipe is enclosed in another tube). Coolant (hot steam or boiled pulp) is moving in the annulus.
Conclusions of research
The advantages of tubular autoclave leaching before the following: simplicity, since it uses the serial production of high pressure tubes, rather than the thick-walled vessels of stainless steel, designed and manufactured by special order; no need for mixing devices: the pulp is mixed due to turbulence moving through the pipes of small cross section; for heating the pulp is used almost the entire surface of the pipe, and not only the surface of heat exchangers tubes, as is the case in an autoclave. The disadvantages of tubular variant can include the following: A large area of the pipe placement (but it can be reduced if the tube placed in several levels); difficulty of cleaning the internal surfaces of precipitation; in this case malfunction a mechanical cleaning method is mainly used and chemical cleaning by special agents; but it increases the cost of production and causes environmental problems.
