Speciality «Forcefield Security of employment»
Gap analysis and improvement activities elating to the integrated dedusting air at the horizon 1146 m mine F.E. Dzerzhinsky
Scientific adviser: Vladimir Yaylo
Resume
The abstract on the theme of graduate qualification work
Contents
Purposes and problems of the student work
Conclusions and future research
Timeliness
Coal industry was and remains industry with the most harmful, heavy and dangerous conditions of labour.
The modern methods of coal extraction and making of the development making works by formation of plenty of dust and hit of it in the atmosphere of the mine working making I which people work.
A fight against dust, as with professional harmfulness, predetermining possibility of workers disease of dustborne etiology, is an intricate engineering and organizational-technical problem. A decision of which is possibly only at complex application of different ways of prevention, decline dust formation, dust neutralization and dust ladenness of mine air.
Purposes and problems of the student work
On the mine named after Dzerzhinskoy there are 5-6 cases of disease pnevmokoniozom and dustborne bronchitis annually. Therefore a primary objective is a decline of dust-ladenness of air.
For achievement of this purpose it is necessary to decide the followings tasks:
— to conduct the analysis of modern methods and facilities on complex dust ladeness of mine air and measures on the decline of disease of dustborne etiology;
— to estimate efficiency by dustborne measures on a mine;
— to develop the complex of measures on the decline of dust-ladenness of air.
Digest result work
A mine the named after Dzerzhinskoy was founded in 1860.
The last reconstruction of mine was executed in 1987, which included the reconstruction of main skip shaft of Pugachevka with a simultaneous input in work of new horizon 1026 m. A mine is unsealed by four centrally located shafts: "Pugachevka»"; "№4", "Central", and "New"
The shafts of «Pugachevskiy« is passed to the mark 1263 m. Destination of shafts — serves for delivery of useful mineral from a mine simultaneously for delivery of rock. A shaft is a ventilation installation, I.e. the outgoing stream from the mine is given out a foregoing shaft.
Barrel №4 passed to the mark 1213 m. A shaft is intended for the serve of fresh air in a mine. At the same time a shaft serves for lowering and delivery of people from operating horizons 916 m codes and 1026 m codes, and also from the prepared horizon 1146 m.
On a foregoing barrel, lowering and delivery of long measures, and also delivery of rock is produced from horizon 916 m. A shaft the «Central» at the moment is on a reconstruction. In future a shaft will serve for lowering of materials and long measures on horizon 1026 m.
A shaft the «New» is passed to the depth 843 m codes and does not operate presently. In according to a project «Dneprogiproshakht» a shaft is subjected to liquidation, I.e. shaft stations and buildings are liquidated, and a shaft it self is being filled up by rock.
A mine named after Dzerzhinskoy is attributed to dangerous on the sudden extrass of coal and gas, Method of ventilation of mine works off steep layers suction.
Exhaust air from a mine is given out by ventilator of main ventilation of ВЦД-47У, set on-the-spot near a vent shaft of Pugachevka. Second ventilator of ВЦД-47У is a reserve.
Methods and facilities of fight against a dust
Complex dust neutralization of mine air will be realized on three, to up to a point associate directions: decline of dust neutralization, diminishing of dust neutralization (passing of appearing dust to the self-weighted state) and cleaning of air from a soaring dust.
At existent technologies of excavation of coal and making the development preparatory workings by the basic method of decline of pyleobrazovaniya there is the preliminary moistening of coal array by festering of water in a layer through shpury or short mining holes, bored from the face in the direction of its pushing, and in the cleansing workings — also through long mining holes, bored parallell to the backwall of lava. For the improvement of wettableness of coal at his preliminary moistening surface-active matters are used. For the preliminary moistening of coal in an array the next equipment is applied.
Drilling of shpurov or mining holes to 45 mm carry out a diameter by hand electro — or pnevmosverl, and at a necessity the boring drilling of short mining holes to 56 mm is applied by portable perforators.
For the boring drilling from the preparatory making of long mining holes the borings settings of SBG-1I, «START», BAE-15 and NKR-100I are applied.
Pressurizing of mining holes and shpurov is carried out the hose hydrolocks of «Taurus-45», «Taurus-50», GT-45, GT-60, WENT-45 out, AG-4A.
Festering of water is produced by a high-pressure pump settings of UNR-02, UIP, UNSH-00, UNSH-01 and UNG, providing pressure to 32 MPa and serve of water to 90 l/mines.
Control of volume of swing water is carried out by water-meters - meters of kryl'chatogo type of UVK-20, UVK-25, SVKHK-1,6, SKHVK-4; pressure of water is measured by manometers.
Efficiency of the preliminary moistening of coal array does not exceed 70%. Therefore for the decline of pylepostupleniya practically at all production processes used different kind irrigation is irrigation of mountain mass through attachments and sprayers, pnevmogidrooroshenie, tumanoobrazovanie and vodovozdushnoe ezhektirovanie.
Effective dust neutralization, including cleaning of dust-laden air and irrigation of mountain mass water simultaneously, is arrived at application of cylindrical and conical water-rived ejector of EC-100, EC-250, EK-80, EK-1-110-500 and other. Principle of work of vodovozdushnogo ejector (pic.1) consists in that due to discharging, created by aquatic torch of sprayer, dust-laden air, formative with the dispergated water shlamovidnuyu mixture, which, in its turn, heads for suppression of dust.
