Сontent
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3.Review of research and development
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Issues of construction and adjustment of geodetic free networks is given much attention. They are used to solve the problem of estimation of deformations, while fitting the photogrammetric builds networks in optimization problems. As an example of effective use of high-rise nets can reduce the problem of stability analysis of high-rise frame basis.
It should also be noted that from the perspective of a systems approach free networks are more holistic construct, whereas the non-free networks are their special cases. Therefore it is sometimes advisable to geodetic networks as free calling, and then turned into a non-free, fixing all the original data.
1. Theme urgency
As you know, the creation of geodetic networks differs in a number of features due to the fact that their design is performed for a specific object (often in built-up area). In contrast to the general engineering and geodetic networks, geodetic networks have a complex configuration, characterized by the violation of the geometrical requirements for geodetic networks. In addition to the accuracy of geodetic networks, involving stake out individual structural elements of detail increases as the object under construction. All of the above aspects have necessitated widespread use in engineering and geodetic surveying practice of free networks. So urgent is the study of the accuracy of a geodetic network.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
Development of an approach is to consider the influence of the choice of initial data on the accuracy of a geodetic network.
Main tasks of the research:
- Set features adjustment-free geodetic networks.
- Identify the impact of the choice of initial data on the accuracy of a geodetic construction of engineering structures.
3.Review of research and development
At the present time is receiving increasing attention to the adjustment of geodetic free networks.
First of all let us explain what we mean by free geodetic network in the context of this work.
Free geodetic network - to build a geodesic, in which the number of input variables is not enough for the orientation, zoom and fixed network in the appropriate space.
Lack of initial values in the free geodetic networks, and therefore non-zero defect of the matrix system of normal equations leads to some changes in methods of adjustment of this type of networks.
The main advantage of free constructions is independent of the input data errors, allowing you to fully appreciate the quality of the measurements [9].
The source [9] presented the following classification of free networks based on the value of the defect matrix of normal equations (d):
- Maximum free network -
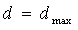 ;
;
- Semifree -
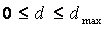 ;
;
- Zero-free -
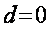 .
.
The most widely used in the practice of surveying software construction have a zero-free construction, which is caused by the following:
- Zero-free networks are useful for local constructions, which are used in the construction of most engineering structures.
- Since in a zero-free constructions
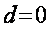 , commit the necessary unknowns does not distort the geometry of the network, ie their use does not lead, using the term structural mechanics, to the tense system, which takes place at the traditional geodesic constructions in the form of proprietary networks.
, commit the necessary unknowns does not distort the geometry of the network, ie their use does not lead, using the term structural mechanics, to the tense system, which takes place at the traditional geodesic constructions in the form of proprietary networks.
- As a result, network adjustment as a zero-free are the coordinates in the desired system, for example, in the coordinate system of principal axes of the building [9].
Consider the basic aspects of the adjustment of geodetic free networks.
Adjustment-free geodesic constructions parametric method leads to a parametric coupling equations with the function of the parameters x measurements l, which is compiled for each measurement.
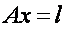
The coefficient matrix of parametric equations of the amendments is a defect d (for leveling networks of d = 1 for the planned network d = 4, for the space - d = 7). As a consequence, the coefficient matrix of normal equations  is degenerate and the solution of normal equations
is degenerate and the solution of normal equations
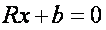
Is given by:
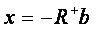
Where x - vector of the unknown unknowns;
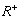 - pseudoinverse matrix;
- pseudoinverse matrix;
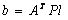 .
.
As we can see the solution is performed using the pseudoinverse matrix 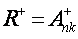 .
.
The main computational difficulties in fitting the free networks are related to the definition of pseudoinverse matrix.
There are many ways to find the pseudoinverse matrix, we list only some of them:
- The method of calculating the matrix element-wise
 .
.
- Method of Augmentation.
- A method based on spectral decomposition of the matrix R.
- Method Grevilya.
As a result of the master's work will be decided next scientific mission: to identify changes in the accuracy of the parameters that are defined in geodetic networks, depending on the accuracy (error) input data and the location of the source data in the network.
Adjustment of geodetic networks in this work is performed in several stages:
- Initially, the free equalized network, with fixed coordinates of any point of the network and the directional angle of any direction from him.
- Further, based on the results of the free adjustment, will be re-leveling with the fixation of different input data in geodetic networks, which allow you to select the best option adjustment depending on the task at hand.
Using this approach to equalize the geodetic networks eliminates the errors of initial data and taking into account only the errors of measurement. This is necessary in order to fully assess the quality of measurement engineering and geodetic networks.
