Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Review of scientific articles
- 2. Urgency of an issue
- 3. Purpose and the subject matter of the thesis
- 4. Mathematical model of the trolley with a load
- 5. Laws of control of the movement mechanism
- Conclusions
- References
Introduction
During the operating of the crane there is a constant change of direction of movement of the crane, the jack-lift and a hanger. Thus, the work of the lifting mechanism consists of processes of lifting and lowering of the load and processes of lifting and lowering of an empty hanger. To improve the productivity of the crane the principle of combining the crane operations is used. The time of pauses during which the engine is off on and the mechanism doesn't work, is used for suspending the load on the hook and releasing of the hook and for the preparation for the next process of operations of the mechanism. Every process of movement, can be divided into the periods of unsteady movement (during which there is acceleration or deceleration of moving mass of the load and the mechanism) and the period of movement with steady speed.
For cranes of general purpose with the machine drive operating modes are established: easy, medium and hard. For each mechanism the operating mode is defined separately, the mode of operation of the crane as a whole is set on the main lifting mechanism.
Usually crane has two bogies: trolley of movement and load jack-lift. Jack-lift is only one, but in some cases, their number can be increased to two.
The drive of the hanger has rather strict requirements: it must provide fast and at the same time, smooth acceleration, constancy of acceleration irrespective of the speed of switching of contacts of control pedestal, the possibility of reversal, high reliability and stability of the work in conditions both high and low temperatures, and also at high humidity, dust content of environment and presence of aggressive gases and smoke.
Use of optimal operating modes of the load jack-lift allows: to reduce dynamic loads of the mechanism of movement of the jack-lift, providing lack of blows; to avoid fluctuations of the load that is fixed on flexible suspension [1].
1. Review of scientific articles
Quality of many technological processes depends on movement of loads by hoisting-and-transport machine. Questions of optimization of modes of movement of crane mechanisms are considered in works of such scientists as V.P.Balashov, N.A.Lobov, B.V. Kvartalnov, V.I.Klyuchev, Yu. A. Bortsov, B. Sh. Burgin, V. N. Tishchenko, G.G. Sokolovsky, L.B.Masandilov, R.P. Gerasimyak, I.Ya.Braslavsky and others.
Now for the vast majority of erecting crane of bridge type as the electric drive use of the asynchronous electric drive (AED) is rational. In Odnokopylov’s work [3] the mathematical model is developed for research in various operating modes of AED of the mechanism of lifting of the crane. It takes into account the elastic nature of the mechanical parts of the crane, the influence of the electromagnetic brake, the saturation of the induction motor, the presence of a conversion device. Informative parameters of AD are established and developed, characterizing the mass of the cargo on the hook (hanger) of lifting crane to limit its carrying capacity.
In Loveykin V. S. work the dual-mass dynamic settlement scheme "the trolley- load" is made. Results of optimization of transitional modes of movement of the trolley with freight through integrated criteria are analysed. Optimization of modes of movement of the crane cart with freight by means of complex criterion is developed. The structure and the general algorithm of work of system for realization of optimal control by the crane trolley in practice is published [4].
Despite rather deep research of the problem of fluctuations of cargo, some ways that allow to avoid fluctuations, are connected with dynamic loadings that are not desirable. Some ways can't be put into practice. Besides, not all the ways provide full elimination of fluctuations at the end of a way of the trolley or don't eliminate them during movement. The majority of well-known ways of elimination of fluctuations of the cargo doesn't provide desired modes of movement that doesn't allow to use possibility of the span crane.
In this regard, there is a need of definition of optional laws of movement of the crane trolley. Important question is justification of structure and algorithms of work of system which could realize optional control of crane trolley [2].
2. Urgency of an issue
Rocking of cargo is the reason of irregular movement of the crane trolley additional loads of elements of the load-lifting machine. They create inconveniences that threaten the safety of workers, reduce the productivity of loading and unloading transport operations. Fluctuations of the cargo complicate aim guidance of the cargo grasping device and cargo installation on the set place. Especially it refers to the loads with large dimensions [5].
