Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. MANET
- 4. Comparison analysis of existing routing protocols
- 4.1 Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector
- 4.2 Optimized Link-State Routing
- 4.3 Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol
- 5. Designing telecommunications access network based on broadband technology Wi-Fi Mesh.
- Conclusion
- References
- 4.2 Optimized Link-State Routing
Introduction
The telecommunications industry – it’s industry without which today can not function fully no other organizations, service or company.
Today we can see the rapid growth of mobile devices in the population and, therefore, potential users who want to have a fast wireless Internet access, and at any point and without breaking all connected sessions.
The class networks with variable topology is one of the alternative approaches to meet the growing requirements for telecommunications
1. Theme urgency
This type of network is slowly but is quite confident entered in our lives. Those developing the standards and technologies are arising problems such as defining the operating conditions that will justify the expected efficiency and bring economic benefits from the introduction of the technology being developed and run it in production.
Relevance of the study of the dynamics these networks, confirmed necessity know the nature and frequency of topology changes that in the future be able to determine the best ways to implement such networks.
Currently still a little published works in Russian and very few works of Ukrainian researchers for routing algorithms in wireless networks. But we can not say this about foreign information space.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim of this work is to study the different ways to deploy this type of networks, as well as an analysis of routing protocols and identify the best criteria and methods of cooperation in wireless networks with variable topology. The challenges are to determine the most effective method of resource management wireless network, which will be able to maintain their performance regardless of changes in the current network settings
3. MANET
A mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a self-configuring infrastructureless network of mobile devices connected by wireless. All nodes are both end users and intermediate routers. Can be connected dynamically in an arbitrary manner. Are decentralized, self-organizing networks that consist of mobile devices that are very often disconnected and connected to their neighbors and, therefore, can free to change their topology.
The advantages of MANET
– Ability to transmit data over long distances without increasing the transmitter power;
– Resistance to changes in the network infrastructure;
– The ability to quickly reconfigure in an unfavorable electromagnetic environment;
The main problems MANET:
Today, there are several classes of problems:
– The problem of noise;
– The problem of ensuring security of transmitted data;
– The problem of the overall network capacity;
– The problem of the effectiveness of routing methods
4. Comparison analysis of existing routing protocols
The existing routing protocols on the basis of the work can be divided into proactive and reactive. Let us consider the features and differences.
4.1 Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector
AODV (Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector) – a dynamic routing protocol for mobile ad-hoc networks (MANET) and other wireless networks. There is a reactive routing protocol, ie sets a route to a destination upon request. As the name implies, to calculate routes using distance-vector routing algorithm.
4.2 Optimized Link-State Routing
OLSR (Optimized Link-State Routing ) – routing protocol for MANET, which can also be used for other wireless networks. OLSR – a proactive routing protocol, which uses messaging greetings and controls to obtain information about the topology of the network.
4.3 Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol
Hybrid routing protocol HWMP (Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol) combines the two modes of construction of ways: Reactive and proactive, which can be used both separately and simultaneously in the same network. It uses broadcast packets. The routing protocol HWMP is mandatory for all devices standard IEEE 802.11s, as the default protocol.
5. Designing telecommunications access network based on broadband technology Wi-Fi Mesh.
MESH is a type of networking where each node must not only capture and disseminate its own data, but also serve as a relay for other nodes, that is, it must collaborate to propagate the data in the network. Another advantage in the use of this technology is the fact that the Mesh-network constructed using common wireless standard – Wi-Fi. The advantages of this solution are obvious – a wide range of cheap consumer devices standard defines the commercial success of the project.
The planned network will contain the following information services are:
– Internet;
– Database;
– Voice calls (the technology VoIP);
– IP-surveillance.