Since the solution of most engineering problems are significant, not only the absolute values of errors and their direction with respect to the parties the network. This is because the construction of many buildings strive to achieve the lowest-possible errors on the "responsible" direction. In order to visually display the direction of propagation of errors for each variant equalization error ellipses were constructed (as shown in Picture 1), which allow to analyze the results of leveling networks and choose the best option.
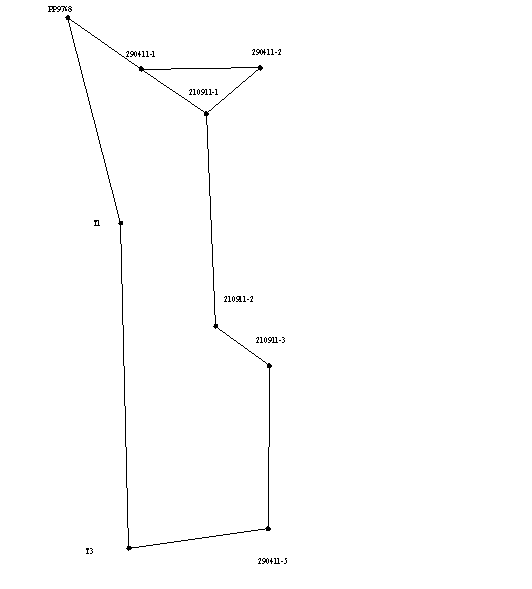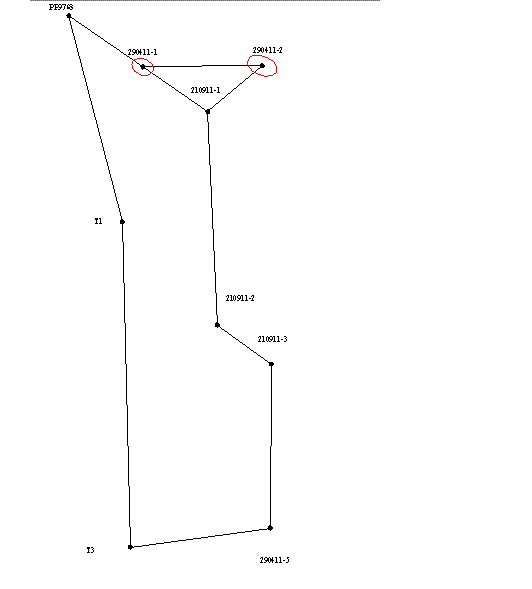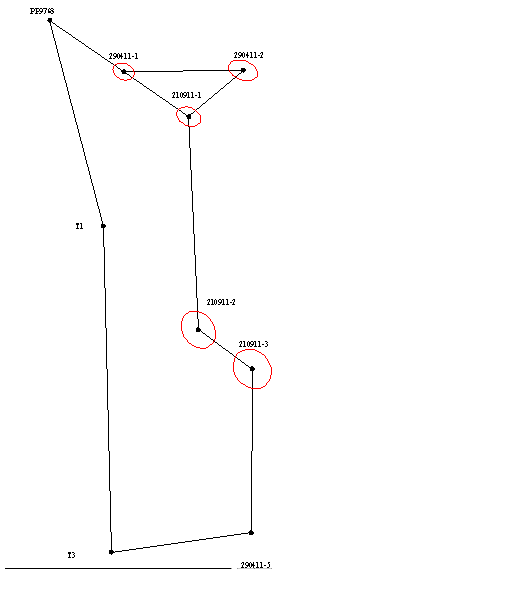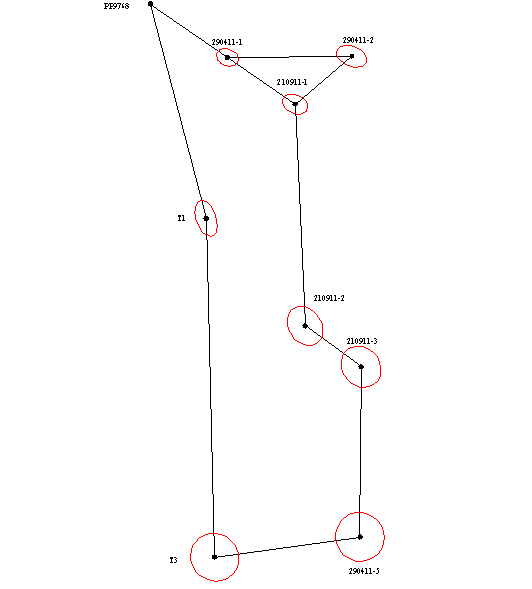
Picture 1 - Error ellipses
Conclusion
The theory of free adjustment of geodetic networks assumes a generalized value, and it becomes clear to her keen interest of many scientists. Naturally, a number of issues of free adjustment each author interprets in his own way, but the general direction of research is to combine different approaches to equalization.
