Summary on the theme of master's work
Content
Goals and objectives of master's work
Purpose of master's work – the development of potential measures to improve the safety of the people spread area of fire gases in fires in inclined workings with upward ventilation, developed through the use of a virtual model of mine ventilation network of the mine to them. Kalinin.
To achieve this goal it is necessary to solve the following problems: to analyze the ventilation circuit, air distribution, to develop a computer model of the mine using the «IRS Ventilation – PLA», to assess the stability of ventilation at fires in inclined workings of the mine, and develop measures to improve the sustainability of ventilation; explore the area spread of fire gases from fires in inclined workings and explore the exit routes of miners from the area gassing.
1. Relevance of topic
Analysis of coal mine accidents shows that the underground fires are one of the most common types of accidents. Fires in inclined workings are characterized by the rapid spread of flame, and fire them due to the much greater difficulties, than other workings.
The simplest and most effective way to increase the stability of the network airing in case of fire in the development of the ascending movement of the air is closing fire doors in front of the hearth fire, that not only increases the stability of ventilation, but at the same time reduces the intensity of a fire. Therefore, the appropriate emergency response plans include closing fire doors following the fire, and in those cases, when you do not want to increase the resilience of ventilation. However, if a fire broke out in a branch without a fire door, closing fire doors (for example, at the top or bottom of the slope) may violate the (worsening) the stability of other ventilation openings [1].
The action of heat in the development of depression fire with upward ventilation same direction as the main fan depression. As a result, the air flow in other mines (usually in a nearby fire branch) can change direction (tip). Rollover air flow leads to an expansion zone zagazirovaniya, poses a threat to the appearance of fire gases on evacuation routes, which can lead to more victims [2]. Therefore, place rollover vent stream you need to know in advance and to provide for measures to ensure the stability of the ventilation openings, and such a calculation is possible only by using specialized software.
Thus, the urgent task is to develop possible measures to improve the sustainability of mining ventilation at fires in inclined workings with upward ventilation, developed through the use of virtual model of the mine ventilation network of the mine to them. Kalinin.
2. Probable scientific novelty
First assess the stability of mine workings ventilation at fires in inclined workings with upward ventilation, using a computer model of the mine ventilation network of the mine to them. Kalinin.
Technology problem solving mine ventilation with complex software «IRS Ventilation – PLA», is defined by a sequence of actions, including the stage of preparing the initial information. At this early stage, it is necessary to prepare a scheme of ventilation shafts before putting it into the computer. The peculiarity of this training is to apply the scheme of ventilation in the form of a sequence (network) connected between each other, branches. Each node of the network links between them, two or more output (branches), or part of production, as a rule, the coding schemes of ventilation is carried out in preparing the mine to the depression survey. In this case each node and branches in the diagram is assigned a certain number (Fig. 1).
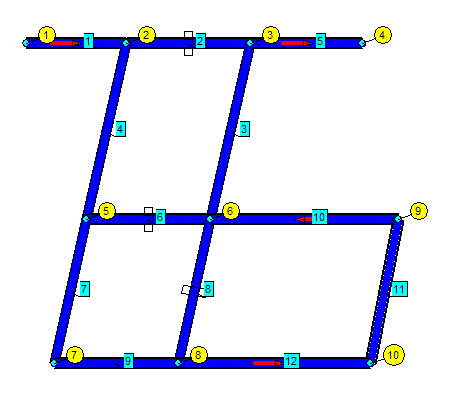
Figure 1 – Simplified diagram of the field gradient
(1 – vozduhopodayuschy drift; 2 – upper sboyka ; 3 – walker; 4 – bias)
Stability of air flow in mines is estimated at a fire after the introduction of the production ramp source of thrust, simulating the thermal depression fire. Destabilization of ventilation in case of fire is possible in those mines, where, after the introduction of the thermal depression stop or change the direction of air flow.
