Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study, research methods
- 3. Rationale for selection of work and construction sucker rod pumps for drilling local washing
- 4. Advanced technology drilling sucker rod pump
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In this paper we investigated methods of drilling in absorption of drilling fluid and the construction of submersible pumps. The analysis shows that the pump rod is the most simple and reliable. However, their use is difficult because of their imperfection.
The paper presents the design of sucker rod pumps for local cleaning, which is in the Donets Basin allows drilling in the areas of catastrophic or absorption in the zones of influence of mine workings in the unstressed regime, with the possibility of selection of the fluid supplied to the slaughter, and with an axial load on the rock cutting tool is continuously adjustable over a wide range.
1. Relevance of the topic
When drilling for coal in the Donbass often drilled in the zones of influence of mine workings. This drill is accompanied by disastrous acquisitions. Serve the water from the surface is not profitable, and sometimes impossible due to the collapse of the borehole walls.
In such conditions it is better to drill in the residual liquid column with different submersible pumps, creating a hole in the local circulation of drilling fluid.
At the present time in our country and abroad use many different means and ways to drill with the local flushing, submersible pumps produced in absorption of drilling fluid designed for different operating conditions, which differ structurally and on the principle of action. Their analysis shows that one of the most simple of pumps are submersible rod pumps.
Famous rod pumps vary the design of units for transmitting rotation of the drill pipe to the auger set of valves. Nodes to mitigate the impact piston at the extreme points.
However, used a simple device for rod pumps for drilling with the local flushing share common drawbacks:
– axial load on the rock cutting tool can be created only by the weight of drill pipe that are installed on the pump rod;
– with reciprocating drill rock cutting tool is separated from the bottom, resulting in damage to the core and its samozaklinke;
– there are bumps on the piston top and bottom of cylinder pump. These attacks resulted in damage to the pump and the core loss of the core barrel.
In addition to increasing the supply of submersible pump must use a double acting pump with a complex system of valves.
2. The purpose and objectives of the study, research methods
The purpose of this paper is to improve the design of sucker rod pumps for local cleaning, which is in the Donets Basin allows drilling in the areas of catastrophic or absorption in the zones of influence of mine workings in the unstressed regime, with the possibility of selection of the fluid supplied to the slaughter, and with an axial load on the rock cutting tool is continuously adjustable in the a wide range.
To achieve this goal are determined by the following:
- Analysis of existing structures for drilling rod pumps with local flushing of the face.
- Improvement of methods of calculating rod pumps for drilling with a local washing and determination of its operating parameters.
- Improvement of construction boom pump for drilling with a local washing
- Development of technology for the use of advanced design sucker rod pumps for drilling with a local washing.
Research methods. The problem is solved by compiling and analyzing patent and literature, theoretical research, implementation research and design work.
The scientific novelty. Refined method of calculating the sucker rod pumps for drilling with the local flushing, which allowed to study the regularities of advanced devices with a choice of an effective combination of design and size of the mechanism of hydraulic parameters: hydraulic pump – well.
The scientific and practical significance of the results. The scientific value of the work consists in the possibility of using the obtained theoretical model and application of knowledge obtained in the drilling industry.
The practical significance is expressed in the creation of an efficient design boom pump, which provides in the Donbass efficient drilling in areas of local washing catastrophic absorption or zones of influence of mining by ensuring that drilling in the unstressed regime, with the possibility of selection of the fluid supplied to the slaughter, and with an axial load on the rock cutting tool continuously adjustable over a wide range.
3. Rationale for selection of work and construction sucker rod pumps for drilling local washing
The most simple to manufacture and use are rod pumps. However, their use is difficult because of their imperfection. Almost all rod pumps do not have a reliable design of the device to soften the blows of the piston in the extreme points. Strikes led to a decrease in service life of pump components and do not take away from the core structure intact blows. It is therefore necessary to provide a device for mitigating the impacts.
During the drilling of the known range of sucker rod pumps auger breaks away from the face, which can lead to jamming of the core and to the cessation of circulation of the fluid. It is therefore necessary to provide for retention of the cylinder head. The presence in the pumps, as a rule, one does not allow the piston to regulate the amount of the fluid during the drilling of small diameter wells. During the drilling of well – known sucker rod pumps can not be promptly adjusted axial load on the hard rock cutting tools, since it usually depends on the weight of drill collars.
