Abstract
«Research of electromagnetic method of data destruction from magnetic carriers»
A. Riabtsev
IntroductionTo protect private data, which can be kept on magnetic media, organizing- security and organizing -technical measures that let to block possible channels of data leakage are used.
Deleting of data recorded on magnetic media can be carried out with the help of programmed wiping of specified files, physical deleting of medium or changing of magnetic characteristics of coating [10].
For urgent destruction of private data it is reasonable to use the method based on demagnetization and magnification of magnetic layer of medium. So, this method will let to carry out the operation on data destruction in comparatively short time, but will demand formation of strong magnetic fields with amplitudes, which are determined by characteristics of thin-film media layers.
Purpose of the research
The purpose of the Master's Thesis is to research electromagnetic method of data destruction out of magnetic media for its effectiveness, speed performance, energy output, reliability and practicality of use in implementation of complex system of data protection (CSDP). To reach the desired goals it is necessary to carry out:
-analysis of the work of modern magnetic media and devices for deleting and recovering of standard and additional data;
-analysis of effect of impulsive magnetic fields on magnetic media;
-modeling of devices for making of electromagnetic effect for drives on hard magnetic discs (DHMD) and modes of work;
-experimental researches of effects of pulsed fields on DHMD;
-offering ideas concerning brining the method of data hiding in CSDP to life.
Actuality of the work
In modern world information is playing an important role in human activity. It is one of means of goods the price for which is varied from a kopeck to millions. And the damage from unapproved distribution of information can be measured by different sums of money. Very often data destruction provides less costs then if these data fall into the wrong hands. Electromagnetic method of data destruction from DHMD is simple in realization, safe, cheaper in comparison with other ways of impact on DHMD and will continue to be relevant as long as given types of media exist and even 20-30 years.
Assumed scientific newness
Qualitative improvement of technical characteristics of devices; for implementation of pulsed magnetic fields of definite value taking into account modern researches and constructive application of new magnetic dist drives; adaptation of the researched method of data destruction in CSDP.
DHMD as source of potential threats of information security
Layout of private data in devices of computers’ long-term non-volatile memory offers an opportunity to form particular channels of data leakage. At this date drives on hard magnetic discs (DHMD) are the most wide-spread devices. Wide use of DHMD is explained by the number of good functional qualities, such as reliability, speed of access and comparative cheapness per unit of stored information.
The features of DHMD, which are favorable to operations with the usage of technical reconnaissance equipment (TRE) are:
- large volume of stored data, from hundreds of Mbytes to tens of Gbytes;
- nonvolatility of stored data, because presence or lack of power supply doesn’t influence on its condition;
- absence of manufacture of DHMD in Ukraine.
Data leakage is possible on such scenarios:
- retrieval of data, selected by definite feature and archived in technical zones, from DHMD in the process of its use as part of computer system or computer net;
- data storage on DHMD with following imitation of breakdown.
In the first case direct data hosting is possible (with the use of radio relays, hardware backdoors, undocumented network power).
The second variant of data leakage is effective when goal-oriented delivery of computer equipment of definite organization with further guarantee service of computers at supplier firm or service centre is occurred.
Ways of destruction of data stored on DHMD
Nowadays there are several ways of destruction of data stored on DHMD. Destruction means cancel or deleting of data from hard disk in such a way that it is impossible to restore data neither with the help of handling on computer using definite computer software (CS) nor with the help of laboratory means (for example, study of surfaces of magnetic plates with the help of scanning microscopy).
Methods of destruction of data on DHMD are divided into three large groups:
1. Programmed, based on destruction of data recorded on magnetic medium by means of standard devices of data record on magnetic media. In case of destruction of data on DHMD by the programmed method it can be used again in other computers after installation of new operation system and apps. Destruction is occurred by simple and natural way, it is data rerecording. Rerecording is the process of recording of unclassified data in the storage where private data were kept earlier.
2. Mechanical, connected with mechanical damage of the bases on which the magnetic layer is applied. Magnetic layer is data physical medium.
3. Physical, connected with physical principals of digital recording on magnetic medium and based on rearrangement of the structure of magnetic material of the medium’s recording surfaces.
By the way of influence on the medium:
- without destroying of herm camera and recording surfaces of DHMD;
- with destroying of DHMD.
