Ρontent
- Introduction
- Orthopantomography as a method of X-ray
- Analysis of modern methods X-ray metric
- The object of the reserch
- Contrasting images
- Conclusions
- List of sources
Introduction
High prevalence of dental disease, periodontal tissues and their complications, anomalies and deformations of the maxillofacial region account for a high percentage needing orthopedic, ortodonticheskomi and complex treatments. In their treatment of X-ray examination is not only used for primary diagnosis, but also to assist the dentist in the implementation of a number of remedial measures and monitoring their quality.
Orthopantomography (panoramic zonografiya) over the past 30 years has become the main method of x-rays of the teeth-jaw system. This was facilitated not only the breadth of the review, objectivity and good quality images of dentition and jaws, but also reduce the time study, low doses of irradiation of patients and highly informative.
Diagnostic capabilities of orthopantomography is wide enough, however, to date assessment of ortopantomogramm (XCTD) is carried out visually, without any quantitative analysis, and thus, to some extent subjective. Assessment of information received dentists make on their own, relying on his experience. Your doctor may not notice small details in the image that the system permits, or skip faint structure visible on the background noise in the image due to the complex structure of the surrounding (or sverhlezhaschih) tissues. In today's time is not created such software that would perform automated image processing ortopantomogramm and, based on the results obtained exhibited a provisional diagnosis.
Orthopantomography as a method of X-ray
Orthopantomography (X-rays of the teeth) is a new method of X-ray, which is a panoramic picture of the teeth. This is a very important tool for the dentist. There are times when only using orthopantomography can detect changes in the tissues of the tooth.
In clinical use film and digital orthopantomography. Digital is more modern and convenient to use. They take a survey on the screen. Thus, the digital orthopantomography allows the doctor to immediately correct diagnosis.
On the panoramic images are expanded in-plane image of the body and alveolar jaw with all teeth. In dentistry panoramic radiography is used as a principal and as an additional method of examination. In a short time at low radiation can obtain information about the status of all teeth and surrounding tissues, the structure of the bones all over, discover hidden cavities.
Orthopantomography to evaluate the condition of teeth:
fit crowns
The status of the bone septum
jaw bone
Availability of periapical changes
the location of wisdom teeth
The status of permanent teeth buds
Among the advantages of orthopantomography emit more informative. Already at an early stage can identify inflammation of bone tissue. The disadvantages include orthopantomography layering (one-third of cases) shadows on each other crowns of upper and lower premolars.
Orthopantomography indispensable if you plan to therapeutic, surgical and orthopedic treatment. It also allows you to control the quality of dental fillings.
The object of the reserch
Periodontium a single morpho-functional complex, including the gums, periodontium, alveolar bone and tooth tissues. In the periodontium may occur various pathological processes: inflammation, degenerative and tumor.
Diseases of the prevalence of periodontal tissues in second place after the decay, and after 40 years, they prevail. Starting from the age of 12 have observed a few cases of periodontitis in 1920 years of his diagnosed in 32% of the surveyed and the 60-year-old age affection reaches 7080%.
Rasprastranennymi most periodontal diseases are gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontitis.
For proper diagnosis is necessary to consider both clinical and radiographic periodontal status data. Figure 1 shows the diagnostic algorithm used by dentists to determine the type of periodontal disease.
