Abstract
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the research, the expected results
- 3. Overview of Research and Development
- 3.1 Overview of international sources
- 3.2 Overview of research on the topic in Ukraine
- 3.3 Overview of research on the topic in the Donetsk National Technical University
- 4. Object of study
- 5. Object of explorer
- 6. The idea of work
- 7. The first section
- 8. The method of research - Markov Processes
- 9. Planned result
- 10. Novelty
- Conclusion
- List of sources
Introduction
To date, relevant issue is the problem of coal mining in the mines of Ukraine[7]. Coal mining is complicated by factors such as a large depth of development, a high level of rock pressure, lamination of the array, fracturing, water abundance, high gas-bearing formations. The most problematic factor when developing reservoir is low-amplitude disturbance. The difficulty is that to conduct clean-up violations with small amplitude is almost impossible to detect. The distances between the exploratory wells in the hundreds of meters therefore catch violation amplitude of 0.3-1.5 m is almost impossible. In this regard, use of a range of geophysical methods that produce immediate exploration of small-amplitude disturbances. However, they require a significant investment for the purchase of special equipment. The complexity of processing the intermediate data during the work is significant. Besides restore parameters violations and their origin is a task that does not have a unique solution. In addition, the reliability of the exploration is usually not more than 80%.
1. Relevance of the topic
In this regard, it is appropriate to develop new, less labor-intensive and available methods for solving this problem. Effective is the attraction of artificial intelligence methods for the calculation and prediction of low-amplitude disturbance in the array.
2. The purpose and objectives of the research, the expected results
The purpose of the work: to improve the existing technique of the forecast of low-amplitude disturbance. A new approach for the calculation of areas, the emergence of small-amplitude disturbances.
To achieve this goal, the following research objectives:
- Collect the necessary data on actual violations.
- Analyze them.
- Justify and choose a model for the implementation of the forecast.
- Prepare input for stochastic simulation.
- A stochastic simulation of small-amplitude alternating locations violations.
3. Overview of Research and Development
3.1 Overview of international sources
Now the problem is solved forecast malomapplitudnoy disturbance with the aid of a number of geophysical methods [4,5]
3.2 Overview of research on the topic in Ukraine
In Ukraine, the research prediction of small-amplitude disturbances occurring in the rock mass, is engaged in Research and Development Institute of the NAS UkrNIMI
3.3 Overview of research on the topic in the Donetsk National Technical University
Department of Surveying at the Donetsk National Technical University is one of the leading scientific organizations, one of the objects of research in the department is the prognosis of low-amplitude disturbance. This problem has been d.t.t prof. Nazimko VV.
4. Object of study
The process of formation of violations.
5. Object of explorer
Parameters of small-amplitude disturbances (amplitude violations, azimuth, angle of incidence, the distance between violations by vyrobotka).
6. The idea of work
Develop a methodology that will significantly increase the reliability of the forecast of low-amplitude irregularities, and at the same time reduce the cost of the forecast at times.
7. The first section
The first section of my master's work is devoted to the review of existing literature for the analytical review of research on the prediction of low-amplitude disturbance.
- Reliable prediction of violations amplitude ranges from 0.25 to 0.5, violations are not uniform, and their prognosis is almost impossible.
- Use of a range of geophysical methods that produce immediate exploration of small-amplitude disturbances. However, they require a significant investment for the purchase of special equipment. The complexity of processing the intermediate data during the work is significant. Besides restore settings violations and their origin is a task that does not have a unique solution. In addition, the reliability of the exploration is usually not more than 80%.
- Observing the nature of any failures can be tentatively concluded that the interleaved parameter of any failures along the line 5 konveykrnogo southern drift can be represented by a simple information model. Alternated neighboring low-amplitude disturbances can be represented as streams of events that do not occur in a period of time, in this regard, it was decided to use as a method to study Markov processes.
8. The method of research - Markov Processes
Markov process - this is a random process of evolution which, after any given value of the parameter time t is independent of evolution, preceded t, provided that the value of the process at this point is fixed. Due to the relative simplicity and clarity of mathematical apparatus, high reliability and accuracy of the solutions obtained sufficient popularity of Markov processes have received from the experts involved in operations research and the theory of optimal decision making.
Consider a model of which at any given time can be described by one of the N states, where ease of N = 5.
After a certain period of time the model may change state or remain in the same state according to the probabilities specified for these conditions. Times when we record the state of the model, denoted by t = 1,2, and the state at time t is denoted qt. Full description of the model should contain the current state (at time t) and the sequence of all previous states through which the system has passed. In some cases, the description of the model is reduced to the direction of the current and previous state, that is,
In addition, we also believe that the processes occurring in the system are independent of time, as we are told by the right-hand side of (1). Thus, the system can be described as the set of probabilities as aij
where aij - the probability of transition from state Si to state Sj at this time. Since these probabilities are characterized by a random process, they have the usual properties, ie,
Σ j=1aij = 1
Described by a random process can be called open-Markov model, because the output models - a sequence of states, recorded in time. Each state corresponds to a particular (observed) event. In our case, the role of time in the coordinate along the line along which record the violations. And in fact acts as an event of the specific distance between the adjacent small-amplitude disturbances.
