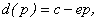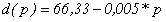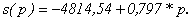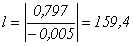Economic-mathematical modeling of the market pricing of cable products with cobweb model
Table of contents
Introduction
At the moment, interest is increased in finding patterns in the problems of balance demand-supply . Interaction, which is formed in the market between supply and demand leads to the concept of equilibrium. Equilibrium – situation at a market in which demand and supply are equal. Different models can be used to find the equilibrium, but nowadays is often used cobweb model.
|
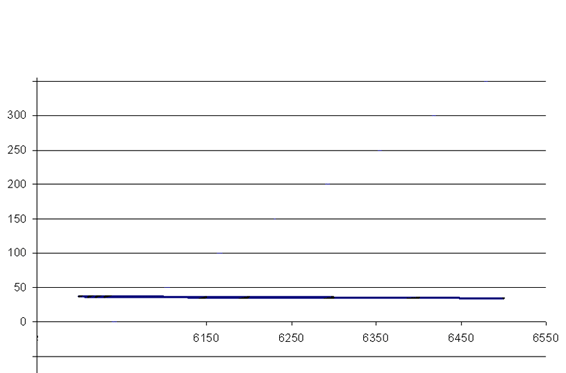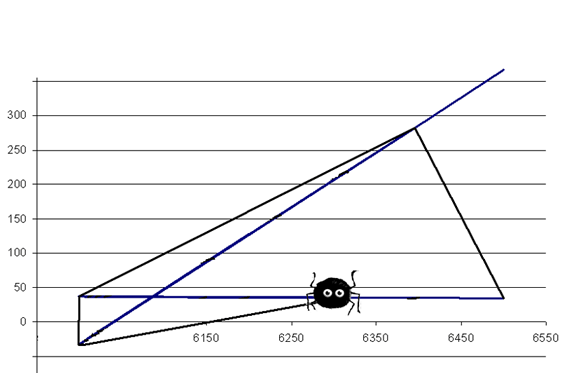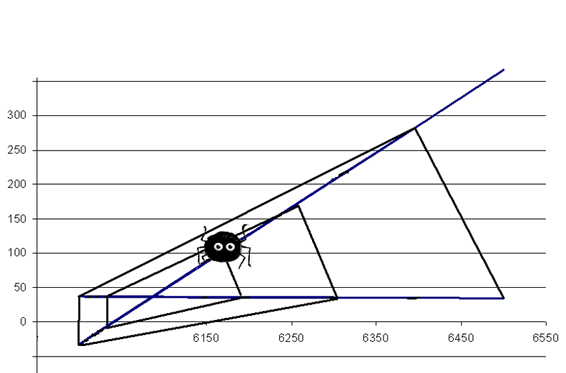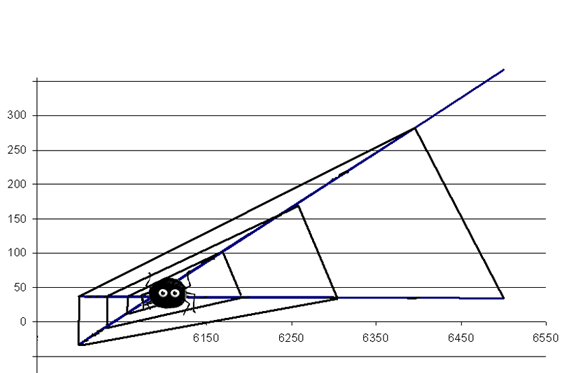
Fig.1 – Cobweb model
(animation: 18 frames, 5 repetition cycles, 52 Кbytes)
|
1. Theme urgency
A model for finding an equilibrium in the problems of demand-supply is topically nowadays. The classical cobweb model applies to this class, it is used as a stable and non stable conditions. In practice, these models help detect and predict the behavior of prices, which helps to make decisions and make recommendations about the behavior of firms in the market.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of this paper is modeling the process pricing model which based on the cobweb model and wires company PJSC Donbasskabel . The function of supply and demand according to PSC Donbasskabel is constructed, regression models of pricing are developed, the equilibrium point is found, the type of equilibrium is determined. Cobweb model is built, and research will be investigated with the help of the package E & FChaos.