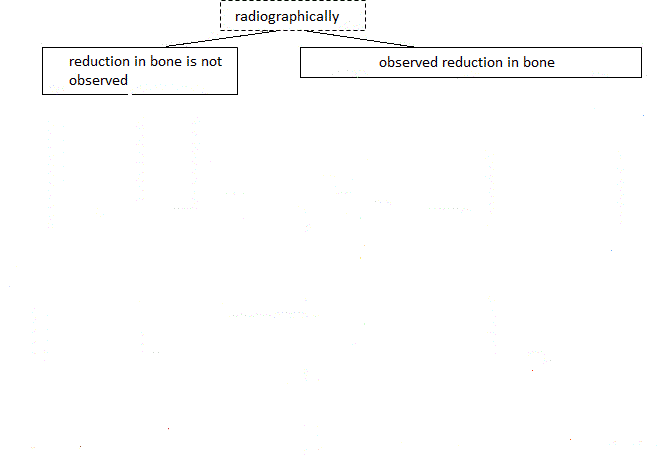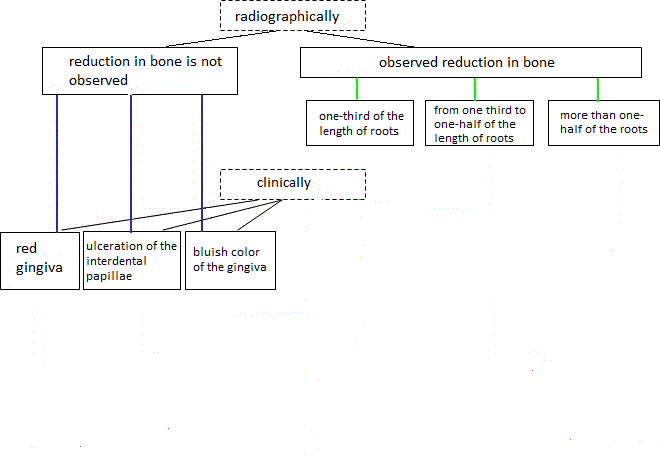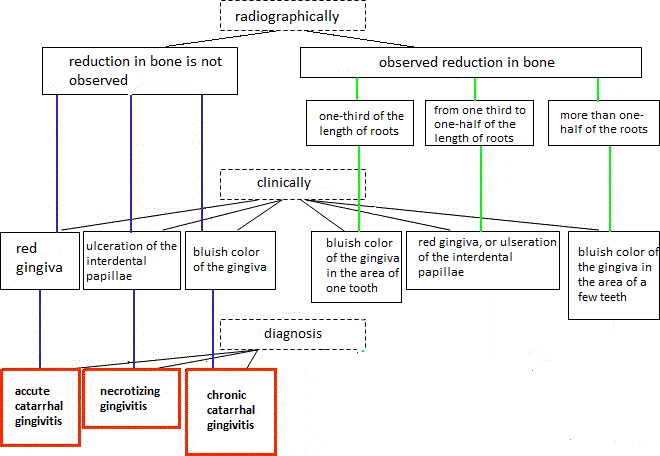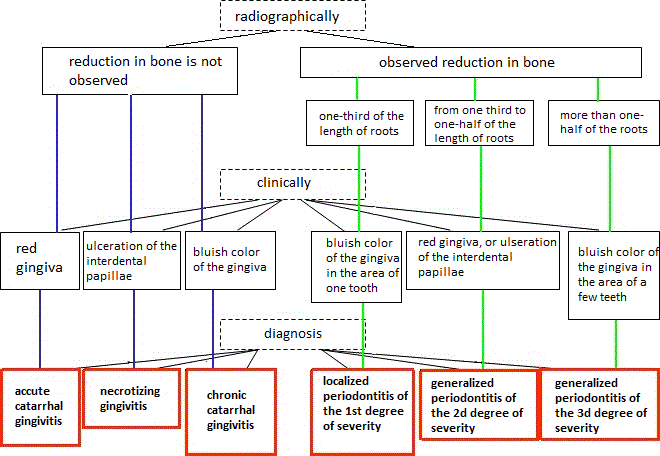
Figure 1 Diagnostic Algorithm
(animation: 4 frames, 5 cycles of repetition, 32.9 kilobytes)
Pictue 1 shows that by using X-ray studies that are based on visual evaluation of panoramic images obtained using orthopantomograph dentist concludes that state-level patient's bone. Only after that the clinical studies and as a result put a definitive diagnosis.
Figure 2 shows the conventional line level of bone in normal and line-level bone in periodontitis (black and white, respectively).
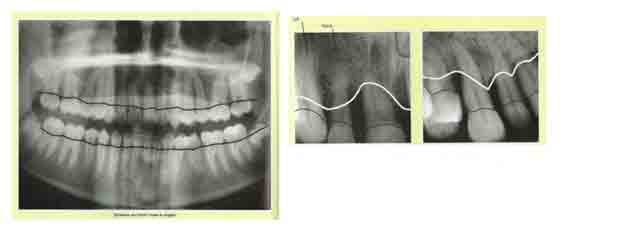
Figure 2 Levels of bone in health and periodontitis
The process of determining the level of deviation from normal bone tissue can be automated using computer image processing.
