Abstract
Сontent
Introduction
Corporate networks – a network scale of one company (the company). Network-scale companies integrate a large number of computers and other telecommunications equipment company. Number of users and computers can be measured in hundreds, and the number of servers – dozens. Enterprise network access can be arranged in different operating conditions, to work on different physical environments and with different access technologies. The level of access is very important, because the spacecraft is responsible for providing high-quality communications services to end users – employees of the enterprise, and is a sophisticated and extensive infrastructure. One of the ways to improve the network is to increase the reliability of information transmission at the level of network access.
Relevance of master's work. Currently, network technologies are the basis of corporate information systems of modern enterprises, whose business requires continuous, reliable operation of the communications and data transfer. An important task is to ensure the fidelity of information transmission in the network. When the faults and failures in the hardware and software of the corporate information system interferes with the normal operation of all system users are also very dangerous breach in the process of information transmission, such as loss of data, or their distortion. Such disturbances in the system lead to large losses of the enterprise. It is therefore necessary to pay close attention to the information processes in the system, monitor its reliability and accuracy of the results of information transfer.
New information technologies require new approaches to ensure the reliability and validity processes data in corporate information systems. For businesses, it is important to the successful integration of modern telephone systems with data networks and computer systems for all applications: voice mail, database access, control systems, etc. These solutions are now a priority for effective operation of businesses and allow extend the network, increase productivity and reliability of transmitted data.
Goal of master's work. Elaboration of model errors in the message stream, which passed through the links of the composite channel (SC) in a telecommunications network, a representative in Fig.1.

Figure 1 - Structure of the composite channel
(animation: 10 frames, 7 cycles of repetitions, 42.8 kilobytes)
Each link is characterized by the IC input and output signals of a given length of time shifted with respect to the input signal to the IC delay intervals, the length of the signal in a part, determined by rate and length of messages is independent of the presence of noise sources other parts of the source of impulse noise (errors) IP, generating pulse noise (error), distributed according to a Poisson distribution with an average repetition rate fj:
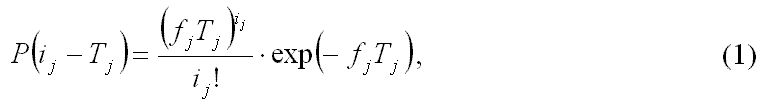
1. Statement of the problem
Evaluation of reliability of information transmitted via telecommunication is made by mathematical models of flows and channels of communication errors. Created a lot of models that take into account the influence of individual factors that characterize the communication channels on the correctness of the information on them: in (1) determined the distribution of errors and the intervals between them at fixed intervals, in (2) determine the parameters of the relationship of impulse noise and employed a stationary symmetric channel c (3) are determined by the probabilistic characteristics of the flow of information in different physical states of the channel in (4) to determine the error stream using a combination of linear and neural network model that can be reduced to a hidden Markov model, in (5) are determined depending on the flow of errors on the size of messages, model of clustering errors, etc.
These models do not account for the fact that the transport system of the telecommunications network may combine the lines of communication with different physical media, technology transfer and sources of interference, that is for the exchange of information formed the composite channel (SC).
2. Solution of the problem
Analysis of passing messages through the links of IC shows that the annealing is the set of errors and errors introduced in each of the links except the first, is a lot of dimensional random variable, the distribution of which in view of the independence of sources of interference links can be found via a one-dimensional distribution (1) IC units:
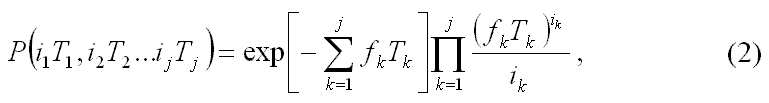
For each link in SC with (2) can be determined by the probabilistic characteristics of the message. The probability of passing the message through a link with no errors:
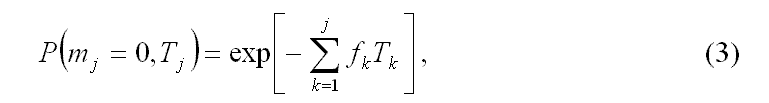
The likelihood of mj error with regard to their group:
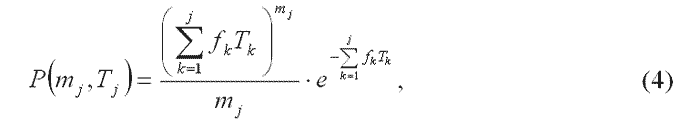
Double errors made in the different levels of SC in communication can be compensated if they get on a bit. The probability of this event
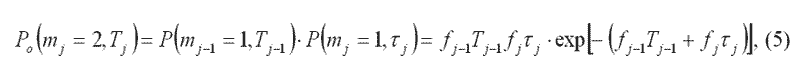
where Tj – the duration of the signal in the bit j-th link coordinate system.
Summary
Based on the foregoing, it follows that the master's work should take into account the following:
- Real telecommunication channels provide a set of individual series-connected channels with different messaging and interferers.
- Sources of interference in CK levels form a stream of errors with one-dimensional Poisson distribution.
- When sending messages on the IC group formed in it an error, which flows in each of the relevant parts of SC are described multivariate Poisson distributions.
- Proposed model allows to define more precisely the probabilistic characteristics of error messages.
Conclusion
- Шиллер Й. Мобильные коммуникации.: Пер. с англ. – М. :Издательский дом "Вильямс", 2002. – 384 с.
- Маковеева М.М., Шинаков Ю.С. Системы связи с подвижными объектами: Учебное пособие для вузов. – Г.: Радио и свиязь, 2002. – 440 с.
- Карташевский В.Г., Семенов С.Н. Сети подвижной связи. – М.: Эко-трендз, 2001. – 299 с.
- Аесенов Б.Е., Александров А.М. Об одном методе исследования потоков ошибок в каналах связи. Сб. «Проблемы передачи информации». М – 1968 – Т4. – Вып. 4. – с. 79–83.
- Арсеньев М.В. Повышение достоверности передачи служебной информации по занятым телефонным каналам. Автореферат на соиск. уч. Степени к.т.н. – М. – 2007. – с.21.
- Деундяк В.М., Жданова М.А. Обобщенная марковская модель источника ошибок q-ичного цифрового канала нескольких физических состояний. Математика и ее приложение: ЖИМО. – 2010. – Вып. 1(7). – с. 33–40.
- Чакрян В.Р. Многомерные стохастические и имитационные модели телетрафика и каналов передачи данных в условиях помех. Автореверат на соиск. уч. Степени к.т.н. – Ростов на Дону. – 2009. – с.17.
- Певнев В.Я., Цуранов М.В. Экспериментальное в канале связи. Электронный ресурс: http://www.nbu.gov.ua.
- Sipila, K., Laiho-Steffens, J., Jasberg, M. and Wacker, A., «Modelling the Impact of the Fast Power Control on the CDMA Uplink», Proceedings of VTC'99. Houston, Texas, May 1999, pp. 1266–1270.
- Ojanpera, T. and Prasad, R., Wideband CDMA for Third Generation Mobile Communications, Artech House, 1998.
