Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Main stages of implementation of tasks
- 3. Scientific novelty of the work
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
This work is devoted to the development of cost parameters for the degassing of coal seams and surrounding rocks.
The main direction of economic development of Ukraine provides for an increase in coal mining in increasingly complex geological conditions. Therefore, the acute problem of maintaining bezremontnogo mine workings. To a large extent it comes to excavation workings, supported in the goaf behind the lava, and exposed to intense manifestations of rock pressure on sewage treatment works. Therefore, the development of efficient, waste-free and low-cost artificial protective structures, including the use of the minimum amount of an ordinary rock with elements of the limit is a very urgent task.
1. Theme urgency
Further development of the formation of mineral deposits in increasing the depth of mining is associated with the problem of ensuring the operational status of extraction workings. In this regard, are becoming more common schemes mining excavation sites in the maintenance of development workings behind the working face, and more and more attention is paid to the development of effective ways and means of development workings. The most affordable on the material costs are the ways of involving the use of an ordinary rock. And, despite the fact that they are among the most labor-intensive, they are most common.
The purpose of master's work:
- Determine the nature of deformation of rocks under the soil stiff legs;
- The establishment of zones of influence security structures in the underlying rocks;
- Development of a design hard protective structures, in which the force acts on the weight of overlying rocks will be redirected away from the excavation.
To achieve the objectives you need:
- reproduce in a model of the full geological and mining conditions that occur in nature;
- compliance with the similarity between the model and the simulated system;
- choice of the scale model that meets the challenges of modeling and identification of initial and boundary conditions;
- selection of models of hard protection structures, which will mimic the security structures in nature with a given geometric and mechanical characteristics.
2. Main stages of implementation of tasks
In solving the problems of mining geomechanics widely used modeling techniques: polarization-optical method, the centrifugal method, the structural models, the method and the method elektroanalogy modeling using equivalent materials.
Among this set of modeling techniques, the most suitable method of modeling with the use of equivalent materials, as it provides an opportunity to fully and ease of play in the models required complex geological conditions and best satisfy the requirements for laboratory studies of processes of deformation and destruction of rocks in the manufacture of mining. The method is based on the replacement of natural rock with artificial materials under conditions of geometric, kinematic and dynamic similarities.
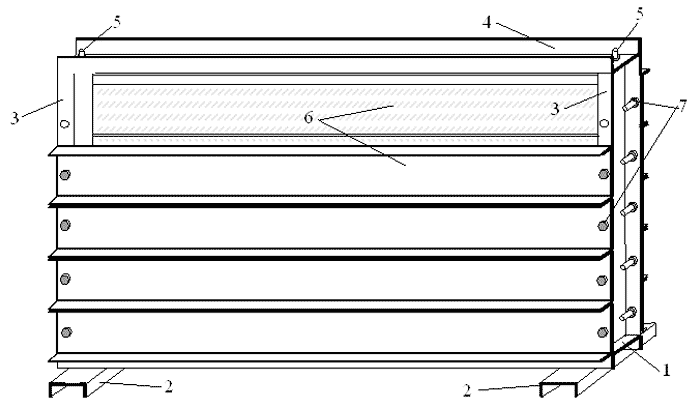
Figure 2 – General view of the stand for a flat simulation method with the use of equivalent materials (1 – bed 2 – sill, 3 – side bar, 4 – upper floor, 5 – pin, 6 – formwork)
Perfected a model with a single support for the establishment of the zone of swelling and two to determine the mutual influence of adjacent rigid structures.

Figure 3 – Overall view of the model with the same support
Dimensions of the box were taken in accordance with the scale modeling and were, in terms of nature: the width – 1.6 m, length – 32 m.
For the reliability of the simulation results we have worked out the same 5 models.
When loading the box pressure P = 0.04 MPa, there was a loss of stability of the rock underlying the building, after which they rushed to the side of the bearing, resulting in swelling observed in rocks from the side of it (Fig. 4).
Swelling occurred in the form of folding of rock layers of the soil with their displacement in the plane of bedding under the
The magnitude of the deformation of rocks in the side of the support has been established the influence of the value of a hard protective structures on the underlying rocks, and determined the magnitude of swelling under these conditions. The results of measurements on the same support revealed that the zone of influence of the hard construction is to 2a (where a – the width of the support), and the maximum swelling was 1.13 m (where m – seam thickness) and was marked at a distance from the support 1.2a (Fig. 4).

Figure 4 – Nature of deformation of rocks with the underlying model of the one pillar
3. The scientific novelty of the work
These results allowed to set the parameters set strict security facility, with which it is possible to prevent extrusion of rocks from the soil in the production of a stamp.
Thus, it is logical to say that strict conservation facility would cost to have a distance of at least two widths of the security structures. In this case, the swelling will occur in the cavity between production and support the band.
Conclusions
Thus, the simulation results we can conclude that the use of rigid supports compensating cavities in weak rocks, soil effectively and that the correct selection of parameters can be maintained roadway in good working order. And if necessary the construction of the wall insulation should be installed the last of the gob.
References
- Руководство по проектированию угольных шахт. – Киев – 1994.
- Ушаков К.З. Бурчаков А.С. Пучков Л.А. Медведев И.И. Аэрология горных предприятий. М., «НЕДРА», 1987. – 421 с.
- Черняк И. Л. Упрочнение пород в подготовительных выработках / И. Л. Черняк – М.: Недра, 1993. – 256 с.
- Галкин, В.В. Невзрывной способ разрушения строительных конструкций при реконструкции зданий / В.В.Галкин, А. Г. Потапов // Монтажные и специальные работы в строительстве. 1983. – № 6. – С. 21–22.
- Заявка 57–119850, Япония, МКИ В 02 С 19/18, Е 04 С 23/08. Композиция для разрушения бетона, дорожного покрытия и т.п. / Нисихара Акио, Мива Мотому, Тада Сюити; Асахи дэнка коге к.к. № 56-5779 заявл. 16.01.81,. опубл. 26.07.82.
- Найданов, К.Ц. Разработка щадящих технологий добычи ювелирного и поделочного самоцветного сырья (на примере Восточной Сибири): Автореф. дис. канд. техн. наук: 25.00.22/ГОУ ВПО «Читинский гос. ун-т». – Чита, 2007. – 21 с.
- Пшеничная, Е. Г. Обоснование рациональных параметров технологии добычи гранитных блоков с применением невзрывчатых разрушающих средств: Автореф. дис. канд. техн. наук: 25.00.22, 25.00.20 / Магнитог. гос. техн. ун-т им. Г.И. Носова, Магнитогорск, 2004, 20 с.
- Артамонов, С.М. Добыча блоков природного камня недробящим способом / С.М. Артамонов, С.Г. Агеев // Строительные материалы. 1985. – № 7. – С. 9–10.
- Шкуматов, О.М. Комбінована технологія розробки прохідницького вибою криволінійно-уступної форми / О.М. Шкуматов, В.А. Галоян // Наукові праці Донецького національного технічного університету. Серія: «Гірничо-геологічна». 2009. – Вип. 10. – С. 70–73.
- Белоконь В.Г. Газоносность угольных бассейнов и месторождений СССР-Москва, «НЕДРА» – 1980 – 217 с.
- Зберовський В.В. Розвиток геотехнологій видобутку метану вугільних родовищ. Вугілля України, 2004, № 7, с. 16–18.