Analysis of modern methods X-ray metric
The correct choice of processing algorithm is crucial for all stages of the transformation of the original image and presents the greatest difficulty.
Pre-treatment consisting in extreme close study to the reference image and normalized. Most often for medical images is spatially invariant operation, shift, change brightness, change contrast, quantization and geometric transformations (scaling, rotation axis). The theory of these transformations are well developed and usually does not cause difficulties in the use of modern computers.
Feature extraction, in which the function representing the processed image undergoes functional transformation, identifies a number of the most essential features, which are encoded by real numbers. Feature extraction is the mathematical transformation of the image depending on the task analysis. This may be a subtraction from a reference, subtract a constant component to avoid disturbing shadows, differentiation, or to highlight the contour of the autocorrelation, frequency filtering, and many others.
Classification of signs. The resulting sets of the previous operation of real numbers, describing the selected features, compared with the reference numbers laid down in the machine memory. Computers on the basis of this comparison classifies the image, ie, assigns it to one of the known species, such as the norm or pathology. A set of real numbers that characterize the selected features, and you can be considered as a point in n-dimensional space. If this space is pre-entered the area occupied by one or another class in the space called feature space, or what happens more often, given the probability density for each class, it is possible with a certain probability attributed this image to a certain class.
Medical images obtained by X-ray, ultrasound or isotopic differ as to the nature of their complexity, and by type of information embedded in them, determined by the mechanism of interaction with the type of radiation used in organs and tissues. However, they have common features that are important to the problem of automatic classification. This, above all, the lack of:
1) the standard rate due to individual characteristics of each organism;
2) the standard of pathology at the vast diversity of its forms.
Thus, a complete automatic classification in the differential diagnosis is still not possible.
Contrasting images
Property image contrast is no less important than the brightness of the property, because of minor variations in luminance contrast levels are unchanged.
Methods for image segmentation (boundary images) for contrast is based on the use of a threshold detector to be used for the identification of low-contrast (contrast), the interior pixels (border) of the image, followed by the use of special techniques, such as wave method to get connected regions (boundaries). As used in this case a threshold detector has the form: ntrastnosti unchanged.
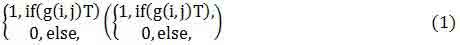
where ΰ given threshold, which is used for classification of image pixels to pixels without contrast and contrast the interior pixels of the border.
For the evaluation of contrast using a discrete approximation of the gradient values in the neighborhood of the pixel of the form:
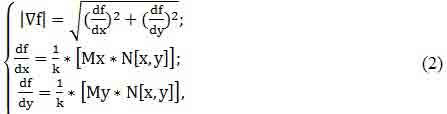
where Mx*N[x,y], My*N[x,y] scalar product of the mask M on the weighting matrix of pixel brightness neighborhood of N.
At the same time to assess the direction of the gradient using the following relationship:

To estimate the gradient of the function at the present time, used a fairly wide range of functions based on the use of masks Roberts, Sobel, Prewitt, and several other. For example, when using the Prewitt masks (Fig.3.a) estimate of the gradient (2) becomes:
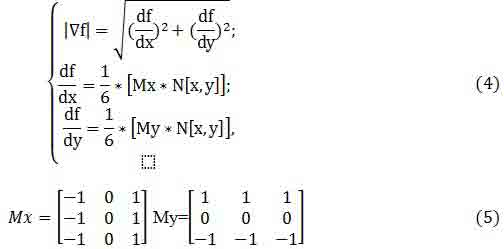
Using the considered assessment of the gradient is characterized by the same weaknesses and strengths, which aimed to use masks, in addition, estimate (2) shall be bound to the directions of the axes. To overcome this limitation, we can go two ways.
First, we can use technology to speed the pair of masks (Fig. 3.b) with an estimate of the maximum gradient criterion, such as g(i,j)=g*=max{ g(ξ)}.