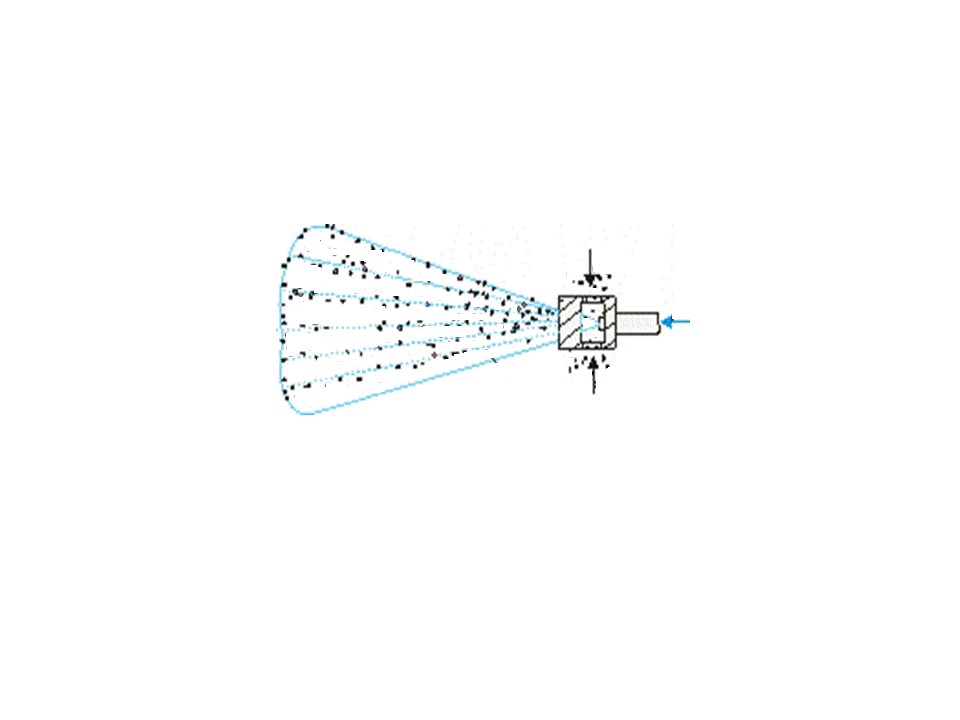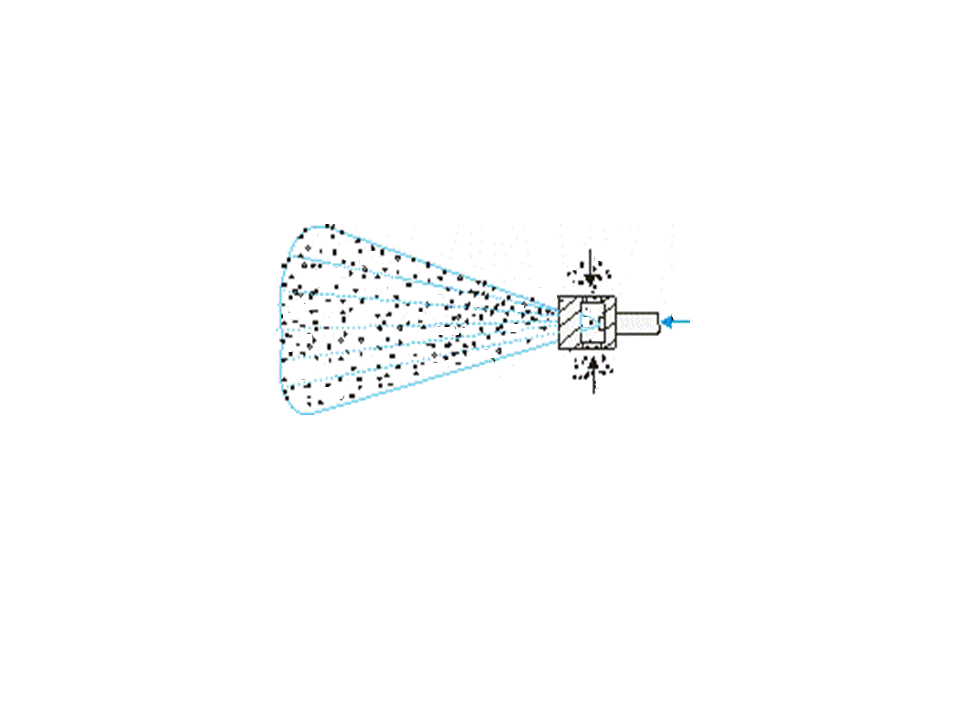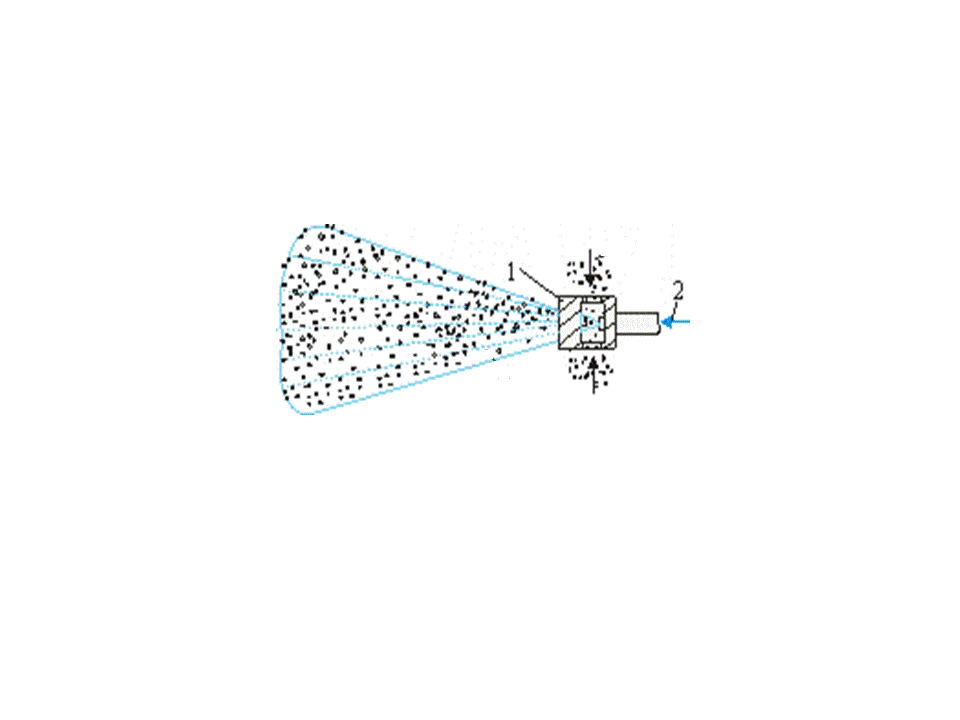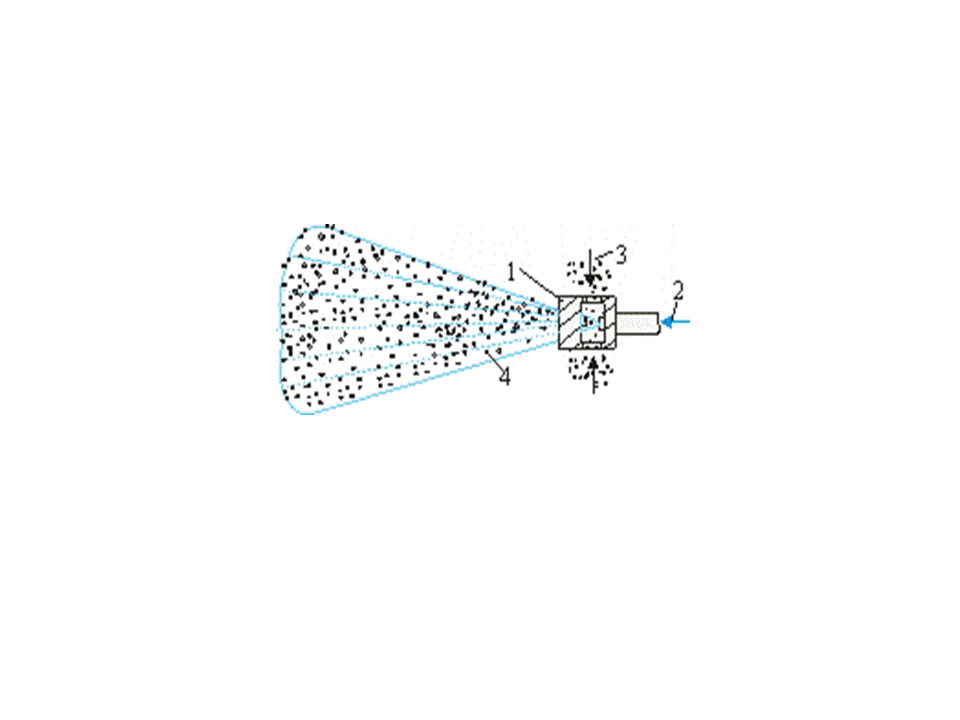
1 – atomizer; 2 – water; 3 – dusty air; 4 – schlamm mixture
Pic.1 –Principle of the water–air ejector
The preliminary moistening of coal in an array
The preliminary moistening of coal in an array must be used at the conduct of stoppings, and also during the leadthrough of making the combines of the electoral operating under the layers of middle power.
Festering of water in a layer in the cleansing making must be produced, as a rule, through long mining holes, bored from the preparatory making parallell to the backwall of lava. Moistening on such chart is applied at the post system by developments, passing of even one of the preparatory making of backwall of lava at the semilongwall of development and at the shield coulisse of steep layers. Mining holes for festering of water can be bored from one or to meet from two making. In shield lavas, festering of water must be produced in the bar of coal prepared to the coulisse (pic.2).