Thus, to eliminate the disadvantages of pumps considered, it is necessary to improve the design pump, which would allow the conditions of the Donets Basin to drill in areas of catastrophic or absorption in the zones of influence of mining to the local wash in unstressed mode, with the possibility of selection of the fluid supplied to the slaughter and axial load on the rock cutting tool is continuously adjustable over a wide range.
In order to eliminate the disadvantages of pumps considered, proposed an improved design of sucker–rod pump, which can reduce the impacts of extreme points, makes it possible to regulate the amount of the pumped fluid and pump smoothly adjust the axial load.
Figure 1 shows a diagram of an improved sucker rod pump.
The pump consists of a piston to generate thrust two, one or more of three pistons to control the pump, the rod 4, 5 cylinders, splined hub for the transfer of rotation 7, 8 and 9 valves.
Figure 2 shows a diagram of the pump in the well.
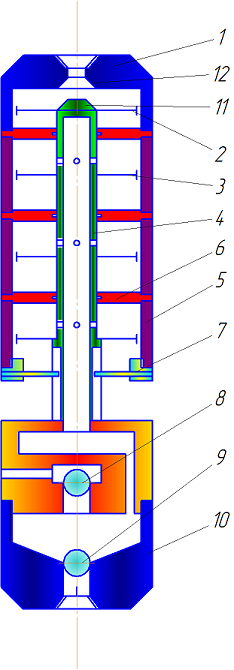
Figure 1 – Diagram of submersible pumps for drilling boom in drilling fluid absorption
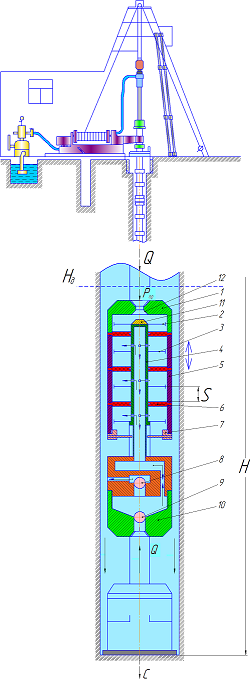
Figure 2 – Scheme of sucker-rod pump in the well
After installing the pump into the well on the drill string ground power is pumped liquid. The pressure of the liquid creates a force on the piston 2, pressing the auger to the bottom shell. Thus, changing the flow and pressure can be adjusted axial loading of the rock cutting tool in a wide range.
Due to the fact that the piston 2, the auger pushes the projectile to the face, core set is not detached from the bottom, which contributes to the preservation of the core.
The torque from the drill string to the auger passed through a set of spline node 7.
This device allows the spline node reciprocating drill core set of job from the face.
Cylinders 5 mobile pumps. In reciprocating the pipe string reciprocating piston cylinder 5 on 3 causes reverse circulation drilling fluid.
In the course of the column rod cylinder 5 moves upward at the top of the cylinder will discharge, causing the absorption of fluids from the well through the drill, the entrance channel in the adapter 10, the ball valve 9.
When moving down the cylinder 5 fluid is displaced into the annulus through the ball valve 8.
To control the pump, you can install the required number of pistons 3. Moreover, for various numbers of pistons and cylinders used only two valves – suction 9 and discharge 8, which greatly simplifies the design of the pump.
The improved pump is a device to soften the blows of the piston at the extreme points.
To do this at the top of the cone is made stationary piston 11 and the movable adapter – tapered bore 12. Getting in the tapered bore cone, and hence the cylinder, encountering additional resistance to slow the speed and the piston stops at the lowest position without a blow.
Provided for in the design of improved device to soften the blows of the piston in the extreme points will increase the service life of pump components, and will take away from the core structure intact blows.
Thus, the use of an improved sucker rod pump in the Donets Basin would allow drilling in areas of disaster or in the absorption zones of influence of mine workings.
Figure 3 shows the animation of the principle of the sucker rod pump in the well.
