Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- The objectives and tasks in the master's work
- Expected scientific novelty
- A review of research and development on
- Current and future results
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Among the global environmental problems is one of the foremost is the problem of fresh water. According to the UN in the next two decades, the world's available fresh water supplies will be regulated.
Ukraine is a country with low maintenance and high water consumption at the same time. Under the influence of anthropogenic factors, hydrodynamic regime and physical &mdash chemical composition of surface water bodies in our country is extremely changed. The worst ecological status of water is observed in the basin of the Seversky Donets River and Azov Sea, ie, in the Donetsk region, where the mining and processing enterprises of heavy industry (of which only in the Donetsk region of more than 800 companies are the first class of danger). Waste water discharged from these companies without the proper (ie, regulatory) purity destabilize the ecological state of the hydrographic network in the region. [1].
Massive source of instability region's water resources are discharged into water bodies poputnodobyvaemye in the production of coal mine water, the total inflow of more than 900 million m3 per year (fig. 1).
In addition to the huge amounts of expiration, mine waters are characterized by high degree of pollution particulate matter (RDT), bacterial impurities and mineral salts, variability of their physical and chemical composition. As part of the most typical contaminants are solids. They are formed and enter the mine water in the process of destruction of the mountain, and when loading and transporting rock. Education and the poor becoming the mine water would destabilize the ecological balance in the region of the hydrosphere; violates the dynamics of groundwater aquifers, draining them, leading to water pollution of surface water resources. Therefore, the current state of the hydrosphere Donbass be assessed as critical. It is characterized by very low (5&mdash10 times less) water availability in Ukraine (only 190 m3/person • year), the highest intensity of the water consumption of fresh water in the country (for example, in the Donetsk region, it is 2.5 billion m3 per year ), exceeding the level of effluent discharge on water consumption by 1.2 billion m3 per year (primarily due to mine water), the lowest natural (background) on the quality of natural waters in Ukraine and at the same time their high anthropogenic pollution (60&mdash70% of tests water samples gave a negative result), resulting in small rivers of Donbass lose status as a central source, and not a centralized water supply. Finally, the crisis of drinking water in the region, aggravated by factors such as chronic backlog in the earlier phases of water resources development pace of construction of sewerage treatment and water; mismatch performance of many existing treatment plants (built 30&mdash50 years ago) to modern requirements. The analyzed regional water problem is compounded by the fact that in recent years has sharply increased the price of drinking and technical water. Currently, process water is released to enterprises at a price ~ 0.5&mdash0.9 grn/m3, and the cost of drinking water up to 9 grn/m3. Apparently we should expect further price increases as the process water, as well as the cost of drinking water. When the consumption of one mine per day on average, 200&mdash250m3 of drinking water company has to spend a year 0.82 million USD.
In connection with the improvement of water resources of Donbass is one of the priorities of state environmental policy.[2&mdash4]
