Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Communication with the scientific programs, plans, and themes
- 3. The purpose and objectives of the research and development
- 4. Methodology and methods
- 5. The practical significance of the results
- 6. Summary of work
- References
- 1. Relevance of the topic
Introduction
The rapid growth of the volume and complexity of the material under study led to the traditional education system was not efficient enough and requires innovative technologies based on the use of information and computer technology [1]. Implementation of social order in the high – technology training and retraining required of new scientific and methodological understanding of the organization of independent work of students using computer means, one of which is an automated training system.
Widespread use of automated learning systems is explained by the following circumstances:
– groups in the population density in the modern teacher is not physically able to carry out the principle of individual learning, yet almost every student in need of constant and continuous attention to the formation of high-grade skills;
– the amount of required knowledge reaches such proportions that conventional teaching methods lead to an overload of students mastering the material surface and, consequently, loss of interest in learning and a sharp decline in its quality;
– automation of labor teacher: controlling students in preparation for the lecture and practical exercises (laboratory and practical work, seminars, etc.), construction of test material, statistical processing of the results of teacher control, minimizing training time for the student;
– course training program can not replace a human teacher, but it can not only complement and enhance the activities of the teacher, and in some areas in which developing independence, creative thinking, it will play a unique role that we now can not even comprehend the fully;
– summarizing the above include: the problem of creating educational programs or courses is relevant;
– computers as a teaching tool in the form of computer-based training systems.
In the educational process of higher education (university) focuses on self-study. Studies on the organization of independent student work has shown that without the training and monitoring programs to organize own work for all students is impossible. The main problem is the different levels of training, the rate and degree of assimilation of the material, education students, as well as have difficulty with their own desire to do [1]. At the moment, many people have personal computers, and a desire to work with them can stimulate a desire to work independently. Using the power of modern computers, allow each person to study the material suitable for a fast sequence providing the material, select the number of repetitions, as the study of a topic, and check that it is learning, that is, test and self test.
This solves the problem of different levels of education among students through customization. The main value of the training program is a convenient, affordable, and intuitive feed material. Ability to control reveals the difficult topic for independent study, and the teacher can give them more time in lectures. In addition, self – learning material is for the student psychologically more attractive than the control by the teacher.
1. Relevance of the topic
This solves the problem of different levels of education among students through customization. The main value of the training program is a convenient, affordable, and intuitive feed material. Ability to control reveals the difficult topic for independent study, and the teacher can give them more time in lectures. In addition, self – learning material is for the student psychologically more attractive than the control by the teacher.

Figure 1 - Students in the period of individual training
2. Communication with the scientific programs, plans, and themes
Work associated with the program training students on the mountain specialties. Topic work is integral to any work in which there are economic part, the technology of coal mining, in the course "Processes of underground mining," as provides for the development of methodical electronic aids. The work associated with the work of the previous editions of undergraduates and is part of a program to automate the analysis of cost parameters.
3. The purpose and objectives of the research and development
The aim is to systematize the development of district costs of shallow reservoirs with a combined, continuous and columnar systems development. Writing lab for students on the course "Processes of underground mining operations».
Idea work is to simplify calculations of the cost of coal mining in the district related expenses. Established program will display the influence of each parameter in the total cost of sewage treatment works for your situation. Development of laboratory work, will allow students more accessible to understand what processes occur in the abatement slaughter, and as any factor affects the situation in the slaughter of abatement as a whole. By changing any parameter, the machine will print the result, and several variants of calculation will clearly see how and how to affect change in the parameters.
4. Methodology and Methods
Methodology and research methods – engineering, engineering – economic calculations and comparisons.
5. The practical significance of the results
The results will contribute to the development of a more rapid understanding and assimilation of educational materials that the teacher gives the student according to the curriculum prepare students mountain specialties. Visibility and graphical representation of results is important when trying to make the student an adequate output to the current technical and economic situation, understand what to look for when developing options for mining, and more rational. Also consider the important factors in engineering calculations passports excavation sites.
6. Summary of work
Under precinct costs mean unit costs, ie costs attributable to a ton of coal mined, taking place in the performance of the mining process – holding production, maintenance (maintaining) the generation, transportation of coal generation, coal mining in the lava and the like [2].
Method of establishing cost parameters can be based on an analysis of specific data on the coal mines, or costing more, so – called "simulation calculation [3]." The method of analysis of specific data of coal mines, which was used IGD Skochinskiy, now appears to be a little realistic for the following reasons:
1. Financial Statements of private mines closed in most cases;
2. Considerable variation in prices and tariffs for individual mines makes the process of obtaining and processing raw data is very time consuming and inaccurate.
The method of calculation modeling is based on a detailed costing for the implementation of the test process using the existing production rates by type of activity taking into account the geological conditions in calculating the value of wages, a detailed accounting of consumables and energy when calculating the cost of these items, the calculation of depreciation taking into account the variation in prices of equipment [4].
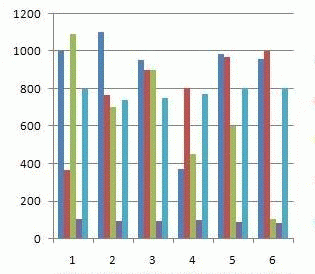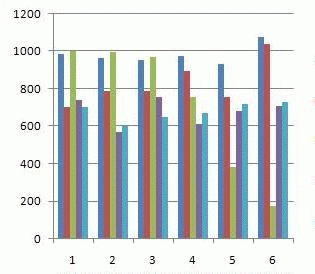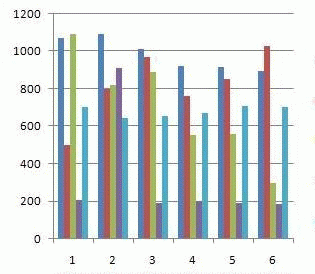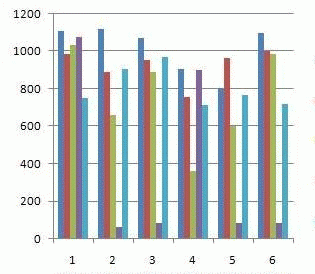
Animation 1 – Gravics costs depending on the precinct
(5 cycles, 5 frames, delay of 0.5 s., size 145 KB)
The essence of modeling calculation is as follows:
1. Developed economic-mathematical model of the unit costs of implementing the works under study form of mining. The value of the cost of each process is defined as a function of the impact of natural, technical and economic factors.
where Рi is the value of the i-th influencing factor.
2. Set the possible range of changes affecting factors (minimum and maximum values Pimin Pimax) and the value of each factor, the most common at the present time (mean Picp).
Ranges of influencing factors.
3. Vychislyaetsya investigated the value of the parameter value for all "average" values of the influencing factors of the Ccp.
4. Calculate the value of the parameter values in the range from minimum to maximum values for each variable in turn.
5. Plotted in dimensionless coordinates.
6. The method of "least squares" equation is derived based.
This factor takes into account the deviation of the test parameter value of "average" value of its deviation from "average" values of the factor-factor of influence factors.
These actions are carried out for all accepted for consideration of influencing factors.
If value of the coefficient of influence factors in the studied range does not vary by more than 3-5 %, this factor is considered to be a little influence in determining the value of the parameter is excluded from consideration.
Список источников
- Материал из Википедии – свободной энциклопедии [Электронный ресурс]. – Дистанционное обучение.