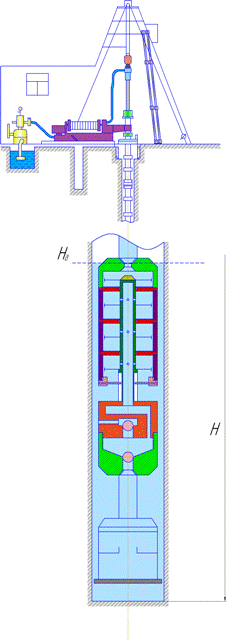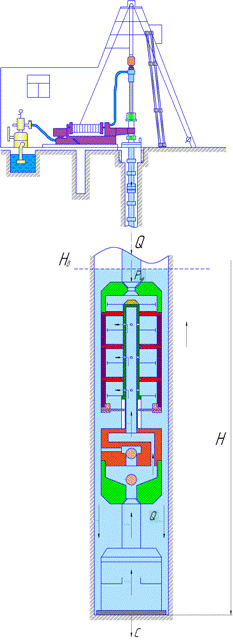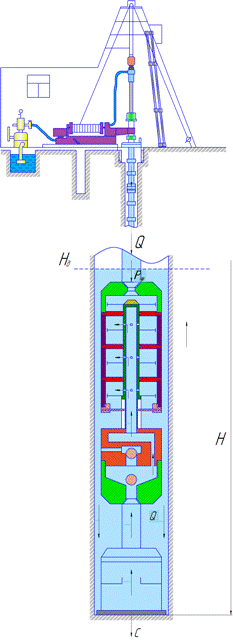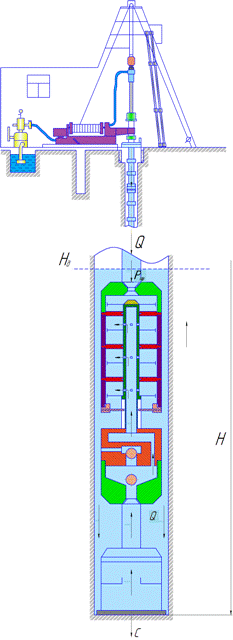
Figure 3 – Animation of the principle of the sucker rod pump in the well
(animation: 7 frames, 10 cycles of repetition, 195 KB)
Figures 4–12 shows the basic units of sucker rod pump.
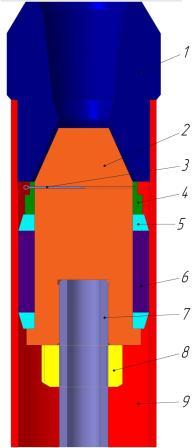
Figure 4 – The node to create an axial load
1 – adapter;
2 – piston;
3 – pin; 4 – crown nut;
5 – ring screw–down;
6 – cuff; 7 – stock;
8 – nut; 9 – cylinder
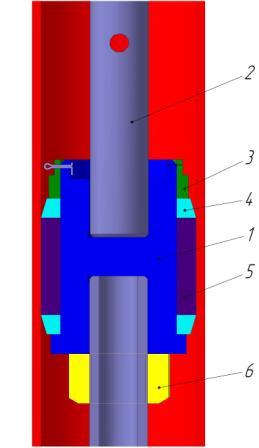
Figure 5 – The node to control the pump
1 – piston; 2 – stock;
3 – crown nut;
4 – ring screw&ndahs;down;
5 – cuff; 6 – nut

Figure 10 – Site guide
1 – nipple;
2 – union nut;
3 – cuff;
4 – spacer ring;
5 – bush; 6 – stock;
7 – cyliender
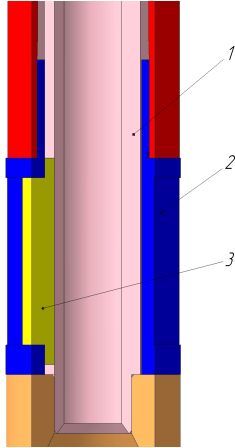
Figure 7 – Splined site
1 – stock;
2 – leading nipple;
3 – key
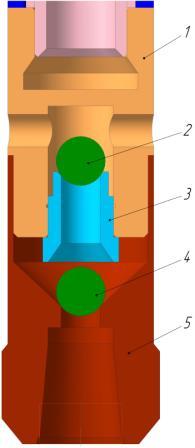
Figure 8 – Valve assembly
1 – nipple slave;
2 – discharge valve;
3 – the valve seat;
4 – suction valve;
5 – the lower adapter
Advanced technology drilling sucker rod pump
Before using the pump unit checks to see whether the necessary technical documents: passports, technical specifications, installation, setup and installation and assembly drawings, assembly plant construction, etc. Next, check the completeness of the pumping equipment.