3. Review of research and development
Classical economists were the discoverers of the theory of the equilibrium. The idea of general equilibrium was expressed L. Walras, and then Marshall [3] and the economist Piero Sraffa [4] developed this topic. In the second half of the twentieth century the properties of this model were studied by R. Allen [5]. Then, these studies were continued by such scientist – O. Lange [6], S. Beer [7] and others. Nowadays the most famous scientists who developed the cobweb model are: C. Chiarella [8], C.H. Hommes [9–10], A. Matsumoto [11] and others. Among national sources: V.V. Shevchenko [12], T.M. Borovskaya [13], A.A. Mospan [14–15] and others can be excreted.
Among the national source very few researches on the subject are found. One of such research is the work of Shevchenko V.V. – Использование паутинообразной модели при принятии перспективных решений . In this paper, the author makes a classification of pricing equilibrium prediction approaches. The author examines the practical use of the cobweb model.
The next research is the work of Borovskaya T.M. – Моделювання і оптимізація процесів розвитку виробничих систем з урахуванням використання зовнішніх ресурсів та ефектів освоєння . In the work author generalize function of supply and demand in the cobweb model. Function as a parameterized logical dependence and general production function are introduced in the article. The main constraint in the constructed model is the capacity of the market.
Next works are the works of Mospan A.A., Nazarova I.A. – Реализация паутинообразных моделей динамики цен на основе программного пакета E&F Chaos , Моделирование динамики рыночных цен на базе нелинейной паутинообразной модели ценообразования . In these studies several species of cobweb are examined model to study the dynamics of market prices. An example of the construction and study the model using the E & F Chaos [14–15].
A significant contribution to the study of cobweb model made professor of economic dynamics Cars Hommes, who wrote a multitude papers on research cobweb model, also he developed various types of cobweb model. Paul Bedford and Chris Bloor who worked in this sphere built a cobweb model for financial stability in New Zealand [16].
4. Development the cobweb model of the dynamics in copper prices
Researches of the pricing of copper processes is considered as an example on the company PJSC Donbasskabel . This company produces cables and wires of two types, containing aluminum or copper strand. The report examines the supply and demand for copper, which influence of the supply and demand for copper cabling and wiring products, as copper is a significant part of production costs.
Cobweb market model – a model depicting the trajectory of the state of equilibrium when the supply or demand response is delayed [1].
Let following notation, let the p – the price, d – the demand, s – the supply. It is assumed that d(p) and s(p) are continuous, while if the price p – is small, then d(p)-s(p)>0 , and when prices is high then d(p)-s(p)<0. Under these assumptions there is an equilibrium price p*, that satisfies the equation d(p*)=s(p*) [2].
Data PJSC Donbasskabel were used while building a cobweb model. The first stage of the study is to construct regression models of supply and demand for products as a function of copper prices in the package EXCEL and plotted in Fig. 2–3.
|
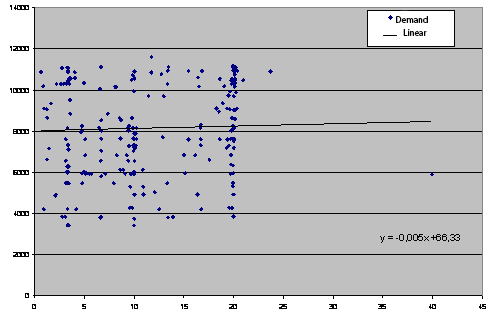
Figure 2 – The demand function of copper PJSC Donbasskabel
|
Suppose the number of copper wire, for the production of cable products is selected depending on the previous year prices. Thus the lag time duration per unit time (in this case a month) should be taking into account into supply function [2].
|
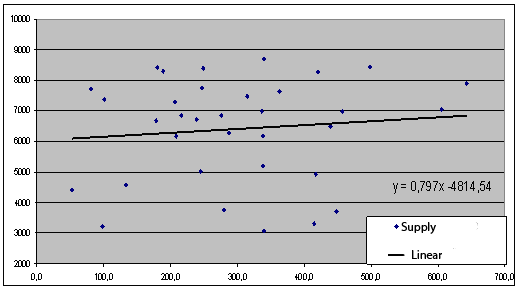
Figure 3 – Supply function of copper
|
Now suppose that a function (1).
|
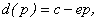 | (1) |
where c>0, e>0 – designated the parameters, such that there exists an equilibrium price p*. Based on the above example, the demand of copper will be presented by the following equation:
|
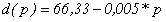 | (2) |
Assume that s(p)=a+b*p. Then offer of copper will have the form (3).