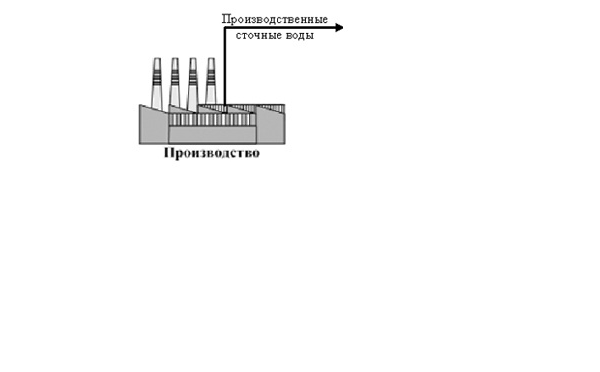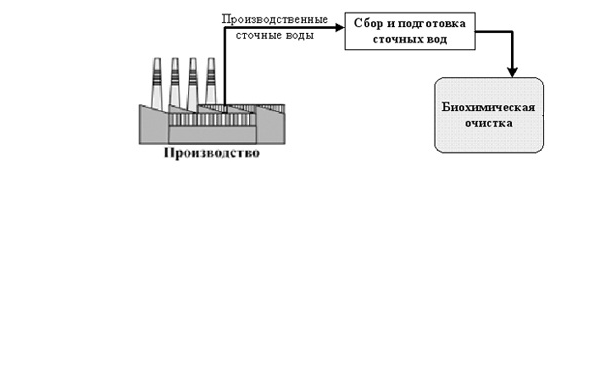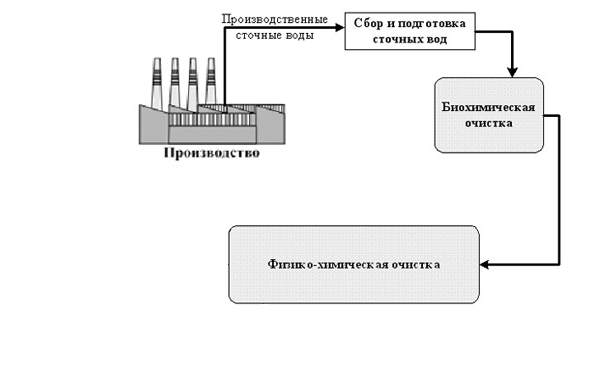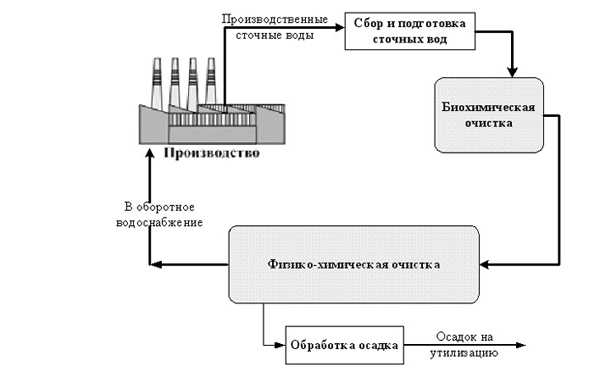
Figure 1 – Process flow diagram of treatment facilities.
Analysis of the published scientific and technical literature shows that in general the problem of industrial waste water (including mine) may be different ways:
- the prevention of its occurrence on the principles of a waste&mdashfree production, which is a priority for the future. However, the introduction of these technologies require significant investment. In addition, it should be borne in mind that a completely waste&mdashfree technology is very problematic;
- discharge of mine water into water bodies in compliance with the conditions that the concentration of pollutants in water bodies, which is created by sewage, together with the background concentration of contaminants does not form a mixing zone in excess of maximum permissible concentration (MPC). This way (even with hygiene requirements) is undesirable. This is explained as having a place of general gradual deterioration of water quality of water bodies, and the fact that due to changes in background composition of the water source to ensure compliance with the requirements of MCL must be some way to clean discharged water;
- purification of mine waters with subsequent use of treated water for their own use of mining enterprises, and for other (related) companies of the economy.
Mine water purification involves the implementation of three main stages:
- clarification of water through the extraction of suspended solids;
- decontamination;
- demineralization (primarily the extraction of heavy metals).
The problem of mine water demineralization many years does not find a practical solution, and remains a major environmental problem in the coal industry from the perspective of a systems approach. Its partial solution is possible, based on conditioning (adjusting the ionic composition) mine water by dilution with clean water. Regulation mine water requires conditioning of mandatory pre&mdashtreatment by clarification and disinfection.[5]
Expressed our analysis indicates that the task of preventing the negative impacts of mine water problem of preventing the negative impacts of mine water discharged to surface drainage network, the components of suspended solids
(RDT) and the bacterial impurities
in the previous decades in the coal industry of Ukraine was solved by direct gidroohrannyh activities to direct discharge of water. Most of these activities include the construction of ponds on the surface of various designs one of which is shown in fig. 2 (the first stage of the process) and in some cases, filters and ponds (the second stage of the process). [6] However, experience has shown that technical solutions lighten mine water in the ground conditions are inherent in the major disadvantages:
- the complexity of the technological schemes and application design of treatment facilities;
- the need to use in the purification processes in large quantities of scarce and expensive chemicals, silica sand, absorbents and other materials (the agents themselves are polluting water);
- the high cost of wastewater treatment plants (6 to 15% of assets);
- lack of flexibility to respond to changing conditions of admission to the input of polluted water treatment plants, namely, the change in flow rate (flow time) and especially the quantitative and qualitative composition of impurities contaminated water;
- the lack of simple and reliable solutions for cleaning containers and vehicles from the water treatment residuals (ie, the "tails" in the form of precipitation, leachate, etc.), filling the regeneration apparatus (filter loading, sorbents, etc.), as well as for storage of residues and waste;
- the exclusion of significant land areas under the treatment plant.