Potential subscribers in the facility should be divided into four main categories, which will have access to the services which they are allowed. It will:
Category 1 – Administrative and management staff (management and employees of the institution)
Category 2 – Security
Category 3 – Business subscribers (members of conferences and events)
Category 4 – Active subscribers (visitors to the exhibitions and conferences)
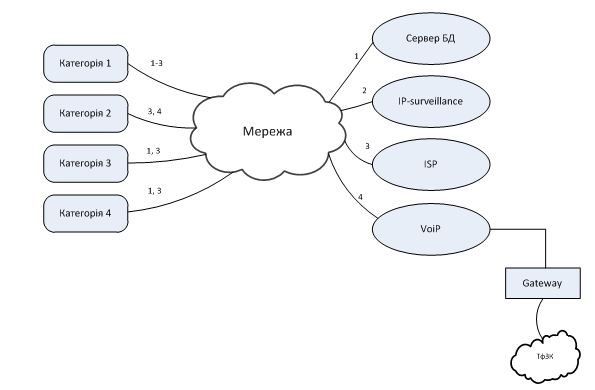
Figure 1. The information model of the object.
The IEEE 802.11n technology based on OFDM-MIMO.
The transmitter in such system sends the n independent signals using n antennas. At the receiving side each of the m antennas receives signals, which are superpositions of n transmission signals from all antennas. It is important to note that the use of the MIMO multiple transmitting and receiving antennas can increase channel capacity by the implementation of several spatially separated subchannels, wherein the data is transmitted in the same frequency range.
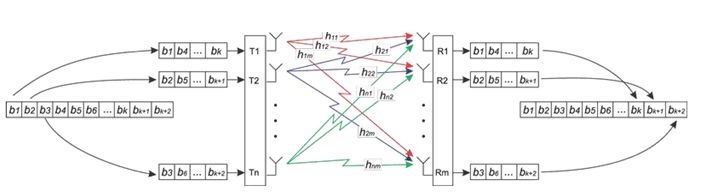
Figure 2. The principle of the implementation of MIMO technology
Compound client devices in a common wireless network will do, regardless of at which point they are active at this time. Our network will consist of a full mesh routers connected by radio link. Several of these access points will need to be wired connected to the allocation switch. Output to WAN may be implemented in various ways.
To deploy metro MESH networks commonly used two-tier hierarchy, which is based on high-power mesh routers by type MSR 4000 that make up the core of the network and a two-module radio link routers interconnected to each others.
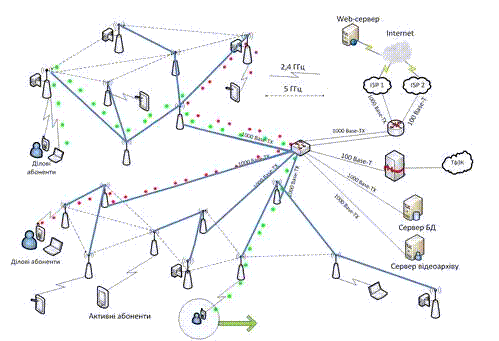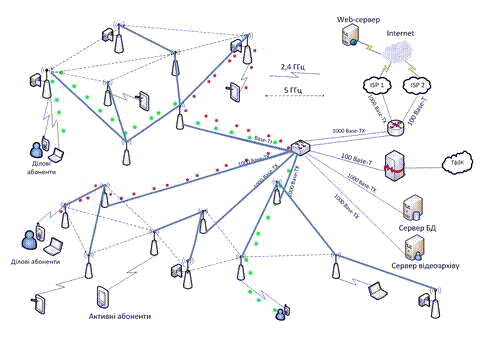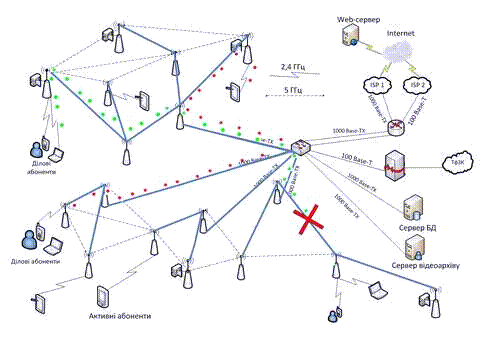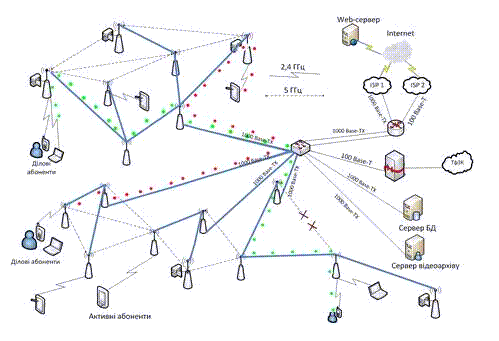
Figure 3 – The dynamics of the wireless network with variable topology
(Animation: 5 shots, 5 cycles of repeating, 109 Kb)
Presented above animation shows the progress of of functioning designed network technology based Wi-Fi Mesh.