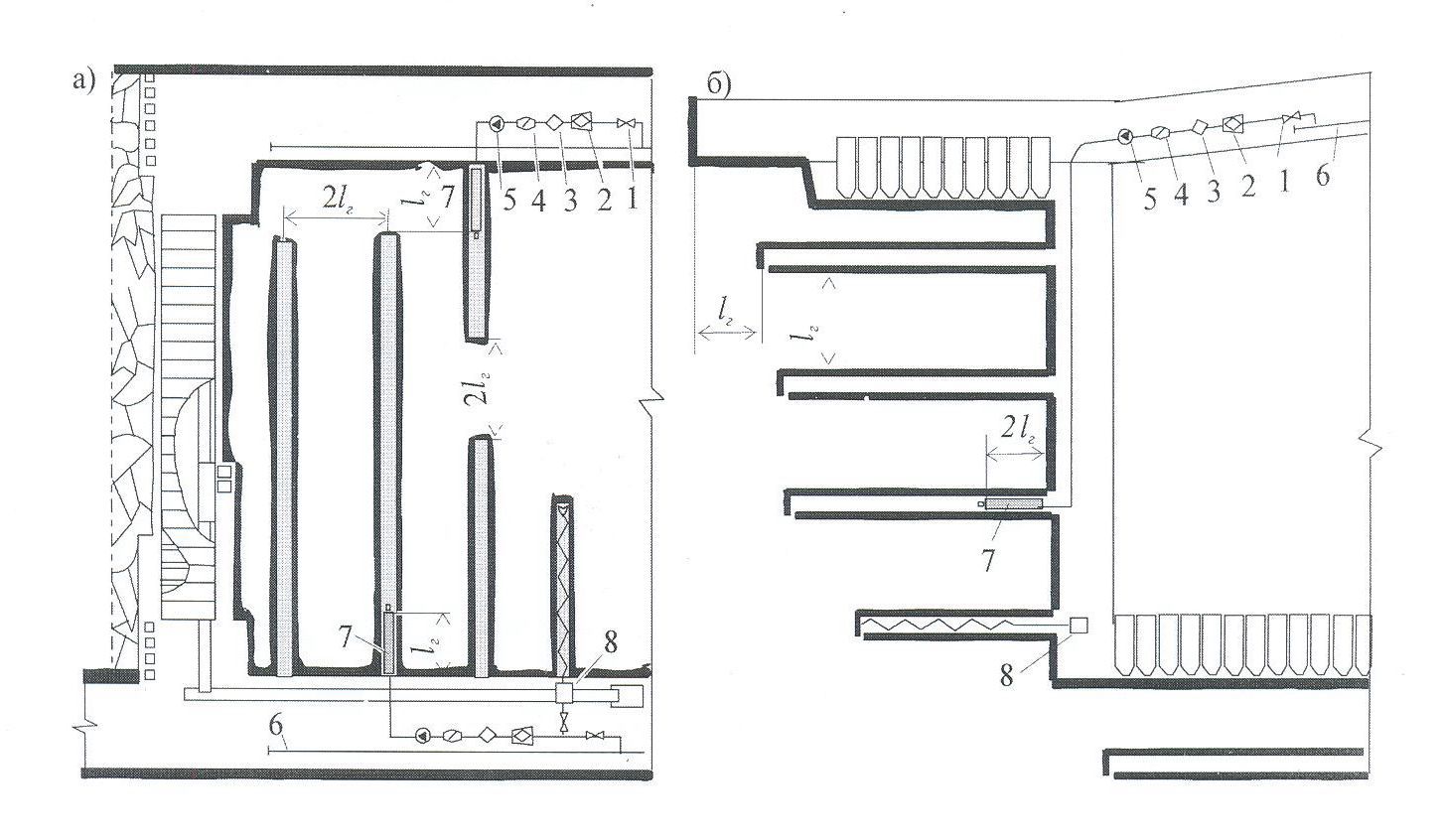
1 – a valve; 2 – a filter a drift; 3 – a metering device of smachivatelya; 4 – a flowmeter; 5 – the pumping setting high-pressure; 6 – a drift pipeline; 7 – germetizator; 8 – a boring machine-tools
Pic.2,3 – Flowsheets of festering of water from the preparatory making in the cleansing backwalls of declivous layers (a) and at a shield coulisse on steep layers (b)
Length of mining holes is accepted from the condition of providing of moistening of coal on all length of lava and exception of gust of water in the preparatory making, and at well-drilling from two making to meet in a nearby mining hole.
The depth of pressurizing of mining hole must recover the extent of off-loading influence of making and 10-15 m. is accepted.
Dust neutralization of air in the cleansing working
Except the preliminary moistening of coal layer, in cleansing faces walls the measures of dust neutralization and dust neutralization of air are used at the followings production processes:
— at the extraction of coal;
— on the gatehead of lava;
— at a extraction and loading of coal in niches, stoves and cutting;
— at the pneumatic book-mark of mine-out space and laying-mark of rubble bars.
If the applied facilities of dust neutralization do not provide the decline of dust-ladenness of air to PDK, dust neutralization of air is additionally produced outgoing from the cleansing making.
During work of extracting machine on layers with the high category of production processes on a dustborne factor can be used also sucking and catching of dust, if it is foreseen by a technical document on a machine.
Mechanized krepi is completed by facilities of irrigation on the requests of mines, if it is necessary in connection with the enhanceable level of dust-ladenness. Thus the serve of water to the irrigatory devices of extracting machine and mechanized krepi must be carried out on separate pipelines with the independent including of irrigatory pumps.
At preparation of niches facilities of dust neutralization are foreseen both at the coulisse of coal and at loading of mountain mass. At a drill and fire system of coulisse of coal the boring drilling of shpurov is carried out with washing; irrigation of the put aside dust on-the-spot in the distance a to 20 mcode from the blown up charges or explosing of charges with water with the specific expense of 1,5-2,0 l/m2, application of water-spray curtains and gidrozaboyka of shpurov. At a hammer coulisse application of mechanical picks with a built-in irrigatory device or irrigation of surface of backwall is foreseen in the area of destruction of coal. Regardless of method of coulisse of coal irrigation of the removed coal is foreseen before loading.
