Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. Goals and Objectives
- 2. Relevance of the topic
- 3. The scientific novelty
- 4. Review of Research and Development
- 5. The impact of waste dumps on the environment
- 6. The formation of the ecological network of Donetsk region at the expense of man-made elements
- Findings
- References
Introduction
The current state of biodiversity, the methods and scope of use of its resources in the Donetsk region do not meet modern requirements of a balanced nature. The current system of using fitoresursov focused increasingly on the use value of biodiversity and does not account for its environmental and social values.
Environmental situation in the Donetsk region can not be dramatically changed in the direction of improvement due to the high anthropogenic impact on the environment. However, it is important to understand the direction of environmental processes and trends of environmental pollution and the possible consequences and risks for the environment and population.
1. Goals and Objectives
Objectives of the study – based on a detailed analysis of the ecological system to develop methods for expanding the ecological network of Donetsk region at the expense of additional elements of rock dumps. To achieve the goals necessary to accomplish our
tasks:
- To consider the main characteristics of the ecological network and make the analysis is developed in this direction;;
- Identify the main principles of formation, preservation and use of ecological networks;
- To analyze the environmental situation in Donetsk region;
- To establish the influence of rock dumps on the environment, health and sanitary living conditions;.
Object of study: the breed heaps of Donetsk region.
Subject of research: application of waste dumps, which can be used as elements of the ecological network.
2. Relevance of the topic
The relevance of the theme determined by the need for economic and spiritual revival of industrial cities, the direction of the structure of these cities, the solution of demographic problems, increase the environmental quality of life and the Donetsk region of Ukraine as a whole.
Thus, the problem of the environment in the Donetsk region is quite acute, so its study and solution of a rather hot topic for researchers.
3. The scientific novelty
Setting the conservation of biological and landscape diversity is important for achieving sustainable development. Under this strategy, by 2015, should be established European Econet, which will connect the securities in the environmental sense, areas with preserved or near the natural vegetation of the system of ecological corridors.
The idea of establishing Econet Donetsk region has a fairly deep significance. Reforming waste dumps on the elements of ecological networks, provides the usefulness of the structure and solves one of the main problems of the Donetsk region: the problem of mining waste dumps, which occupy vast areas of land, harming the environment and public health.
4. Review of Research and Development
The main source is a Pan-European strategy for the conservation of biological and landscape diversity (Sofia, 23-25 zhovtnya p 1995). [1]. Important sources include: the concept of a separate national networks (laws, regulations), national concepts – regional and local programs.
In addition to these sources, it should be noted of Dr. Shapar AG and k.b.n Skrypnyk AA And representatives of the Institute of Natural Resources and Environment National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Dnepropetrovsk, where the theme of ecological networks is discussed in great detail their articles.
Among the materials faculty, graduate students and undergraduates can be identified DonNTU of V.S. Laktionova, R.G. Sinelshchikov [5]; V.S. Laktionova, R.G. Sinelshchikov, V. Zalewski [6]; Popchenko D.S., Artamonov V.N. [7].
5. The impact of waste dumps on the environment
In the process of underground coal mining on the surface of the rock is given of the preparation and clean-up, cleaning and restoration of mining, which usually slept in a heap. It depends on the number of system development, mining and geological conditions, the method of coal extraction, etc. Issued on the rock surface is stored in different size and shape of the piles – conical, crested, plateau-like (flat), combined. (pic. 1 (а, b), pic. 2).
picture 1 а) – Tapered blade breed.
picture 1 b) – Tapered blade breed.
picture 2 – Flat blade breed.
They occupy large areas of agricultural land, reduce the productivity of adjacent land, polluting gases and dust, as well as violating the hydrogeological regime of the area. In addition, water (preferably containing toxins), flowing down from the dumps, destroying the vegetation on site. Dumps are located near population centers, worsen sanitary living conditions [8].
In order to completely eliminate the danger posed by dams, they must be disassembled and disposed of the breed. However, it concerns the dumps that are not reclaimed and samoozeleneni. Because if the blade samoobnovilsya,
then destroy the natural ecosystem created makes no sense. Such areas should be used rationally. For example, to incorporate them into the elements of the city as an ecological network of restored areas.