The review of literature issues showed that in studies of the crane mechanisms it is rather in details considered dynamics of their movement throughout transitional modes. Considerable attention is given to a problem of elimination of fluctuations of load. However, most of the proposed methods for solving this problem do not satisfy the requirements of modern processes of load transportation. Thus, operation of the crane cart is obliged to provide high operational efficiency of the crane, and the load on the crane trolley should be minimal [6].
Taking into account all these moments the problem of elimination of fluctuations of freight that suspended on a flexible rope is rather actual.
3. Purpose and the subject matter of the thesis
The purpose of the thesis is elimination of fluctuations of load at the expense of formation formations of optional transitional modes of movement of the crane trolley and system development which will provide desirable operating impact on the lifting mechanism.
To achieve this goal it is necessary to solve the following problems:
- to make the analysis of existing researches that deal with the elimination of fluctuations of load;
- to define laws of traffic control of the mechanism of lifting in which fluctuations are eliminated;
- to develop a system of carrying out experiments and to investigate the main characteristics of movement of model of the trolley with the load suspended on it;
- to offer the functioning scheme of traffic control of the mechanism of lifting, on the basis of the conducted researches;
- to show the positive aspects of using the control system of the four wheel drive mechanism.
4. Mathematical model of the trolley with a load
For the research of the movement of the load-lifting mechanism was made the three-mass dynamic scheme (fig. 1).
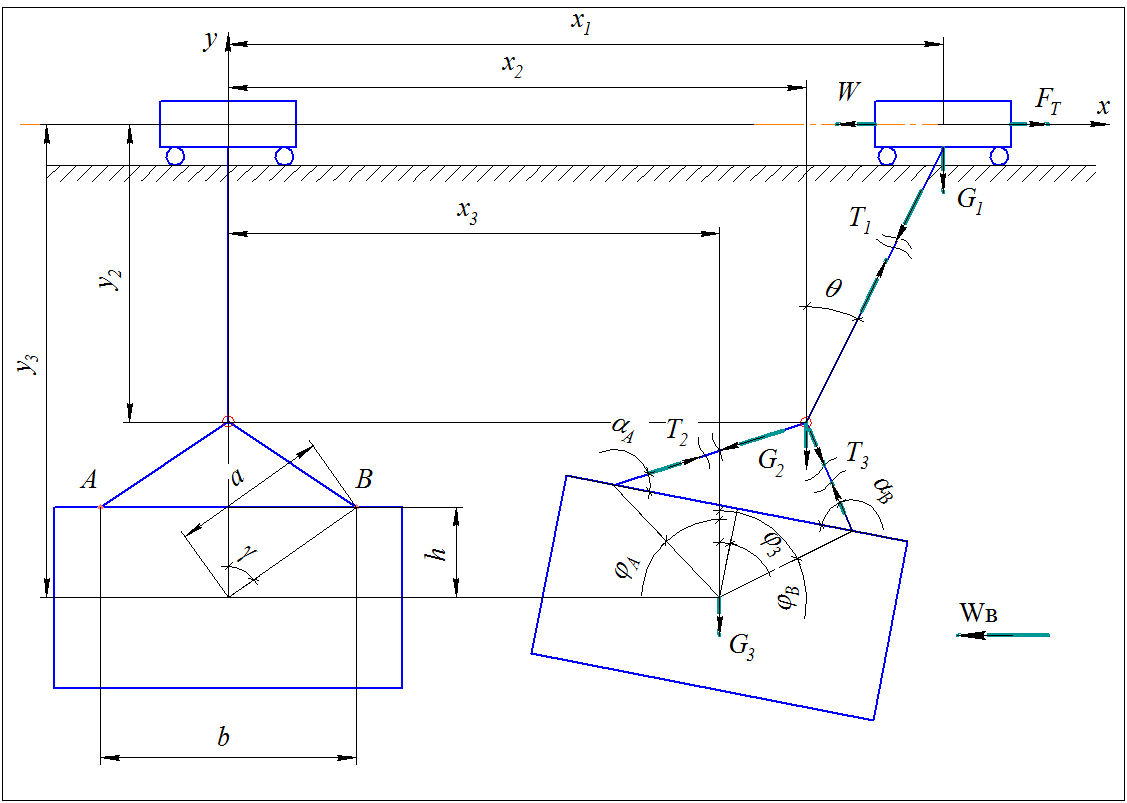
Figure 1 - Rated dynamic scheme of movement of the load-lifting mechanism