Suppression of dust at the movable points of loading is carried out irrigation of coal water by umbellate or cone sprayers. Sprayers are set above the mestome of loading, so that a torch was recovered by the hearth of pyleobrazovaniya. At speed of air more than 2 m/ss are equipped shelter of area of loading of coal, and at the high level of dust-ladenness shelter with the ejecting action of water is used.
In the mechanized cleansing backwalls of steep layers at the pryamotochnoy chart of ventilation the irrigatory system is used with the pumping setting with pnevmoprivodom. At presence of podsvezheniya of outgoing stream the pumping setting and podborschik of backwall pipeline (pipelines) can be used electrically-actuated, disposed on a fresh stream.
In backwalls with pnevmoenergiey the irrigatory setting with pnevmoprivodom is disposed on a vent horizon (pic. 4).
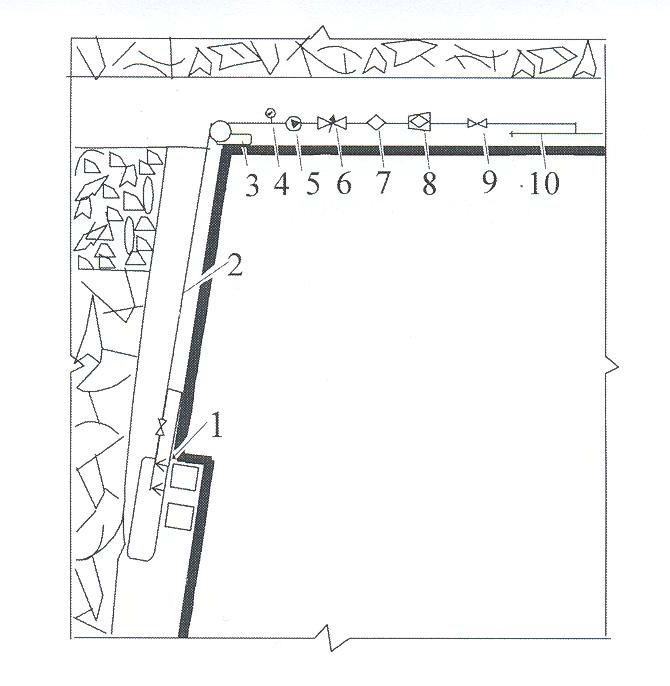
1 – irrigatory devices of combine; 2 – the backwall plumbing; 3 – shlangopodborschik; 4 – a manometer; 5 – the pumping setting; 6 – a valve guided; 7 – a metering device of smachivatelya; 8 – a filter of shtrekovyy; 9 – a valve; 10 – a drift pipeline
Pic.4 –A flowsheet of irrigation at the combine coulisse of steep layers
In backwalls with the use of electric power the pumping setting is electrically-actuated disposed on a haulage (conveyer) drift.
In the cleansing backwalls of thin steep layers at dust-ladenness of air more than 500 mg/m3 and in the case of necessity limits of rate-of-flow on irrigation used pylepodavlenie suds.
At a combine coulisse it is recommended to apply pylepodavlenie suds on layers by power a to 0,9 mcode and speed of air in a backwall at ascending ventilation no more than 2 m/ss. At a shield coulisse application pylepodavleniya suds is recommended in backwalls at the ascending chart of ventilation at a speed of motion of air a to 3,5 m/s.
At descending ventilation of combine and shield backwalls and in potolkoustupnykh backwalls with a hammer coulisse limitation on speed of air is not set. Penogeneratory set in combine lava in overhead part of lava under a windway, in shield lavas along konveyero-struga and area of unloading of coal in uglespusknuyu stove, in potolkoustupnykh backwalls in 4-5-ohm overhead ledges one by one in every ledge (pic. 5).
Pressure of the water given in the metering device of penogeneratora must make 0,4-0,8 MPa, and a specific expense of liquid through a metering device must be 15-25 l/t.
At a pneumatic book-mark provided: moistening of attle; impermeability of book-mark pipelines; periodic obmyvka of surface of making is in the places of settling dust; rate of movement of air in the area of book-mark no more than 2 m/ss.
For the decline of pyleobrazovaniya during the leadthrough of book-mark of rubble bars in lavas of steep layers moistening of pedigree mass is produced water or solution of smachivatelya before loading of it in trolleys.
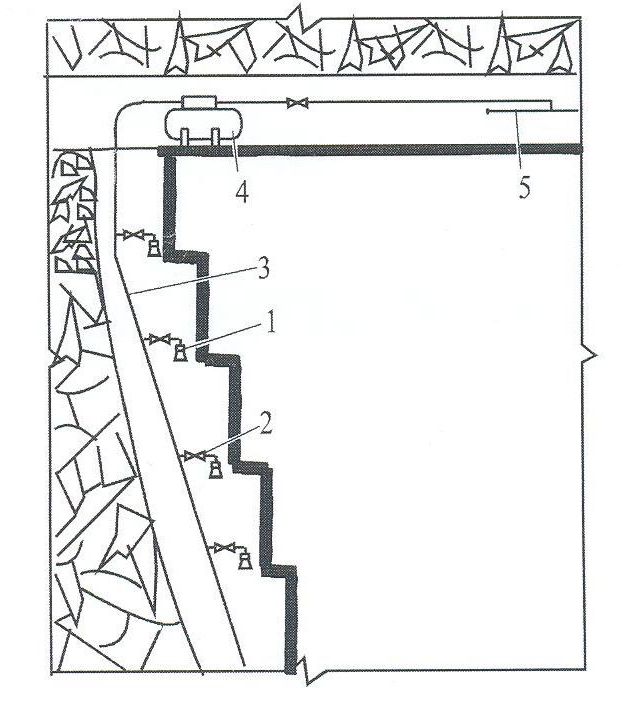
1 – penogenerator; 2 – a valve; 3 – the backwall plumbing; 4 – a metering device of smachivatelya; 5 – a drift pipeline
Рис.5 – A flowsheet of application of suds at the hammer coulisse of coal on steep layers
Conclusions and future research
Based on this work wecan make the following conclusions:
—comprehensive use of various methods to prevent, reduce dust, dust suppression;
—reduction of dust coming (junction formed dust in suspension);
—cleaning the air from a soaring dust;
—high-quality implementation of measures to combat the dust;
At this stage, the increasing application finds a comprehensive dust removal mining, the need for new methods and activities, increases the percentage of workers with pneumoconiosis disease.