Figure 1 shows a plan of mine workings. On this fragment can be clearly seen, as can often occur in an array of low-amplitude violation.
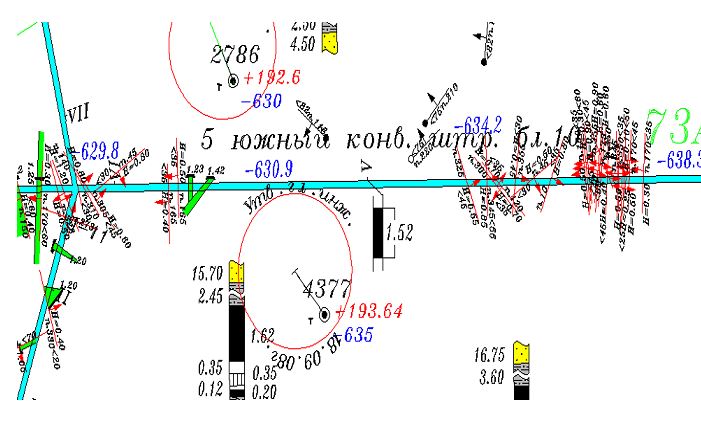
Fig. 1 Detail Plan mining M 1:5000
Distances between disorders from 70 to 500 meters, the amplitude of 0.25 to 0.5 meters. angle varies in the range from 35 ° to 50 °. shows that violations are unevenly distributed, so anticipate their location and parameters is very difficult. [1.2] Watching the occurrence of violations of nature can make a preliminary conclusion that the parameters chereduemye occurrence of violations along the line 5 konveykrnoho south roadway may be represented by a simple information model. Chereduemye neighboring small-amplitude disturbances can be represented as streams of events that do not occur at one time.
To construct a heuristic model was made stochastic simulations were calculated transition matrix of distances. TABLE 1.
| Distance | 0-68,75 | 68,75-137,50 | 137,50-206,25 | 206,25-275 | 275-343,75 | 343,75-412,50 | 412,50-481,25 | |
| State of transition | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | Summ |
| 1 | 0,71782182 | 0,118811881 | 0,059405941 | 0,059405941 | 0,024752475 | 0,01980198 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 0,583333333 | 0,166666667 | 0,027777778 | 0,027777778 | 0,027777778 | 0,083333333 | 0,083333333 | 1 |
| 3 | 0,818181818 | 0,045454545 | 0,068181818 | 0,068181818 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 0,578947368 | 0,105263158 | 0,157894737 | 0,157894737 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 0,666666667 | 0,166666667 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0,166666667 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 0,555555556 | 0,333333333 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0,111111111 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
TABLE 1. The matrix of transition states
Using the transition matrix, and probability theory, calculations of transitions from one state to another, the result is clearly visible in the graph shown in Figure 2
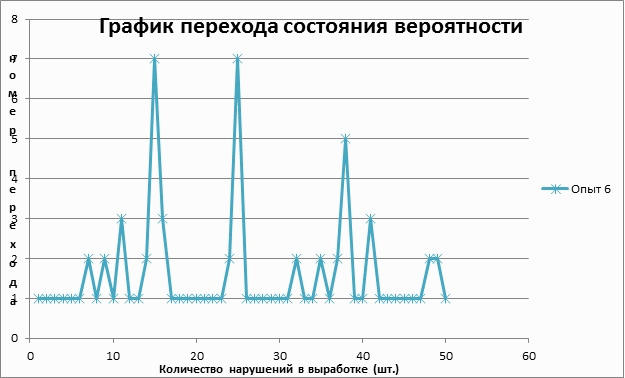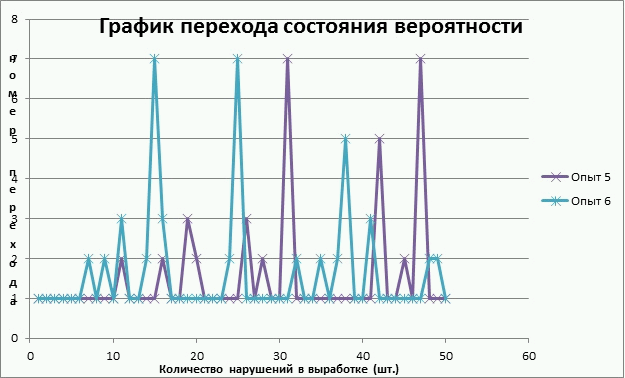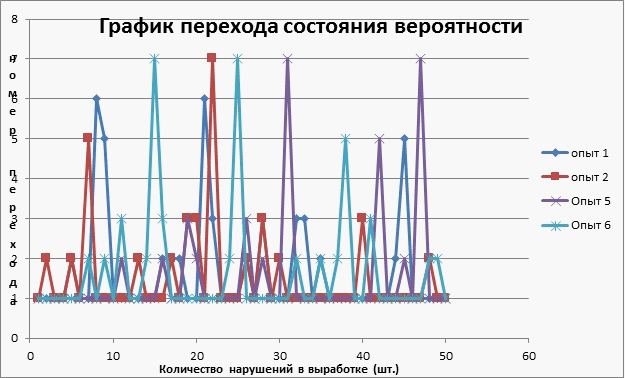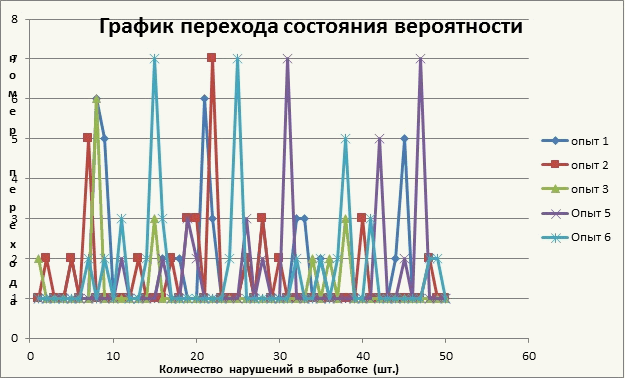
Fig. 2 Schedule of the state transition probabilities (5 frames, 5 loops,202 kb)
9. Planned result
- Get the forecast methodology violations along the route of the future generation.
- Analysis and summary of the results.
10. Novelty