This numbering allows the identification of all the production of the mine, or portions thereof, and to determine the actual direction of movement of air in them. In preparing the scheme of ventilation shafts, to represent it in electronic form, is unacceptable to simplify it. Under the simplification means joining a ventilation network nodes to one or the schematic representation of ventilation, the series connection of several workings of one branch (Fig. 2).
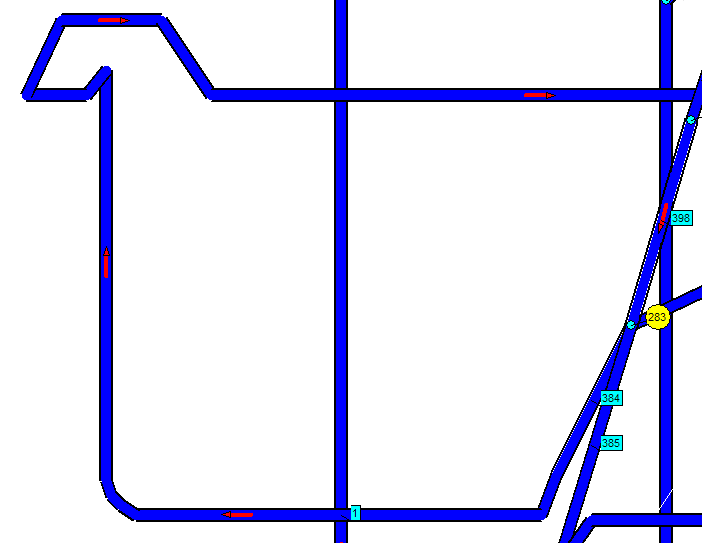
Figure 2 – Simplified diagram of the external leakage paths and installation of fan
The need for such a detailed representation of the ventilation circuit in the computer due to the fact, that the openings in the series may be areas with different angles of inclination and the geometric parameters, that form the different conditions of the fire and movement of people. In simplifying the ventilation schemes are possible errors in construction zones spread of fire gases and modeling of heat sources traction.
Using the model it is possible to solve the problem of ventilation when the air flows in the main ventilation facilities will differ from the actual no more than 10% [3].
The need for such a detailed representation of the scheme of ventilation in the computer due to the fact that the series connection of workings may be areas with different angles and geometrical parameters, which form a variety of conditions for the development of fire and movement of people. In simplifying the ventilation circuit, when several nodes, which are places of conjugation (connection) mining, are replaced by one (contract), are also possible errors in the construction of the zone of fire gases, the best routes of movement of persons and modeling effects of heat sources traction (natural draft, the thermal depression is a fire).
To ensure the sustainability of ventilation must be installed to control the resistance of the branch 1.0 kMyurg 254 (auxiliary field gradient formation h7 ) and a branch 287 (native western airway reservoir h7). After installing the control reversal does not occur (Fig. 5).
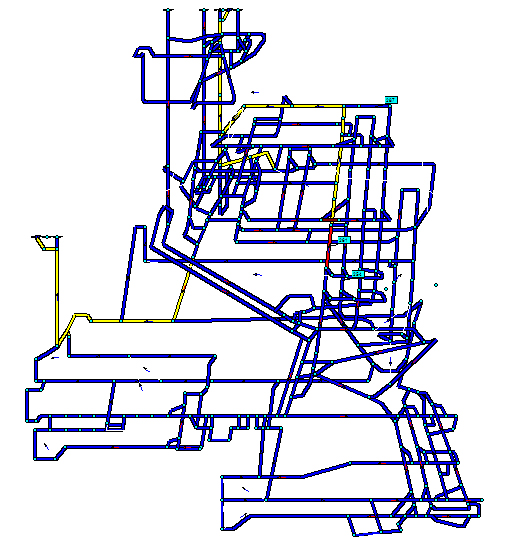
Fig. 5 – Area gassing after amplification ventilation
In Fig. 6 demonstrated the situation of a fire in a model of the Kalinin mine.