References
- Кирин Б.Ф. Борьба с пылевыделением в шахтах / Б.Ф. Кирин, В.П. Журавлев, Л.И. Рыжих. – М.:Недра, 1983. – 199 с.
- Физико-химические основы гидрообеспыливания и предупреждения взрывов угольной пыли /В.И. Саранчук, В.Н. Качан, В.В. Рекун и др. – К.: Наук. Думка, 1984. – 209 с.
- Смачивание пыли и контроль запыленности воздуха в шахтах / Р.Р. Кудряшов, Л.Д. Воронина,М.К. Шуринова и др. – М.: Наука, - 167 с.
- Предотвращение выбросов угля и газа с помощью щелевой разгрузки / Николин В.И., Александров С.Н., Яйло В.В., Фридман Г.М. - Киев: Техника, 1992. - 150 с.
- С.Н. Александров, Ю.Ф. Булгаков, С.Г Лунев, В.В. Яйло. Охрана труда в угольной промышленности (учебное пособие для студентов горных специальностей высших учебных заведений). Донецк: ДонНТУ, 2005. 520 с.
- Яйло В.В. Предотвращение внезапных выбросов угля и газа с использованием комплекса КБГ // Изв. вузов. Горный журнал. - 1996. - №2. - С. 61 - 66.
- Яйло В.В., Рубинский А.А., Бондаренко А.Д., Васильченко В.И О возможности использования динамики концентрации газа для прогноза газодинамических явлений // Способы и средства создания безопасных и здоровых условий труда в угольных шахтах. Сб. научн. трудов МакНИИ. - 1999. С.
- Суханов В.В., Петулько С.Н./ Производственная пыль/. Медицина труда в угольной промышленности/: Сб. - Донецк: Изд-во ГП НИИ медико-экологических проблем Донбасса и угольной промышленности. 2000., 21c.
- И.П. Чеботков, П.Я. Заставенко/ Бурение глубоких скважин в выбросоопасных пластах Донбасса/. – Киев: Техника. 1964., 168с.
- Краснюк Е.П. Пылевые заболевания легких у рабочих промышленного производства Ук)
раины. Укр. пульмонол. журн. 1998; 4: 13–16.
- Предотвращение выбросов угля и газа с помощью щелевой разгрузки / Николин В.И., Александров С.Н., Яйло В.В., Фридман Г.М. – Киев: Техника, 1990. – 98 с.
Resume
The abstract on the theme of graduate qualification work
Purposes and problems of the student work
Conclusions and future research
Coal industry was and remains industry with the most harmful, heavy and dangerous conditions of labour.
The modern methods of coal extraction and making of the development making works by formation of plenty of dust and hit of it in the atmosphere of the mine working making I which people work.
A fight against dust, as with professional harmfulness, predetermining possibility of workers disease of dustborne etiology, is an intricate engineering and organizational-technical problem. A decision of which is possibly only at complex application of different ways of prevention, decline dust formation, dust neutralization and dust ladenness of mine air.
On the mine named after Dzerzhinskoy there are 5-6 cases of disease pnevmokoniozom and dustborne bronchitis annually. Therefore a primary objective is a decline of dust-ladenness of air.
For achievement of this purpose it is necessary to decide the followings tasks:
— to conduct the analysis of modern methods and facilities on complex dust ladeness of mine air and measures on the decline of disease of dustborne etiology;
— to estimate efficiency by dustborne measures on a mine;
— to develop the complex of measures on the decline of dust-ladenness of air.
A mine the named after Dzerzhinskoy was founded in 1860.
The last reconstruction of mine was executed in 1987, which included the reconstruction of main skip shaft of Pugachevka with a simultaneous input in work of new horizon 1026 m. A mine is unsealed by four centrally located shafts: "Pugachevka»"; "№4", "Central", and "New"
The shafts of «Pugachevskiy« is passed to the mark 1263 m. Destination of shafts — serves for delivery of useful mineral from a mine simultaneously for delivery of rock. A shaft is a ventilation installation, I.e. the outgoing stream from the mine is given out a foregoing shaft.
Barrel №4 passed to the mark 1213 m. A shaft is intended for the serve of fresh air in a mine. At the same time a shaft serves for lowering and delivery of people from operating horizons 916 m codes and 1026 m codes, and also from the prepared horizon 1146 m.