Figure 1: m1 – the mass of the jack-lift; FТ – gross tractive effort; W – resisting force to trolley movement; T1 – tension force of the rope; T2, T3 – tension forces of strops; G1 – the terrestrial gravity of jack-lift; G2 – hook terrestrial gravity; G3 – load terrestrial gravity ; φ3 – turning angle of the load; αА, αВ – the angle between the load and the strop; θ – deviation angle from the initial position of the rope; h - vertical distance between the center of the terrestrial gravity of the load and a fixing place of the strop; b – space in between the fixing places of strops; a - the distance between the center of terrestrial gravity of the load and the fixing places of strops;
Using the equations of motion of a solid body [7], the system of the differential equations is made:
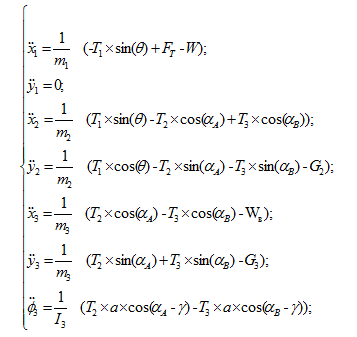
5. Laws of control of the movement mechanism
For carrying out optimization of transitional modes of movement of the jack-lift have been used the laws of management of mechanism for moving the trolley.
All the laws that were used in the whole or partially eliminate fluctuations of the load and dynamic loading of the mechanism of the drive of the trolley and the crane metalwork that provides smoothness of movement of movement mechanisms.
The most effective law of speed control of movement of the trolley on transitional areas of movement is trapezoidal tachogram of the trolley movements with optimized stop area. For this law of the equation of movement of the trolley on the stop area is set by the interpolated polynomial with the knots which have been evenly located on the piece of tо.
The condition of a significant reduction in rocking of load after a stop of the trolley is optimization of values of relative speeds (interpolation knots) (V1/V... V6/V) on the stop area. Selection of values of relative speeds demands the account of such quantities as the mass of the load, length of the rope and the time of the stop. For trapezoidal tachogram of the trolley movement with the optimized stop area at tо = 3,85 с, m3 = 5000 kg, l10 = 6 m by the alternating-variable descent method, the rational modal values of relative speeds V1/V = 1, V2/V = 0,58, V3/V = 0,48, V4/V = 0,28, V5/V = 0,38, V6/V = 0 were received, at that the maximum deviation of the cargo from a vertical after a stop of the trolley movement is 0,008 m which is considerably less than for other tachogram.
