

Metal objects around us rarely consist of pure metals. Alloys - a system consisting of two or more metals, as well as metals and nonmetals, with properties inherent to the metallic state.
Nickel, along with chromium is an essential component of many alloys. He gives steel high chemical resistance and mechanical strength. For example, a well-known stainless steel contains an average of 18% chromium and 8% nickel. For the production of chemical equipment, nozzles, aircraft, space rockets and satellites requires alloys that are stable at temperatures above 1000 ° C, that is not destroyed by oxygen and combustible gases and possess with the best strength steels. These conditions are satisfied alloys with high nickel content.
Nichrome is used in electric heaters furnaces for all industries, household appliances and aids the thermal effect. Widely used in high electric furnaces, kilns firing and drying of various electrical devices of the thermal effect. Used as a heating element and resistor. Has a high heat resistance, ductility and dimensional stability. Also Nichrome is used as a refractory (heat resistant) alloy and chemically resistant alloy in certain aggressive environments.
For electrical resistance furnaces as a heating element using a wire cross-section from 0,5 to 10 mm made of deformed semifinished nichrome, inconel or kronita. Melting of these wrought alloys are in arc furnaces with magnesite lining. Smelting nickel alloys in air is accompanied by oxidation and saturation intensity of the melt with hydrogen. These processes predetermine the contamination of the melt inclusions of solid insoluble oxides of alloying components and the formation of blowholes and porosity in castings. Protection from the intense interaction with the gases is achieved by using flux, consumption of which is 2-10% by weight of the melt.
With the help of flux can not completely suppress the dissolution of hydrogen, so one of the most important operations in the smelting of nickel alloys is a refinement of their dissolved gases. This operation is carried out by pointing at the end of smelting slag oxidation, which causes the boiling bath. To restore oxidative slag using iron oxide Fe2O3, nitrous NiO nickel or manganese dioxide MnO2.
Dissolved hydrogen can be removed as melt blowing argon.
Another of the main conditions associated with melting of nichrome is to prevent contamination of molten sulfur and carbon, drastically reducing the operational properties of the alloys.
Greatly simplify the technology of melting of these alloys is possible using the technology of electroslag chill casting (ECL) from recycled materials, which eliminates the above difficulties in the smelting of this metal in electric arc furnaces, namely: at EKL no contact of molten metal with air, highly basic fluxes allow deep enough conduct refining of metal from the sulfur and significantly reduces waste of alloying components (in this case - chrome). Then, at a joint casting of metal and slag in a metal mold, the latter prevents metal contact with the atmosphere and at this stage of the process.
In this work we have carried out several batches:
1) using a consumable electrode alloy Cr20Ni80 welded TIG welding of exhaust heating elements - pieces of wire with a diameter 2 ... 10 mm (Picture 1a).
2) using non-expendable copper water-cooled electrodes with plasma spraying of its working parts of boron nitride, and the charge in the form of the same bars, but not cooked and fed to the furnace by the piece (Picture 1 ).

As the flux of flux used stamps AN-295.
Casting experienced alloys was carried out in a metal mold with an inner diameter of 40 mm and a height of 500mm. From these castings samples were taken for chem. analysis and metallography.
Table 2 presents the results of chemical analysis.
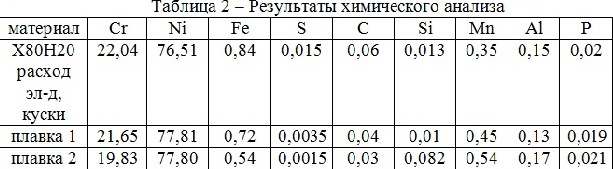
Based on the results of chemical analysis, we can conclude that this alloy in both cases, fully complies with the GOST. Thus, the technology of electroslag chill casting can be applied for nichrome recycled.