Before descending into the well pump and re–entry is an external examination, check condition of rubber components, spline node and other nodes. Checks tightness of ball valves and ease of movement spline node. Body parts are checked for their lack of any damage, nicks and cracks.
Before you begin, check pump must be completely smooth and easy to control parts of the unit.
On receiving the jetty going to weasel set in accordance with the physical and mechanical properties of rocks from the emergency response redrille adapter and rod pump.
By the core set of semi–joins the elevator supplied with the rig, set down in the hole and the plug is installed on the chock.
Then, in the same way up the pump rod and is connected with core set.
Rod Pump with core set down on the drill pipe into the well and set below the dynamic level at 3–5m. The descent is performed by the usual method of lowering – hoisting operations.
After lowering the pump into the well drilling is pumped into the well water under pressure, which corresponds to the required geological and technical design axial load on the rock cutting tool. Given by rotation and is given in the drilling of geological and technical design long voyage.
When drilling is reciprocating the drill string to a height of 1m with a frequency of 8 strokes / min.
When operating the pump operation should continuously monitor the correct operation of its individual components, fixing any abnormalities, which are eliminated at the first stop of the pump.
During the operation, after lifting the pump to the surface regularly for preventive checkups. Known faults are recorded in a removable magazine, which is the primary document describing the technical state of equipment. Based on this log are determined by timing, nature and scope of the inspection repair, timeliness, which ensures the safety of equipment and continuity of the pump unit.
After removal from the wells, washed with water pump, disassembled, all moving parts are lubricated with grease US–2.
Conclusion
In the absorption of drilling fluid to flush the local slaughter the easiest way is to drill to drill with the creation of flushing rod pumps.
In order to eliminate the disadvantages of sucker rod pump improved scheme is proposed for drilling pump absorption in a drilling fluid.
The pump at the top of the cylinder is an additional cylinder with a piston to regulate the axial load in a wide range. Also at the top of the cylinder is installed cone and adapter – taper groove, which allows you to soften the blows of the piston in extreme positions.
To control the pump, you can install the required number of pigs by using only two valves – suction and discharge, which greatly simplifies the design of the pump.
Thus, the developed design has a significant advantage over the known and it allows you to use the pump in the Donbass.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2012. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Пилипец В.И. Насосы для подъема жидкости/ В.И. Пилипец. – Донецк: РИА, 2000. – 244 с.
- Волков А.С., Волокитенков А.А. Бурение скважин с обратной циркуляцией промывочной жидкости/ А.С. Волков, А.А. Волокитенков. – М.: Недра, 1970. – 184 с.
- Анурьев В.И. Справочник конструктора-машиностроителя/ В.И. Анурьев. – М.: Недра, 1978. – 920 c.
- Неудачин Г.И., Пилипец В.И. Погружной пневматический насос / Г.И. Неудачин, В.И. Пилипец. – М.: ЦНИИЭИУголь, №27, 1976.
- Есьман И.Г. Насосы / И.Г. Есьман. – М.: Недра, 1954. – 288 c.
- Лисикян К.А., Докукин В.И., Документов И.И. Штанговые глубинные насосы / К.А. Лисикян, В.И. Докукин, И.И. Документов. – Баку: Азнефтеиздат, 1945.
- Неудачин Г.И., Пилипец В.И. Исследование рабочего процесса погружного поршневого гидроприводного насоса / Г.И. Неудачин, В.И. Пилипец. – М.: ЦНИИЭИУголь, №687, 1976.
- Неудачин Г.И., Пилипец В.И. Погружной насос для перебурки водопоглащающих горизонтов с местной промывкой забоя (Расчет рабочих параметров погружных поршневых насосов с гидроприводом) / Г.И. Неудачин, В.И. Пилипец. – М.: ЦНИЭИУголь, № 12, 1976.
- Неудачин Г.И., Пилипец В.И. Штанговый поршневой насос для откачки жидкости из стволов шахт, пройденных бурением / Г.И. Неудачин, В.И. Пилипец. – М.: ЦНИИЭИУголь, № 12, 1976.
- Неудачин Г.И., Пилипец В.И. Погружной пневматический насос / Г.И. Неудачин, В.И. Пилипец. – М.: ЦНИИЭИУголь, №27, 1976.