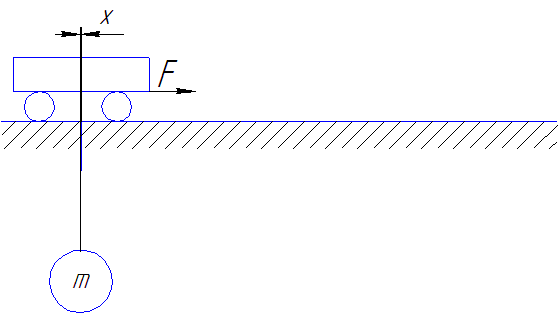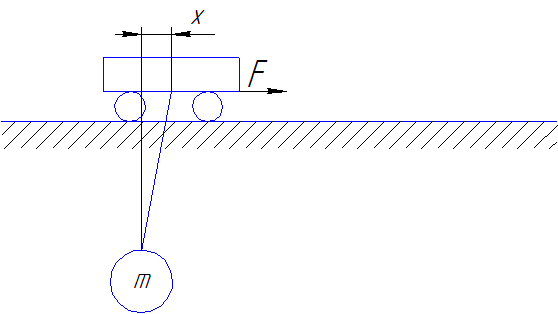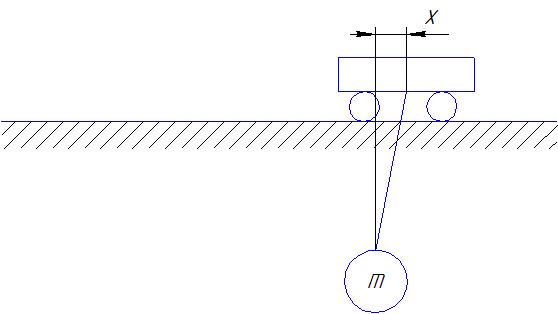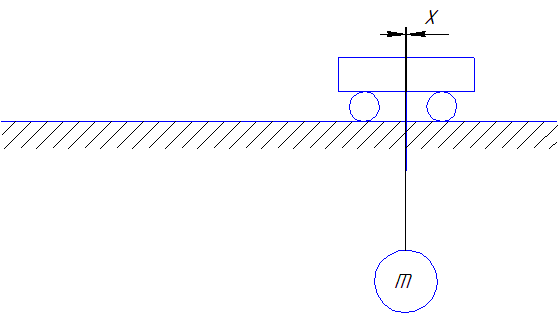
Figure 2 - The scheme of the trolley with a load in the application of the control law Keystone tachogram moving trolley optimized stop portion
(done in mp_gif_animator, 8 frames, 6 reps, delay between frames 0,45 sec.)
Conclusions
- In the thesis the mathematical model of movement of the trolley with the load is developed and realized in Mathcad system;
- The laws of movement of the trolley are received, they in the whole or partially eliminate cargo fluctuations that provides smoothness of movement of movement mechanisms;
- The mathematical model is developed on the point of the rational law of a speed control of movement of the trolley of the bridge crane on the stop area that almost excluding residual fluctuation of the load. For tо = 3,85 s, m3= 5000 kg, L1= 6 m, Vдл=0,8 m/s the maximum deviation of load from a vertical after the stop of the trolley is 0,008 m that is much less, than for others tachograms with similar parameters.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2013. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Абрамович И.И., Березин В.Н., Яуреи А.Г. Грузоподъемные краны промышленных предприятий. – М.: Машиностроение, 1989. – 360 с.
- Дорофеев А. А. Разработка и исследование систем электроприводов, обеспечивающих бесперекосное движение мостовых кранов : Диссертация ... кандидата технических наук. – Липецк, 2010. – 231 с.
- Однокопылов И. Г. Асинхронный электропривод механизма подъема крана мостового типа с повышенной безопасностью и живучестью : Диссертация ... кандидата технических наук. – Томск, 2008. – 162 c.
- Ловейкин В. С. Оптимизация переходных режимов движения механизма передвижения тележки грузоподъемных машин/ Ловейкин В. С. , Ярошенко В.Ф. // Весник Харьковского национального технического университета сельского хазяйства шимени Петра Василенка. – 2007 – 460 с.
- Бортяков Д.Е., Орлов А.Н. Специальные грузоподъемные машины.СПб.: Изд-во Политехн. ун-та, 2005. 64 с
- Александров Н.П., Колобов Л.Н., Лобов Н.А. и др. Грузоподъемные машины. М.: Машиностроение, 1986г. -400с.
- Яблонский А. А. Курс теоретической механики. Часть II. Динамика. – Москва «Высшая школа», 1984. – 411 с.
- Очков В.Ф. Mathcad 14 для студентов и инженеров. С.-Пб.: БХВ-Петербург, 2007.
- ГОСТ 1451-77 Краны грузоподъёмные. Нагрузка ветровая. Нормы и метод определения.
- Крановое электрооборудование: Справочник / Ю.В. Алексеев, А.П. Богословский. - М.: Энергия, 1979г.