The developed method is based on the distance between the low-amplitude disturbances whose amplitude varies from 0.3 to 1.5 m, the distance between them from 70 - 400 m Therefore, it is a random variable and not against the law exponentially distribution. The conclusion is made based on the results of the data processing program STATISTIKA (Figure 3). The program is designed for a modern statistical package, which implements all the latest computer and mathematical methods of data analysis. The program is designed for all industries (business, science, education).
It supports all the functions for statistical processing of data plus this: the possibility of charting, data bases, etc. In the program STATISTICA Visual Basic which adds about 10,000 new functions. The syntax for this is fully compatible with the Basic with Microsoft Visual Basic.Versiya English.
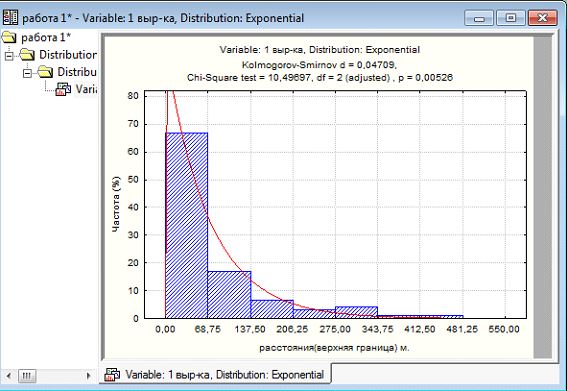
Fig.3 Results data processing program STATISTIKA
Conclusion
In his master work the actual challenge of low-amplitude disturbance prediction method, using artificial intelligence techniques.
Further research is a preliminary study and study analysis techniques uncovered actually set the parameters of small-amplitude disturbances.
When it abstract had been writing the masters work is not finished. Date of finish december 2013. From the original master robots will be available at the supervisor Nazimko V.V.
List of sources
- Tikhonov VI, Mironov MA
Markov Processes
– M, 1977 - Nazimko VV, AV Merzlikin Experience in application of neural networks and genetic algorithms for the prediction of small-amplitude disturbances Proceedings of the Donetsk State Technical University. Series: Mining and Geology. – 2002. – ¹ 54. – C. 177 – 183.
- Nazimko Vladimir Zakharov, VS , Merzlikin AV Weather melkoamplitudnyh faults coal seams using neural networks and genetic algorithms Geotechnology at the turn of the 21st century., V.2. – Donetsk.: Donetsk National Technical University, 2001. – S. 30-32
- Tectonics: Recent Advances by Evgenii Sharkov (ed.) – InTech , 2012 This book is devoted to different aspects of modern geodynamic processes. The text covers up-to-date materials of detailed geological-geophysical investigations, which can help understand the essence of mechanisms of different tectonic processes. (2950 views)
- Statistical Physics of Fracture, Friction and Earthquake by Hikaru Kawamura, et al. – arXiv , 2011 We review our research regarding the dynamics and the statistical properties of earthquakes, mainly from a statistical physical viewpoint. Emphasis is put both on the physics of friction and fracture, and on the statistical physical modelling. (1964 views)
- EB Dynkin –
The theory of probability and Markov Processes
– M, 1966. - Surveying: Proc. for high schools. - In two parts / Ed. IN Ushakov. - 3rd ed., Rev. and add. - Nedra, Moscow, 1989. - Part 2/A.N. Belolikov, VN Zemisev GA Moles, etc. - 437 s.