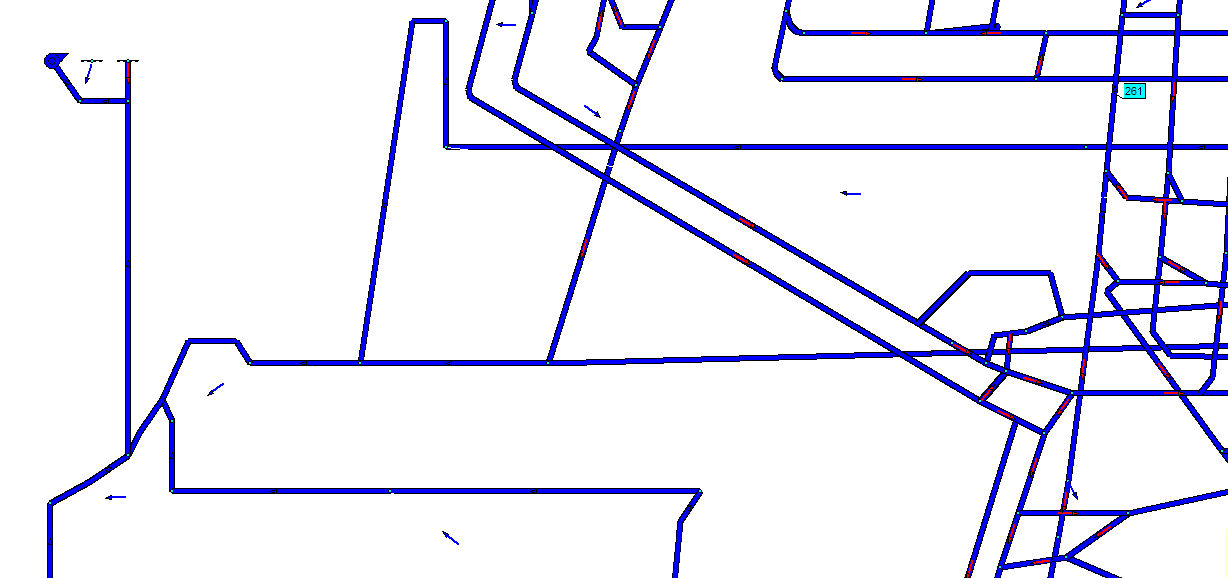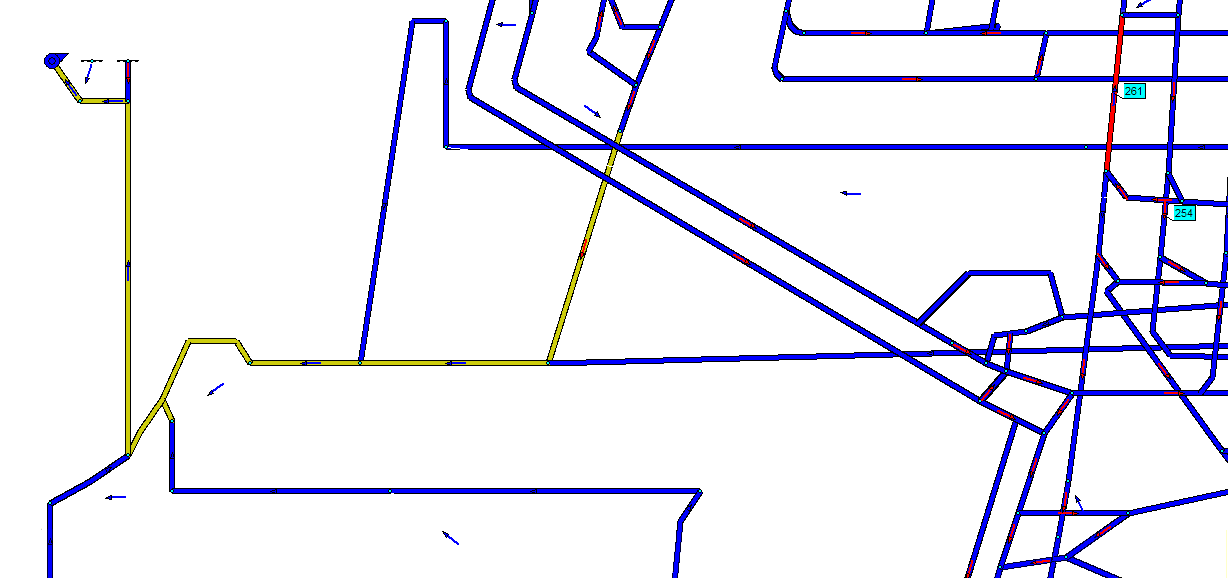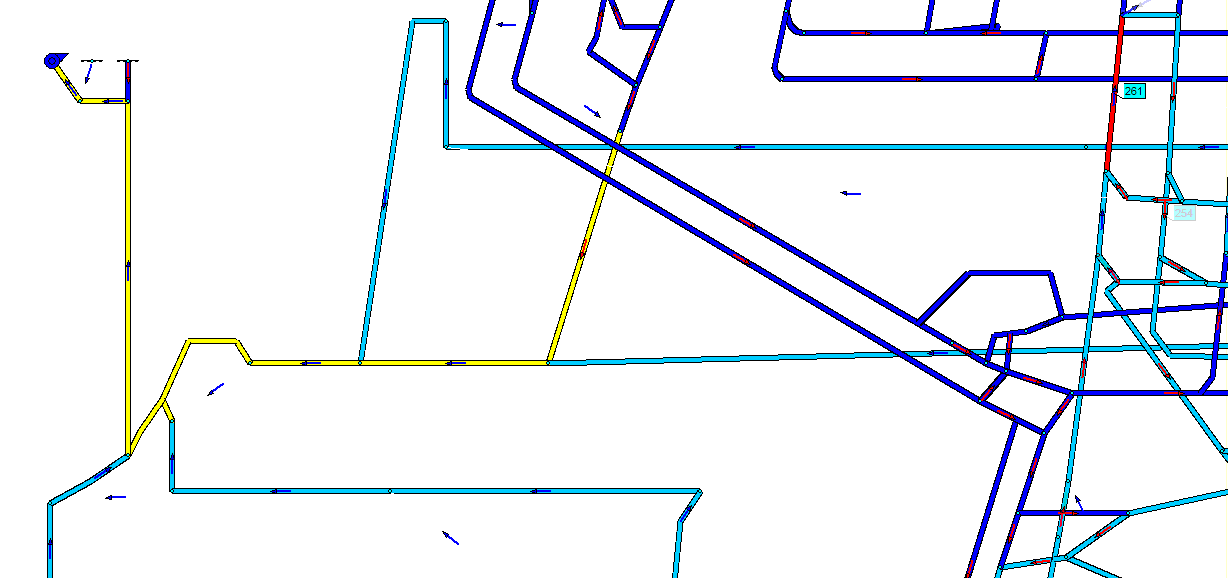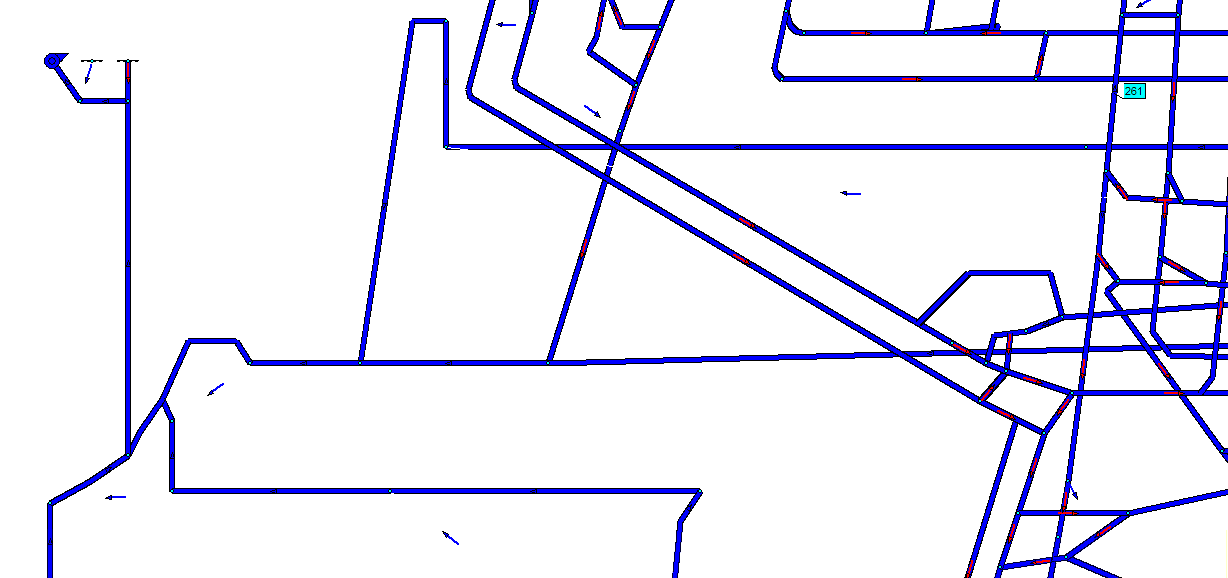
Fig. 6 – Simulation of a fire in a branch № 261 computer model of the mine to them. Kalinin
(Animation: 7 frames, 5 cycles of repetition, 102 kilobytes)
(Blue color – its original state, yellow color – zone spread of fire gases to rollover air flow, the color
blue – zone of fire gases spread after breaking air flow, the color red – branch in which there is a fire)
Conclusion
In the course of the master's work, in a review of the scheme of ventilation, air distribution, developed a computer model of the mine with the help of the program «IRS Ventilation – PLA». Ensuring the sustainability of mining