|
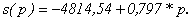 | (3) |
Plot the supply and demand of copper in Fig. 4.
|
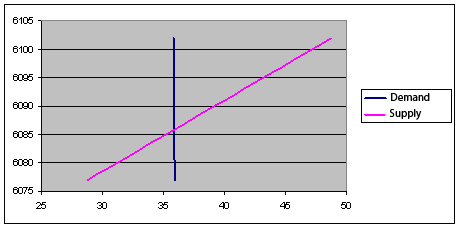
Figure 4. Graph the supply and demand of copper
|
Equilibrium is reached in point: p=6086 $ per ton, Q=35,9 ton.
Возможны случаи:
1. If |l|<1, where l=b/e. In this case the equilibrium is stable [2].
2. If |l|=1, then q(i) the values alternate around the equilibrium state.
3. If |l|>1, then {q(n)} diverges, and the equilibrium is not sustainable.In our case (4):
|
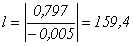 | (4) |
|l|>1 – this means that {q(n)} diverges, and the equilibrium is not sustainable. This means that if you change the price, supply and demand will set a new equilibrium.
Conclusion
Nowadays studying in the cobweb model has gone far ahead. This model helps to study the internal pricing mechanism, to determine the parameters that affect the system as well as to analyze the system and make recommendations on behavior in the system. Cobweb model is a complicated machine, which allows to explain the process of changing prices, as well as to determine the control system market prices.
Master's work is not yet complete when writing this abstract. Final completion: December 2012. The full text the
and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or Scientific adviser that date.
References
- Beчкaнoв Г.C., Beчкaнoвa Г.P. Паутинообразная модель [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа: http://www.inventech.ru
- Коврижных А. Ю., Конончук Е. А., Лузина Г. Е. Методы вычислений в экономическом моделировании // Учебно-методическое пособие – Екатеринбург 2008– 231с.
- Маршалл А. Принципы экономической науки, М.: Прогресс, 1993.
- Сраффа П. Производство товаров по средством товаров.
- Ален Р. Математическая экономия: Пер. с англ. – М.: Из-во иностр. Литературы, 1963 – 667 с.
- Ланге О. Оптимальные решения ndash; М.:Прогресс, 1967 – 286 с.
- Бир С. Киберенетика и управление производством ndash; М.:Наука, 1965 – 388 с.
- Chiarella C., Xue-Zhong He, Peiyuan Zhu Fading memory learning in the cobweb model with risk averse heterogeneous producers // School of Finance and Economics. ndash; Australia, 2003 – 45 p.
- Hommes C.H. Heterogeneous agent models in economics and finance // University of Amsterdam, Tinbergen Institute, CeNDEF, – Amsterdam, 2005 – 70 p.
- Diks C., Hommes C., Panchenko V., Roy van der Weide E&F Chaos: A User Friendly Software Package for Nonlinear Economic Dynamics, Amsterdam, 2008 – 26 p.
- Matsumoto A. Ergodic Cobweb Chaos // Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, Niigata University – Japan, 1996, Vol. 1, p. 135–146
- Шевченко В.В. Использование паутинообразной модели для принятия перспективных решений // Наукові праці ДонНТУ, Серія економічна, Випуск 87, с. 142–146
- Боровская Т.М. Моделювання і оптимізація процесів розвитку виробничих систем з урахуванням використання зовнішніх ресурсів та ефектів освоєння // Монографія. – Вінниця, 2009, с. 36–46.
- Моспан А.А., Назарова И.А. Реализация паутинообразных моделей динамики цен на основе программного пакета
E&F Chaos // Информационные управляющие системы и компьютерный мониторинг – Донецк, ДонНТУ–2010
- Моспан А.А., Назарова И.А. Моделирование динамики рыночных цен на базе нелинейной паутинообразной модели ценообразования // Тезисы IV Международной научно-практичной конференции молодых ученых, аспирантов, студентов
Современная информационная Украина: информатика, экономика, философия , Том II, г. Донецк, стр. 210 – 214
- Bedford P., Bloor C. A cobweb model of financial stability in New Zealand // Discussion Paper Series, – New Zealand, 2009 – 22 p.
|