Physical methods of destruction of data on DHMD
Nowadays the usage of physical means connected with rearrangement of the structure of magnetic material medium’s recording surfaces is the best way for providing reliability of destruction of data without destroying the medium.
To cancel data on magnetic plates of DHMD it is necessary to dispose discontinuities of magnetization vector of recording surface’s parts having data about preceding records.
Above-noted change of the structure of the field of magnetization vector of magnetic layer can be realized by several absolutely different ways:
- by means of flash heat of the material of medium’s recording surface till the unit of leak of medium’s magnetization (Curie units);
- by means of demagnetizing of medium’s recording surfaces;
- by means of magnetization of medium’s recording surfaces till maximum possible values of magnetization (save).
- combined. Heat and magnetization or heat and demagnetizing.
Magnetization. The method is based on the fact that in case of DHMD the superposed magnetic field is considered as analogue of the field formed by magnetic heads during recording. If the characteristics of superposed field exceed field density made by heads for such value, on which magnetic save of the material of disk surface is occurred, then all magnetic domains will be reoriented on direction of this superposed field and all data on DHMD will be destructed.
Hysteresis effect while magnetic reversal by superposed magnetic field is typical for ferromagnetics. Under the influence of superposed magnetic field orientation of elementary magnetic fields formed by cyclical motions of electrons in atoms of ferromagnetics is occurred. As the result sizes of magnetic domains oriented by the direction of superposed field are increased. After extinction of external action changes in sizes and orientation of magnetic domains are partially saved. Magnetic remanence of the substance is appeared. It is trace rested in ferromagnetic by external action. Devices, which read recorded data registered that particular magnetic remanence of the medium’s material. [13]
Peculiarities of data cancel from lamellate hard disks by pulsed magnetic field
Data cancel from DHMD is realized by successive exposures of longitudinal (laid in the plane of the disk) and cross (orthographic to the plane of the disk) magnetic field with such impulse parameters:
- longitudinal field; amplitude 720-760 kA/m, pulse duration on the level 0,5 - 1,36-1,4 ms;
- cross field: amplitude 640-650 kA/m, pulse duration on the level 0,5 – 5,2-5,4 ms;
Quality of data cancel is controlled by methods of atomic force microscopy by means of registration of magnetic relief of surface of every disk in several places before and after influence by pulsed magnetic fields. After the influence 5 patterns of remanent magnetic relief were taken from different areas of every surface of every disk. On the figure 1 magnetic relief of the disk surface with recorded data is shown and we see that atomic force microscope «Smena A» [12] provided spatial resolution in magnetic image at least 50 nm with high contrast between physical zero and one.
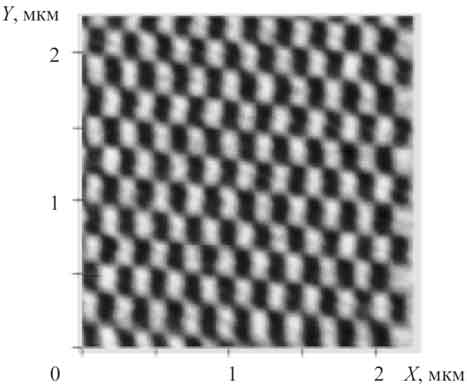
Fig.1 Magnetic relief of disk surface with official information
On the figure 2 we can see magnetic pattern of the surface of one of disks of three-plate hard disk after the influence of magnetic fields of cancelling device. It is obvious that data is completely cancelled. On every surface of every disk magnetic relief was taken off in 5 points. The whole 30 patterns are identical to the pattern shown on the figure 2.This fact confirmed full data destruction on DHMD.
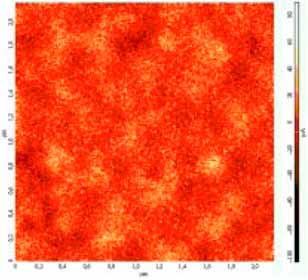
Fig.2 Typical pattern of magnetic relief of the surface of one of hard disks after influence of pulsed magnetic field
Unlike this case, the same influence on disks of DHMD of another company doesn’t lead to full data cancelling. On the figure 3 we can see areas, where all data is cancelled and areas with its fragments. Of cause reading of the data by standard magnetic heads of DHMD is practically impossible. This relief can be visualized by the methods of atomic force microscopy, but recovering of data fragments is connected with technical difficulties. Partial data cancelling is apparently connected with screening of pulsed magnetic field by metal elements of DHMD. Aluminium substrates (thickness – 1mm) of magnetic disks also played an important role there.