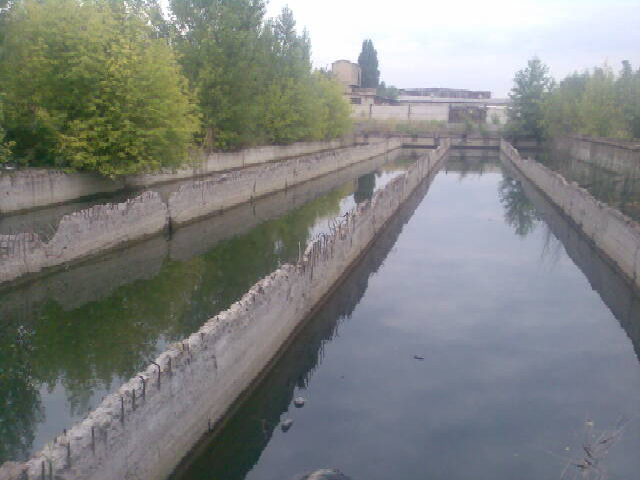

Figure 2 – Horizontal sump pit
These drawbacks lead to two negative consequences:
- discrepancy between the design of real effectiveness of treatment facilities (usually under natural conditions, much lower than the real effectiveness of the project);
- Second, limiting the full application of technological schemes and facilities for water purification.
Thus, although according to some institutions (DonUGI, Dongiproshaht), the problem is solved lighten mine water and with adequate funding can be withdrawn from the agenda, but experience shows that to remove from the agenda the issue of clarification of mine water is premature and imprudent. Moreover, there are several reasons:
- First, almost 80% of the mine pumps on the surface of the water with a concentration of 300mg / l, thereby increasing the load on the surface treatment plant, quickly reduced the efficiency and reliability of their work, especially the filters;
- Second, high levels of purification, which are listed in the report of the mines, often indicates a weak quality control of mine water for their release into water bodies at the control points;
- Third, the order established by Ministry of Coal Industry of Ukraine № 118 concentration of VZV in mine waters discharged into water bodies, equal to 30 mg / L does not reflect the mechanism of action of the "Sanitary rules and norms for the protection of surface waters from pollution" (SanPiN № 46 30 &mdash88 .) Given the current level of pollution of surface waters of its value must be drastically reduced.[5]
Therefore, to provide the desired effect of treatment of mine water as necessary to improve the known methods and schemes lighten mine water, and the search for new approaches and solutions.
The objectives and tasks in the master's work
The idea of ??robots is to reduce the negative effects of man&mdashmade water control discharges of mine drainage network in the region.
Objective: To develop a combined flow chart clarifying mine water in the hydraulic cyclone &mdash settler &mdash Polyester fiber wall.
Objectives:
- analysis of water problems in the region (the contribution of mine water);
- study the impact of mine water in the hydrosphere;
- research areas management of mine water;
- Assessment of mine water on the conditions of their formation;
- Analysis of mine water control (for example, JSC "Komsomolets Donbass");
- analysis of work used at the mine water treatment facilities;
- Develop proposals for the reconstruction of the horizontal shaft sumps;
- select the type of fibrous filter loading for partition;
- choice of type and dose of the reagent;
- calculation of the parameters of the basic technological schemes;
- Develop recommendations for the use of treated mine water for industrial and other purposes;
- Identification of cost&mdasheffectiveness of the proposed environmental technology solutions.