Summing up all these factors should be noted that the selection of a landscape reserve in disturbed mining lands subject to clear criteria – the subordination of the general trend of creating a chain of elements, zoning established reserves, the maximum utilization of the natural potential for the restoration of ecosystems and the lack of constant exposure to any human activity in areas designated for scientific purposes. The analysis of the topological structure of a model scheme of Donetsk region has shown that from a topological point of view of the chain nuclei of these elements may be they are an area of ??large urbanized area (Pic. 3).
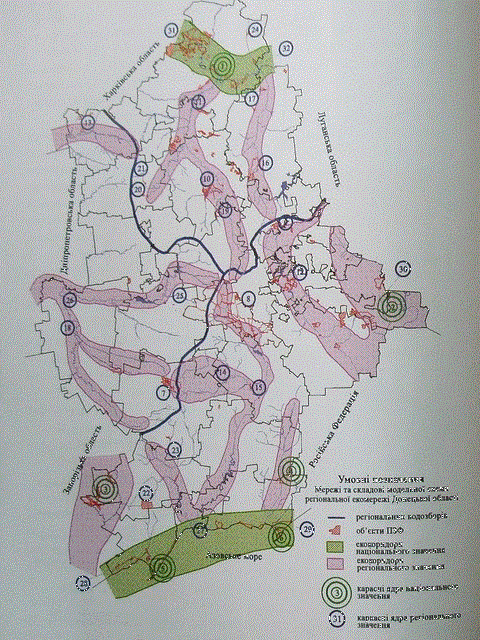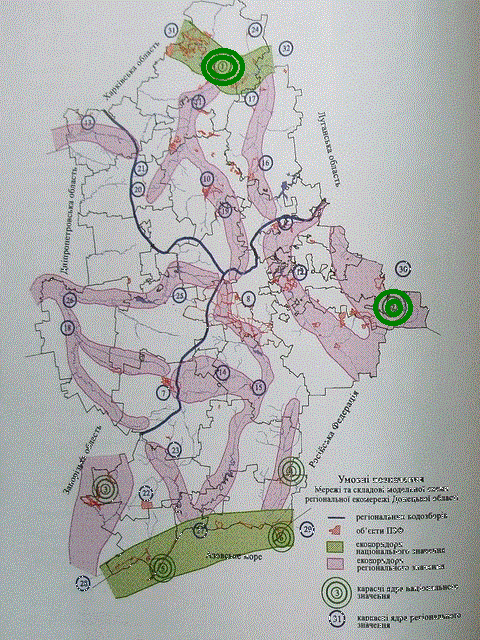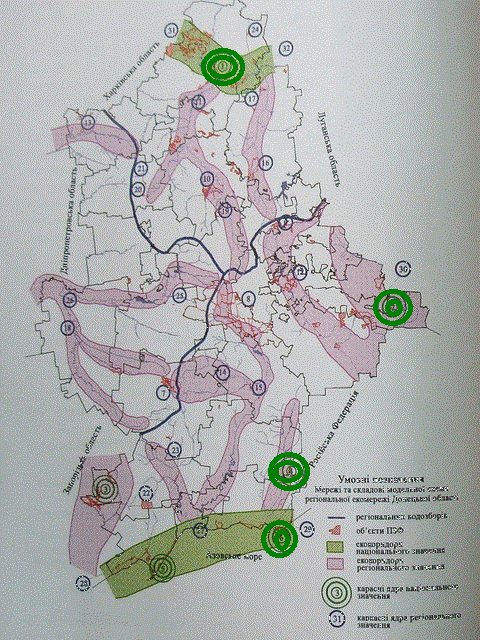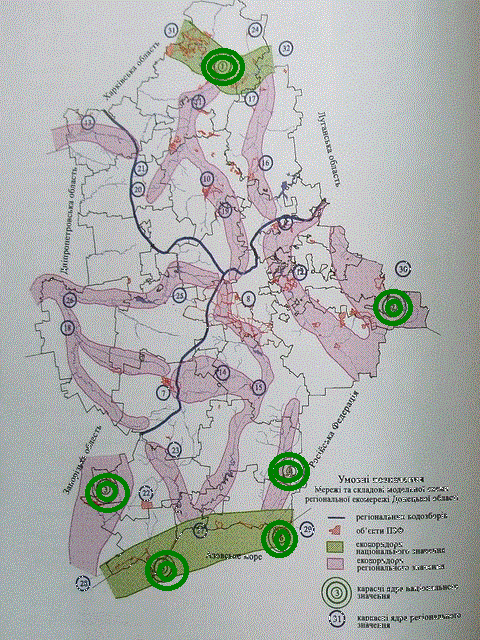
Picture 3 – The model scheme of the ecological network of Donetsk region
(kernel circuit ekokoridorov)
6. The formation of the ecological network of Donetsk region at the expense of man-made elements
To date, in the Donetsk region is situated 582 waste dumps of coal mines and processing plants, of which 130 are burning, polluting the air. The plant has 120 heaps, half of them burning [12].