ventilation at fires in inclined workings, reduces gassing zone, which eliminates the possibility of fire gases escape route people and reduces the number of mines caught in the zone gassing , reducing the probability of getting people in this area.
References
- Трофимов В.А., Кавера А.Л., Калинич Н.М., Негрей А.Г. Влияние увеличения сопротивления наклонной выработки на устойчивость ее проветривания при пожаре ⁄⁄ Материалы Международной научно-практической конференции «Промышленная безопасность и вентиляция подземных сооружений в XXI столетии» – Донецьк. – 2012. – С. 16-18.
- Болбат И.Е., Лебедев В.И., Трофимов В.А. Аварийные вентиляционные режимы в угольных шахтах. – М.: Недра, 1992. – 206 с.
- Булгаков Ю.Ф., Трофимов В.О., Кавєра О.Л., Харьковий М.В. Аерологія шахтних вентиляційних мереж – Донецьк, ДонНТУ. – 2009. – 88 с.
- Руководство по проектированию вентиляции угольных шахт – Киев. – 1994.
- Правила безопасности в угольных шахтах. – К.– 2010. – 422 с.
- Рекомендації по вибору ефективних режимів провітрювання шахт при аваріях ⁄⁄ НДИІД. – Донецьк. – 1995. – 165 с.
- Каледіна І.О., Романченко С.Б., Трофимов В.О. Комп’ютерне моделювання шахтних вентиляційних мереж: Методичні вказівки. – М.: Видавництво МГГУ. – 2004. – 72 с.
- Каледіна І.О., Романченко С.Б., Трофімов В.О., Горбатов В.А. Комп’ютерне моделювання задач протиаварійного захисту шахт: Методичні вказівки. – М.: Видавництво МДГУ. 2004. – Частина 1. – 45 с.
- Борзых А.Ф. Содержание, ремонт и ликвидация выработок угольных шахт – Алчевск: ДонГТУ, 2004. – 614 с.