The object of study &mdash a set of elements to reduce contamination of mine water in the system of diversion of surface water bodies.
Subject of investigation &mdash the physico&mdashchemical and technological processes of extraction of suspended matter in the apparatus and the content of a proposed flowsheet lighten mine waters.
The method of investigation &mdash the system &mdash an ecological approach and experimental studies in natural and laboratory conditions and using the model and real mine water through a special method of sedimentation analysis, the laws of hydraulics and fluid mechanics, to evaluate the experimental results of mathematical methods used in data processing, the definition of quality indicators water was carried out in accordance with existing regulations.
Expected scientific novelty
Scientific novelty of the research is to:
- the development of concepts needed to build a water conservation systems, a higher technological level, taking into account the environmental component, based on pre&mdashtreatment of mine waters from the particulate matter;
- establishing relationships influence the parameters of mine water, such as fibrous filter loading equipment on the characteristics of the amount of clarified water.
The practical value of the work consists in:
- justification for a new direction lighten mine water through the development of water purification technology with polyester fiber loading;
- solving the problem of efficient treatment plant operation based on a combination of methods of centrifugal, gravity clarification and filtration of mine waters;
- Techno &mdash economic feasibility of the proposed flowsheet lighten mine waters.
A review of research and development on:
To date, accumulated a certain amount of scientific and technical information on the scientific &mdash research clarifying aspects of mine water. The work of this plan the most widely represented in the publications DonUGI, Shakhty branch Novocherkassk Polytechnic Institute and Donetsk National Technical University, VNIIOugol (city of Perm). Their results were reflected in the development mine water treatment, including, as a rule, the three main stages: removal of suspended solids (lighting), water disinfection, processing (or storage of sediment). At the same time almost all the schemes used by two purification steps: the first stage &mdash the defense of the second stage &mdash the filtering. To improve the efficiency of treatment facilities at both levels of applied reagents and flocculants.[7]
The technique of purification of mine waters of great importance is given to the sewage plant, because of their efficiency and reliability of their action depends on the work of filters, oxidation units, couplings of compaction and dewatering of sediments, as well as devices for mine water demineralization.
From the standpoint of systems analysis, experience has shown that the technical solution of two&mdashstage technological scheme inherent in the major shortcomings outlined by me above. These deficiencies lead to two negative consequences:
- Firstly, the discrepancy between the design of real effectiveness of treatment facilities (usually under natural conditions, much lower than the real effectiveness of the project);
- Second, limiting the full application of technological schemes and facilities for water purification.
To ensure the desired effect of mine water treatment is necessary as an improvement of known methods and schemes lighten mine water, and the search for new approaches and solutions, the decision is based on an analysis of the above publications.
There are two ways of improving the design of settling tanks:
- Increased stability (laminerizatsii) of water flow in a thin layer (thin&mdashlayer structures with sumps one of which is shown in fig. 3);
- modernization of clarifying tanks by installing them in the "walls" (conditional term) of the fibrous materials
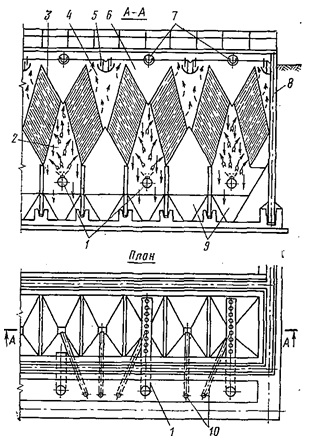
Figure 3 &mdash Tonkosloynыy trubchatыy otstoynyk. 1 &mdash podayuschye raspredelytelnыe truboprovodы 2 &mdash raspredelytelnaya schel 3 &mdash plastmassovыe trubchatыe blocks, 4 &mdash vodosbornaya schel 5 &mdash trays for collection osvetlennoy water 6 &mdash sinus for collection vsplыvayuschyh substances, 7 &mdash povorotnыe pipes for otvoda plavayuschyh substances, 8 &mdash EMKOST 9 &mdash pit for collection and Seal rain, 10 &mdash truboprovodы for Pharmaceutical draft.