The main task during the formation of the Donetsk regional environmental network – a maximum possible coverage of natural areas in the region to enable them as structural elements in order to maintain landscapes, biodiversity, and creating favorable for the population of the natural environment.
Findings
For the Donetsk region is highly relevant to improve the environment and the efficient use of natural resources.
The use of waste dumps as elements of ecological networks and the creation of ecological networks in Donetsk obdasta leads to:
- environmental issues.
- The social and economic problems:
The proposed technology is preferred over other technologies use waste dumps, since it takes into account the interests of:
- landowners and land users;;
- the local population;
- power;
- biocenosis.
In writing this essay master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: December 2012. The full text of the and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after that date.
References
- Всеєвропейська стратегія збереження біологічного та ландшафтного різноманіття. Софія, 23-25 жовтня 1995 р.Виконавче резюме.
- Закон України
Про екологічну мережу України
. Відомості Верховної Ради України (ВВР), 2004, N 45, ст.502. - Закон України
Про природно-заповідний фонд України
. Відомості Верховної Ради України (ВВР), 1992, N 34, ст.502. - Закон України
Про рослинний світ
. Відомості Верховної Ради (ВВР), 1999, N 22-23, ст.198. - В.С. Лактионова, Р.Г. Синельщиков Аспекты проектирования экологической сети Донецкой области как фактора сохранения природных и социально– экологических ресурсов региона/– Материал Всеукраинского конкурса– защиты экологических проектов
Энерго- и ресурсосберегающие технологии в Украине
от 20-21 марта 2006 г. - В.С. Лактионова Формирование экологической сети в Донецком регионе:концепция и реализация /В.С. Лактионова, Р.Г. Синельщиков, В.Д. Залевский/ Охорона навколишнього середовища та раціональне використання природних ресурсів/Збірка доповідей V Міжнародної наукової конференції аспірантів та студентів. Т.1 – Донецьк: ДонНТУ, ДонНУ, 2006. – 273 с.
- Попченко Д.С., Артамонов В.Н. Обеспечение экологической безопасности Донецкого мегаполиса за счет создания экосети/ Сучасні проблеми екології та геотехнологій – 2011/Матеріали VI Міжнародної наукової конференції студентів, магістрів та аспірантів. – Житомир, ЖДТУ – 2011).
- Сохранение окружающей природной среды на горнодобывающих предприятиях: монография / [С.С.Гребенкин, В.К.Костенко, Е.С.Матлак и др.] – под общ. ред. Гребенкина С.С и Костенко В.К. – Д.:
ВИК
, 2009. – 505 с. - Техногенные последствия закрытия угольных шахт Украины: монография / [Ю.Н.Гавриленко, В.Н.Ермаков, Ю.Ф.Кренида и др.] – под ред. Ю.Н. Гавриленко, В.Н. Ермакова. – Д.: "Норд-Пресс", 2004. - 631 с.
- Екологія гірничого виробництва: Навчальний посібник. / 10. Бакка М. Т., Гуменюк І. Л., Редчиць В. С./– Житомір: ЖДТУ, 2004. – 307 с.
- Техногенні території: рекультивація, оптимізація агроландшафтів, раціональне використання // Шемавньов В.І., Забалуєв В.О., Чабан І.П. /Мат. Міжн. Наук.– пр. конф.
Раціональне використання рекультивованих та еродованих земель:досвід, проблеми , перспективи
Дніпропетровськ: Дн-ський агр.ун. – 2006. – С. 16-20. - Земля тривоги нашої. За матеріалами доповіді про стан навколишнього природного середовища в Донецькій області у 2002 році. /під ред. С.В. Третьякова/. – Донецьк: Новий мир. – 2003. – 158 с.
- Закон України
Про екологічну мережу України
від 24 червня 2004 p. № 1864-IV// Урядовий кур'єр. — 2004. — 14 вересня. — № 172.