Conclusion
Thus, the analysis of the current situation confirmed the relevance of the chosen theme, research and planning shows that the development project will be promising in near future.
Each class of protocols has the potential advantages and disadvantages to use them in a mobile Ad hoc-networks. For example, proactive protocols have a clear advantage over the jet in time route planning. In proactive protocols, this process is, in fact, going ahead, and it takes only consider the route from the table, whereas the reactive protocols need to send out a broadcast request and wait for an acknowledgment from the recipient. However, proactive protocols must be constantly broadcasts, which can be spent on a significant proportion of the network bandwidth, especially in large networks with high mobility nodes. On this basis, further research will be aimed at improving the existing routing algorithms and principles of interaction between nodes in the network, in order to obtain the best quality indicators.
References
- Гайнулин А. Г. Управление ресурсами в беспроводных сетях с переменной топологией / Гайнулин А. Г. // – Автореф. дисс. .докт. филос. наук. НГТУ – Н. Новгород: Изд. НГТУ, 2009
- Климов И. А. Пояснительная записка к курсовому проекту по дисциплине «Проектирование средств и систем ТКС» Донецк 2013 г.
- Климов И.А., Червинская Н. В. Сравнение протоколов маршрутизации для беспроводных мобильных Ad-Hoc сетей / Климов И.А., Червинская Н. В. // Автоматизація технологічних об’єктів та процесів. Пошук молодих. Збірник наукових праць ХІII науково-технічної конференції аспірантів та студентів в м. Донецьку 14–17 травня 2013 р. – Донецьк, ДонНТУ, 2013. – С. 76-80
- Определение сетей MANET [электронний ресурс], – Режим доступа:http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/MANET
- Определение сенсорных сетей [электронний ресурс], – Режим доступа: http://habrahabr.ru/post/95011/
- В.М. Винокуров, А.В. Пуговкин, А.А. Пшенников, Д.Н. Ушарова, А.С. Филатов Маршрутизация в беспроводных мобильных Ad hoc-сетях: научная статья. / В.М. Винокуров, А.В. Пуговкин, А.А. Пшенников, Д.Н. Ушарова, А.С. Филатов // Доклады ТУСУРа, № 2 (22), часть 1, декабрь 2010 – С. 288-293
- Терновой М. Ю. «Мобильные сети: IP маршрутизация и алгоритмы MANET маршрутизации»
- Вишневский В., Лаконцев Д., Сафонов А., Шпилев С. Mesh-сети стандарта IEEE 802.11s – технологии и реализация // ЭЛЕКТРОНИКА: Наука, Технология, Бизнес. – 2008. – c. 98-105.
- Технология MIMO [электронний ресурс], 2006 – Режим доступа:http://www.compress.ru/Article.aspx?id=16399
- Позняк В. О. Використання комбінованого алгоритму маршрутизації для мережі Ad hoc / Позняк В. О. // Наукові записки УНДІЗ, No 2(18), 2011. – C. 97-102
- AODV Description [электронний ресурс], – 2010 Режим доступа: http://moment.cs.ucsb.edu/AODV