Findings of the analysis and some recommendations for their use in practice, I have reflected in the published articles and reports on scientific competitions.[8]
The new approach proposed by me is the layout of the content of elements in one of the gravitational and centrifugal extraction filter suspended solids from mine water.
Current and future results
To date, filled in the following stages:
- analysis of the problem of fresh water;
- evaluation of existing schemes clarification on mine;
- set the direction of development of modern technological scheme lighten mine water;
- Identify elements of the new scheme lighten mine water;
- select the type of fiber loading of bulk filtration.
Conclusion
Reducing the impact of technology in the coal mines of Donbass hydrosphere &mdash the actual problem in the region. It requires the implementation of several successive stages, the first of which is the lighting. On the effectiveness of this stage depends, first, the reliability of the equipment other stages, and secondly, the state of water bodies being dumped in the mine water (prevents silting facilities and provided favorable conditions for aquatic life).[9]
Recommended industry and the general regulations clarifying the technological scheme of mine water are cumbersome, require considerable investment, which in the current economic climate is not realistic. In addition, their reliability of such schemes is not sufficient to ensure its efficient operation for a long time.[10]
In this master's work aims to simplify the traditional solutions for the clarification of mine water, bring them in line with the current level. Wastewater treatment technologies. It is helpful not only to dump treated water into surface water bodies, but also find use for them as a source of water supply. The last important due to the lack of security of Donbass freshwater.
Tasks that determine the achievement of this goal, given above, and the results of preliminary studies indicate the possibility of their solution in the final stages of the master's work.
References
- Гребенкин С.С. Физико&mdashхимические основы технологии осветления и обеззараживания шахтных вод/Костенко В.К., Матлак Е.С. и др. &mdash Донецк: "ВИК", 2009. &mdash 438 с.
- Гребенкин С.С . Сохранение окружающей природной среды на горнодобывающих предприятиях/ Костенко В.К., В.М.Павлиш, и др. &mdash Донецк: "ВІК", 2009.
- Гребенкин С.С Физико&mdashхимические основы технологии деминерализации шахтных вод/Костенко В.К., Матлак Е.С. и др. &mdash Донецк: "ВИК", 2008. &mdash 287 с.
- Горшков В.А. очистка и использование сточных вод предприятий угольной промышленности. &mdashМ.: Недра, 1981,&mdash269с.
- Водный кодекс Украины, статья 72 : [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://pravoved.in.ua/section&mdashkodeks/150&mdashvku.html.
- Каталог. Технологические схемы очистки от взвешенных веществ и обеззараживание шахтных вод. Пермь: ВНИИОСуголь, 1986.&mdash70 с.
- Омельченко Н.П. , Коваленко Л.И. Новые технологии осветления шахтных вод с целью их повторного использования. Загальнодержавний науково&mdashтехнічний журнал «Проблеми екології». – Донецьк: ДонНТУ, № 1&mdash2. – 2008. С. 8&mdash12.
- Матлак, Е.С., Огородник Е.Л. Очистка шахтных вод с использованием в осветляющих сооружениях волокнистых перегородок . Збірка праць III Регіональної конференції аспірантів і студентів «Екологічні проблемі паливно&mdashенергетичного комплексу» &mdash Донецьк: ДонНТУ &mdash2012.
- Охрана окружающей природной среды в горной промышленности. В.И.Николин, Е.С.Матлак.&mdash К.; Донецк: Вища шк.Головное изд&mdashво,1987.&mdash192 с.
- Матлак Е.С. Исследование загрязненности шахтных вод/ Е.С. Матлак, И.Ю. Рудакова, Н.В. Казимиренко. &mdashУголь Украины,1983. &mdash № 2. &mdash с.31&mdash32.