Adjustment of free geodetic networks is of great practical importance, since the network stakeout of the site should provide high accuracy stakeout constructs and to exclude errors of input data.
The choice of fixing the original data in the networks of different configurations and has a significant impact on improving the accuracy of adjustment, which is important in the present conditions, when increased demand for precision geodetic constructions required for geodetic support construction of engineering structures.
References
- http://www.dissland.com/ Швец С.В. Алгоритмы уравнивания свободных полигонометрических сетей с контролем грубых и систематических ошибок линейных измерений. Дисс. на соискание уч. степени канд. техн. наук: 25.00.32 М, 2005.
- Матвеев С.И. Единый подход к уравниванию свободных геодезических сетей.// Геодезия и картография.- 1985, вып. 7.- с. 6-11.
- Ганьшин В.Н. Анализ способов уравнивания свободных нивелирных сетей и оценка устойчивости реперов.// Геодезия и аэрофотосъемка. – 1979, вып. 3. – с. 5-12.
- Ганьшин В.Н., Стороженко А.Ф., Ильин А.Г. и др. Измерение вертикальных смещений сооружений и анализ устойчивости реперов. М., «Недра», 1981.
- Усов Д.В., Усова О.О., Ялтыхов В.В. Методика построения равноточных нуль-свободных нивелирных и спутниковых геодезических сетей.// Земля Беларуси.- 2009, вып. 1. – с. 38-40.
- Матвеев С.И. Программа уравнивания свободных нивелирных сетей.// Геодезия и фотограмметрия в горном деле. Свердловск. – 1978, вып. 5. – с. 39-42.
- Йовен И. Применение метода наименьших квадратов для уравнивания свободных сетей. // Геодезия, картография, землеустройство. Болгария. – 1980, вып. 20. – с. 14-17.
- Маркузе Ю.И. Взаимосвязь процедур уравнивания свободных и несвободных сетей. // Известия вузов. Геодезия и аэрофотосъемка. – 1984, вып. 3. – с. 3-14.
- Андоленко В.И. Исследование точности создания сетей специального назначения и разработка методов геодезического обеспечения строительства реакторных отделений АЭС. Дисс. на соискание уч. степени канд. техн. Наук. – М.: МИИГАиК. 1987.- 146 с.
- Князев А.Г. О способах вычисления псевдообратной матрицы при уравнивании свободных геодезических сетей. // Известия вузов. Геодезия и аэрофотосъемка. – 1984, вып. 5. – с. 25-34.
- Ганьшин В.Н. Псевдообращение матрицы нормальных уравнений свободных геодезических сетей. // Известия вузов. Геодезия и аэрофотосъемка. – 1989, вып. 6. – с. 3-5.
- http://book.tr200.net/v.php?id=628858 Большаков В.Д., Маркузе Ю.И. Практикум по теории математической обработки геодезических измерений: Учебное пособие для вузов.- М.:Недра, 1984, 352 с.
- http://www.twirpx.com/file/91607/ Теория матриц./Ланкастер П. – М.: Наука, 1982. – 272 с.
- http://www.nsu.ru/mmf/tvims/chernova/tv/portr.pdf Чернова Н.И. Теория вероятностей: Учеб. пособие/ Сиб-ГУТИ. Новосибирск, 2007. – 128с.
- http://www.mirknig.com/knigi/ Губанов В.С. Обобщенный метод наименьших квадратов. Теория и применение в астрометрии. – М.: Наука, 1997. – 319с.
- http://mirknig.com/knigi/ Чеботарев А.С. Способ наименьших квадратов. – М.: Геодезический факультет и военно-геодезическое отделение Московского межевого института, Издательство Московского высшего технического училища, 1928. – 475 с.
- Разумов О.С. О некоторых свойствах псевдообратной матрицы нормальных уравнений свободных геодезических сетей. – Изв. вузов. Геодезия и аэрофотосъемка, 1981, № 6, с. 3-7.
- Маркузе Ю.И., Хоанг Нгок Ха. Два способа получения псевдообратной матрицы при уравнивании свободных геодезических сетей с применением рекуррентной формулы. – Изв. вузов. Геодезия и аэрофотосъемка, 1985, № 1, с. 14-23.