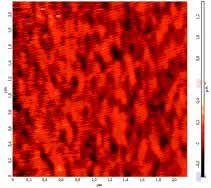
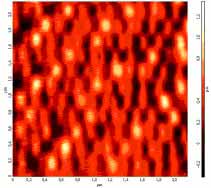
Fig.3
Typical magnetic relief of different areas of surface of one of hard
disks after influence of pulsed magnetic field: a- data is fully
cancelled; b- data is not cancelled
Device of formation of pulsed magnetic fields for modification of magnetic conditions of thin-film media layers
Sources where power of network and capacitive storage comes as an impulse are the simplest switched power supplies for magnetizer. In such device capacitive storage, represented as bank of capacitors with capacity C, is charged to necessary voltage from definite charging device. The charging device is connected to and tripped out the network with the help of commutation device. Processes of connection and tripping of charging device from the network, controlling by power supplies are operated and controlled by the controlling system. The direction of superposed magnetic field is set by the construction and form of the field magnet’s turn. For the maximum productivity of magnetization the superposed field must be applied to the same plane where heads of DHMD’s record work. In this case the effect of magnetization is maximum.[13]
Results of the research
As the result of the research it was established that for data destruction from the modern types of hard disks magnetic impulses of considerable intensity are demanded for overcoming of coercitive force of thin-film magnetic media. It is connected with structure feature of DHMD and materials used in its structure. At this date a lot of devices for data destruction using electromagnetic method don’t satisfy the requirements which structure peculiarities of modern hard disks demand. So, significant improvement of the characteristics is required.
Conclusion
Among different methods of data destruction from DHMD electromagnetic method is the most appropriate one for a number of reason:
1. High reliability of data destruction.
2. There is no breaking of physical integrity of DHMD.
3. High speed of data destruction.
4. Less power usage and it can be energy-independent (work from accumulators)
5. Simple in realization
6. It is applied to different types of DHMD
References
1. Герус С.В., Митягин А.Ю. Особенности стирания информации с многодисковых винчестеров импульсным магнитным полем. [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа: URL: //www.nbuv.gov.ua/portal/Natural/tkea/texts/2010-1/14-17--.pdf
2. Нестерин В.А., Оборудование для импульсного намагничивания и контроля постоянных магнитов.// – М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1986, с. 88
3. Беседин Д.И., Боборыкин С.Н., Рыжиков С.С. Предотвращение утечки информации, хранящейся в накопителях на жестких магнитных дисках.// Специальная техника. №1/2001.
4. Рохманюк В.М., Фокин Е.М. Чисто? Чисто и быстро! Защита информации. //Конфидент, 1998 №5
5. Рохманюк В.М., Фокин Е.М. Аппаратура экстренного уничтожения записей на магнитных носителях.// БДИ, 2000 №5
6. Рохманюк В.М., Фокин Е.М. Способ стирания записей на магнитном носителе и устройство для его осуществления. //Патент на изобретение RU № 2144223
7. Экспертное заключение по итогам анализа устройства быстрого уничтожения информации на магнитных носителях «Стек». //Испытательная лаборатория в системе сертификации ФСБ России.
8. Information Security Products. [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа: URL: http://www.zaoanna.ru/
9. Сайт посвящен компьютерной безопастности. [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа: URL: http://www.epos.ua/
10. Болдырев А.И., Сталенков СЕ. «Надежное стирание информации - миф или реальность?»// Антишпионаж. М. Защита информации. Конфидент, 2001.
11. Беседин Д.И., Боборыкин С.Н., Рыжиков С.С. Анализ возможностей предотвращения утечки информации, хранящейся в накопителях на жестких магнитных дисках (НЖМД). // [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа: URL: http://ess.ru/publications/1_2001/hdd/hdd.htm
12. Сай посвящен приборостроению для нанотехнологий. [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа: URL: http://www.ntmdt.ru
13. Коженевский С.Р., Методы гарантированного уничтожения данных на жестких магнитных дисках.// [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа: URL: http://www.epos.ua/
|
Important comment
In the time of writing of the
author's summary the Master's Thesis has not been finished yet. Final
completion will be on December 2011. The author or his supervisor can
render the full text of the research and materials on the topic after
the date mentioned above.
|