On a foregoing barrel, lowering and delivery of long measures, and also delivery of rock is produced from horizon 916 m. A shaft the «Central» at the moment is on a reconstruction. In future a shaft will serve for lowering of materials and long measures on horizon 1026 m.
A shaft the «New» is passed to the depth 843 m codes and does not operate presently. In according to a project «Dneprogiproshakht» a shaft is subjected to liquidation, I.e. shaft stations and buildings are liquidated, and a shaft it self is being filled up by rock.
A mine named after Dzerzhinskoy is attributed to dangerous on the sudden extrass of coal and gas, Method of ventilation of mine works off steep layers suction.
Exhaust air from a mine is given out by ventilator of main ventilation of ВЦД-47У, set on-the-spot near a vent shaft of Pugachevka. Second ventilator of ВЦД-47У is a reserve.
Complex dust neutralization of mine air will be realized on three, to up to a point associate directions: decline of dust neutralization, diminishing of dust neutralization (passing of appearing dust to the self-weighted state) and cleaning of air from a soaring dust.
At existent technologies of excavation of coal and making the development preparatory workings by the basic method of decline of pyleobrazovaniya there is the preliminary moistening of coal array by festering of water in a layer through shpury or short mining holes, bored from the face in the direction of its pushing, and in the cleansing workings — also through long mining holes, bored parallell to the backwall of lava. For the improvement of wettableness of coal at his preliminary moistening surface-active matters are used. For the preliminary moistening of coal in an array the next equipment is applied.
Drilling of shpurov or mining holes to 45 mm carry out a diameter by hand electro — or pnevmosverl, and at a necessity the boring drilling of short mining holes to 56 mm is applied by portable perforators.
For the boring drilling from the preparatory making of long mining holes the borings settings of SBG-1I, «START», BAE-15 and NKR-100I are applied.
Pressurizing of mining holes and shpurov is carried out the hose hydrolocks of «Taurus-45», «Taurus-50», GT-45, GT-60, WENT-45 out, AG-4A.
Festering of water is produced by a high-pressure pump settings of UNR-02, UIP, UNSH-00, UNSH-01 and UNG, providing pressure to 32 MPa and serve of water to 90 l/mines.
Control of volume of swing water is carried out by water-meters - meters of kryl'chatogo type of UVK-20, UVK-25, SVKHK-1,6, SKHVK-4; pressure of water is measured by manometers.
Efficiency of the preliminary moistening of coal array does not exceed 70%. Therefore for the decline of pylepostupleniya practically at all production processes used different kind irrigation is irrigation of mountain mass through attachments and sprayers, pnevmogidrooroshenie, tumanoobrazovanie and vodovozdushnoe ezhektirovanie.
Effective dust neutralization, including cleaning of dust-laden air and irrigation of mountain mass water simultaneously, is arrived at application of cylindrical and conical water-rived ejector of EC-100, EC-250, EK-80, EK-1-110-500 and other. Principle of work of vodovozdushnogo ejector (pic.1) consists in that due to discharging, created by aquatic torch of sprayer, dust-laden air, formative with the dispergated water shlamovidnuyu mixture, which, in its turn, heads for suppression of dust.

The preliminary moistening of coal in an array must be used at the conduct of stoppings, and also during the leadthrough of making the combines of the electoral operating under the layers of middle power.
Festering of water in a layer in the cleansing making must be produced, as a rule, through long mining holes, bored from the preparatory making parallell to the backwall of lava. Moistening on such chart is applied at the post system by developments, passing of even one of the preparatory making of backwall of lava at the semilongwall of development and at the shield coulisse of steep layers. Mining holes for festering of water can be bored from one or to meet from two making. In shield lavas, festering of water must be produced in the bar of coal prepared to the coulisse (pic.2).

Length of mining holes is accepted from the condition of providing of moistening of coal on all length of lava and exception of gust of water in the preparatory making, and at well-drilling from two making to meet in a nearby mining hole.
The depth of pressurizing of mining hole must recover the extent of off-loading influence of making and 10-15 m. is accepted.
Except the preliminary moistening of coal layer, in cleansing faces walls the measures of dust neutralization and dust neutralization of air are used at the followings production processes:
— at the extraction of coal;
— on the gatehead of lava;
— at a extraction and loading of coal in niches, stoves and cutting;
— at the pneumatic book-mark of mine-out space and laying-mark of rubble bars.
If the applied facilities of dust neutralization do not provide the decline of dust-ladenness of air to PDK, dust neutralization of air is additionally produced outgoing from the cleansing making.
During work of extracting machine on layers with the high category of production processes on a dustborne factor can be used also sucking and catching of dust, if it is foreseen by a technical document on a machine.
Mechanized krepi is completed by facilities of irrigation on the requests of mines, if it is necessary in connection with the enhanceable level of dust-ladenness. Thus the serve of water to the irrigatory devices of extracting machine and mechanized krepi must be carried out on separate pipelines with the independent including of irrigatory pumps.
At preparation of niches facilities of dust neutralization are foreseen both at the coulisse of coal and at loading of mountain mass. At a drill and fire system of coulisse of coal the boring drilling of shpurov is carried out with washing; irrigation of the put aside dust on-the-spot in the distance a to 20 mcode from the blown up charges or explosing of charges with water with the specific expense of 1,5-2,0 l/m2, application of water-spray curtains and gidrozaboyka of shpurov. At a hammer coulisse application of mechanical picks with a built-in irrigatory device or irrigation of surface of backwall is foreseen in the area of destruction of coal. Regardless of method of coulisse of coal irrigation of the removed coal is foreseen before loading.