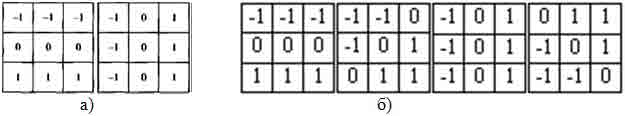
Figure 3 Directional masks Prevvita (a), the rotation of a pair of masks (b)
Second, for the brightness distribution in the neighborhood (assuming a linear character of the distribution), we can estimate the coefficients of the linear regression of the form:

and as an estimate of the contrast of the central pixel neighborhood consider the norm of the gradient of the form:
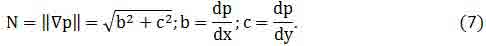
To estimate the contrast to the following numerical approximation of the gradient norm of the form:
where f (i, j) the brightness of the pixel being evaluated, combined with the center of the mask, and f(ξ,μ) luminance of neighborhood pixels which are defined by the position of the mask. In contrast to the classical approach in this case the mask is not defined as a matrix of weighting coefficients, and geometric (Fig. 4). At a basic level, the mask is defined as the image of the circle (Fig. 4a), and composite mask as the image of the circle after circle amended to 8-connected line.
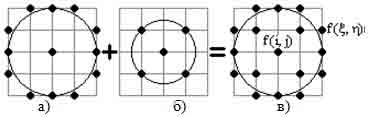
Figure 4 The image of a circle of radius 2 (a), trace a circle of radius sqrt (2) (b), and built their association constituent mask of radius 2 (a)
By overcoming the shadow of the image (with the use of masks is not the type of the proposed minimum radius) and the use of (8), when combined with the mask center pixel of the picture, we can now assess its contrast relative to the background pixel, and not the shadow of the image, the base in this respect is mask of radius 2 (Fig. 4a).
Also, for us now is not important degree of curvature of the boundary. What is important is that at the center of jointly-schenii mask pixel of the picture, among the pixels defined by the position of the mask, was at least one pixel of the background. In order to use masks for differential image processing along the lines parametrize pixel mask the polar angle α, using a parametric representation of a circle with radius ρ centered at pixel (i, j):
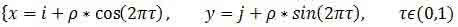
and present the results the direction of
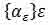
the pixels
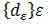
mask matrix-row direction A.
The method of image segmentation by contrast, will continue to be used to determine the level of bone pathology and level at normal.
Conclusions
Panoramic roentgenograph with computer software are various possibilities for the functional diagnosis of clear images of highly informative. However, the interpretation is quite subjective ortopantomogramm since made ??a visual assessment of images. As a result, diagnosis will depend on the physician's experience and from his ability to read ortopantomogrammy.
Considered the possibility of a SCS diagnosis of periodontal disease in ortopantomogrammam, which will automatically perform radiographic stage in the diagnostic algorithm, namely to find the level of the degree of deviation from normal bone tissue, with the help of computer imaging. As a method of treatment chosen for the contrast of image segmentation.
List of sources
1. Description of a computer program for dentists Dental Software [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://www.dental-soft.ru ;
2. Orthopantomography [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://med-dovidka.com.ua ;
3. Digital radiographic systems [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://http://stomfak.ru;
4. The choice of prosthetics in periodontitis [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://www.zub-zub.ru ;
5. Periodontitis diagnosis [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://zdravoe.com ;
6. Periodontitis. The main symptoms of periodontal disease [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://zubki.kiev.ua ;
7. Treatment of gum disease (periodontal disease, periodontal disease) [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://stomatolog.com.ua ;
8. Rabuhina NA, Arzhantsev AP - X-ray diagnostics in dentistry [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://dental-ss.org.ua;
9. Intraoral image. Classic X-rays in dentistry [electronic resource]. Mode of access: http://stomfak.ru;
10. Mukhametshin, L. The method of determining bone density in normal and pathological periodontal operations with biomaterials
series of "biomaterials" / L. Mukhametshin, LR Khusainov, VG Gafarov: Collection of Articles III National Conference of private dentists. Ufa: 2007. S. 8789
11. Semenov, S. The theory of non-adaptive masks for an image-processing / SI Semenov / Biomedical technology and electronics. 2002. Ή 13. S. 3340;
12. Shapiro, L. Computer vision: Per. from English. / L. Shapiro, J. Stockman. M. Bean, 2006. 752.
13. Arzhantsev, AP The diagnostic capabilities of a computer orthopantomography, educational advice / AP Arzhantsev, V. Svirin. Change, 2006. 20c.