Suppression of dust at the movable points of loading is carried out irrigation of coal water by umbellate or cone sprayers. Sprayers are set above the mestome of loading, so that a torch was recovered by the hearth of pyleobrazovaniya. At speed of air more than 2 m/ss are equipped shelter of area of loading of coal, and at the high level of dust-ladenness shelter with the ejecting action of water is used.
In the mechanized cleansing backwalls of steep layers at the pryamotochnoy chart of ventilation the irrigatory system is used with the pumping setting with pnevmoprivodom. At presence of podsvezheniya of outgoing stream the pumping setting and podborschik of backwall pipeline (pipelines) can be used electrically-actuated, disposed on a fresh stream.
In backwalls with pnevmoenergiey the irrigatory setting with pnevmoprivodom is disposed on a vent horizon (pic. 4).

In backwalls with the use of electric power the pumping setting is electrically-actuated disposed on a haulage (conveyer) drift.
In the cleansing backwalls of thin steep layers at dust-ladenness of air more than 500 mg/m3 and in the case of necessity limits of rate-of-flow on irrigation used pylepodavlenie suds.
At a combine coulisse it is recommended to apply pylepodavlenie suds on layers by power a to 0,9 mcode and speed of air in a backwall at ascending ventilation no more than 2 m/ss. At a shield coulisse application pylepodavleniya suds is recommended in backwalls at the ascending chart of ventilation at a speed of motion of air a to 3,5 m/s.
At descending ventilation of combine and shield backwalls and in potolkoustupnykh backwalls with a hammer coulisse limitation on speed of air is not set. Penogeneratory set in combine lava in overhead part of lava under a windway, in shield lavas along konveyero-struga and area of unloading of coal in uglespusknuyu stove, in potolkoustupnykh backwalls in 4-5-ohm overhead ledges one by one in every ledge (pic. 5).
Pressure of the water given in the metering device of penogeneratora must make 0,4-0,8 MPa, and a specific expense of liquid through a metering device must be 15-25 l/t.
At a pneumatic book-mark provided: moistening of attle; impermeability of book-mark pipelines; periodic obmyvka of surface of making is in the places of settling dust; rate of movement of air in the area of book-mark no more than 2 m/ss.
For the decline of pyleobrazovaniya during the leadthrough of book-mark of rubble bars in lavas of steep layers moistening of pedigree mass is produced water or solution of smachivatelya before loading of it in trolleys.

Based on this work wecan make the following conclusions:
—comprehensive use of various methods to prevent, reduce dust, dust suppression;
—reduction of dust coming (junction formed dust in suspension);
—cleaning the air from a soaring dust;
—high-quality implementation of measures to combat the dust;
At this stage, the increasing application finds a comprehensive dust removal mining, the need for new methods and activities, increases the percentage of workers with pneumoconiosis disease.
- Кирин Б.Ф. Борьба с пылевыделением в шахтах / Б.Ф. Кирин, В.П. Журавлев, Л.И. Рыжих. – М.:Недра, 1983. – 199 с.
- Физико-химические основы гидрообеспыливания и предупреждения взрывов угольной пыли /В.И. Саранчук, В.Н. Качан, В.В. Рекун и др. – К.: Наук. Думка, 1984. – 209 с.
- Смачивание пыли и контроль запыленности воздуха в шахтах / Р.Р. Кудряшов, Л.Д. Воронина,М.К. Шуринова и др. – М.: Наука, - 167 с.
- Предотвращение выбросов угля и газа с помощью щелевой разгрузки / Николин В.И., Александров С.Н., Яйло В.В., Фридман Г.М. - Киев: Техника, 1992. - 150 с.
- С.Н. Александров, Ю.Ф. Булгаков, С.Г Лунев, В.В. Яйло. Охрана труда в угольной промышленности (учебное пособие для студентов горных специальностей высших учебных заведений). Донецк: ДонНТУ, 2005. 520 с.
- Яйло В.В. Предотвращение внезапных выбросов угля и газа с использованием комплекса КБГ // Изв. вузов. Горный журнал. - 1996. - №2. - С. 61 - 66.
- Яйло В.В., Рубинский А.А., Бондаренко А.Д., Васильченко В.И О возможности использования динамики концентрации газа для прогноза газодинамических явлений // Способы и средства создания безопасных и здоровых условий труда в угольных шахтах. Сб. научн. трудов МакНИИ. - 1999. С.
- Суханов В.В., Петулько С.Н./ Производственная пыль/. Медицина труда в угольной промышленности/: Сб. - Донецк: Изд-во ГП НИИ медико-экологических проблем Донбасса и угольной промышленности. 2000., 21c.
- И.П. Чеботков, П.Я. Заставенко/ Бурение глубоких скважин в выбросоопасных пластах Донбасса/. – Киев: Техника. 1964., 168с.
- Краснюк Е.П. Пылевые заболевания легких у рабочих промышленного производства Ук) раины. Укр. пульмонол. журн. 1998; 4: 13–16.
- Предотвращение выбросов угля и газа с помощью щелевой разгрузки / Николин В.И., Александров С.Н., Яйло В.В., Фридман Г.М. – Киев: Техника, 1990. – 98 с.
Resume
