Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the system
- 3. The mathematical formulation
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Currently, the major cities of Ukraine have the problem of traffic management, especially in their central parts. This is associated with increased levels of motorization and the presence of a constant historical road network of the city, as well as the availability of parking on the roadway. All this leads to a decrease in the level of safety of vehicles and the capacity of the road network, which cause traffic jam.
Radically improve traffic conditions in the city, in the long term , can be achieved with the implementation of measures of urban nature : the construction of bridges , tunnels, punching new highways . Implementation of such projects requires significant financial investment and time-consuming. The analysis shows that significantly mitigate the situation will allow a set of activities related to the improvement of traffic management in the city , the introduction of computerized automatic control systems of traffic on the road network of cities.
Traffic safety and efficiency of management traffic and pedestrian flow is largely determined by the quality of traffic management, reliability and fault tolerance of software and hardware traffic management systems . Therefore, the development of the principles of traffic management and traffic management systems , the need to use modern communication technologies and management , development management principles is highly topical issue at the moment.
1. Theme urgency
Increasing volumes of road transport, increase speed and traffic and the associated increase in the number of road accidents makes new, higher demands for technical perfection of roads, their condition and engineering equipment, transport and operational characteristics and traffic during operation.
Prerequisite creating a system of traffic management on motorways is the formation of strategic concepts, complex managed object models and algorithms are based on information processing and decision-making control.
2. The purpose and objectives of the system
The purpose of the master's work is to create a "green wave" control system in real time, allowing automate the management of the traffic flow on highways and to improve the capacity and safety.
The main objectives of the system:
- systematic data collection on the state of road traffic on the specified areas of the city;
- ensure the integrity of all data to the server;
- improve traffic flow by controlling the "green wave" on the main streets in real time.
3. The mathematical formulation
Control objects in these systems are the traffic flow at highway and traffic flows at the entrances and exits. Controls are traffic lights at intersections, entrances and exits.
In order to achieve effective traffic management is considered to develop a computer system that allows real-time based on input received will be determined by rational values of the speed of the traffic flow and the duration of the operation of traffic lights.
The system provides the following basic functions:
- collection of data on traffic flow at each registration point;
- data processing and storage business;
- calculation of the recommended values of motion parameters and transfer them to regulate the flow.
Each of these functions performs certain actions.
Collecting data on the transport stream will include:
- measurement of flow rate, i.e. count the number of vehicles per unit time of passing by the recording of the object;
- determination of the number of vehicles that are stuck at traffic lights during the period of burning red light.
Data will be collected in all areas considered intersection in the both sides. Static data will be the distance between intersections, most line parameters ( number of lanes , speed limits , etc.). All information can be collected using "smart" traffic signals [3], which are already used in major cities around the world. "Smart" traffic lights have built-in sensors collect information , which communicate with the server through the GSM-modem. Traffic can also be equipped with cameras that capture additional information. Many have scoreboard countdown showing how much time is left before the change of status lights. All traffic lights are connected to a single traffic control system , which is in the control of traffic lights . Coordinators can change traffic lights from the control room , as well as view all the data that comes from the sensors.
Using the data processing and storage organization the main parameters that characterize the traffic will be stored and processed.
To implement the calculation of the recommended values of motion parameters using computational methods and modeling techniques. One of the most common methods of organizing traffic in large cities, is the principle of the "green wave", by which a certain main roads of the city is defined by the length of traffic signals so as to provide a " green wave ", i.e. providing non-stop traffic through coordinated inclusion green light at intersections. The principle of the "green wave" is shown in the example of the organization of movement on one-way street. [2] Fig. 1 schematically shows a plan for the left street intersections A, B, C, D, E located at the same distance from each other.
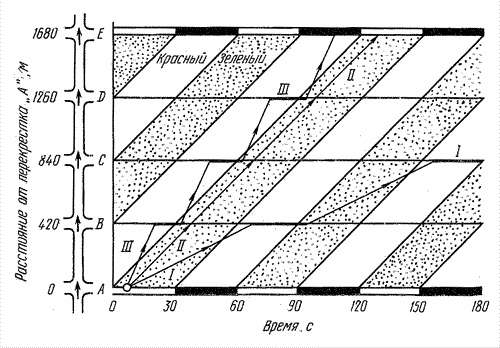
Figure 1 - Graph "green wave" and a diagram of the "way - time" for three cars (for simplicity, the diagram does not show the time yellow signal) (Расстояние от перекрестка = distance from the intersection, Красный = Red, Зеленый = Green, Время = Time)
In the right part of the figure shows a graph in which the horizontal axis represents time and the vertical - the path traveled by the vehicle while driving from the intersection to the intersection A E. Broad shaded bands on the chart - the tape of time during which the vehicle can pass without stopping all crossings, adhering to a certain speed. The velocity is defined as the slope of the belt to the horizontal axis of time. Using this principle in real-time and taking into account the factors affecting the change in the flow characteristics can be improved qualitative characteristics of the traffic flow.
Using the measured values of the characteristics of traffic flow, it will be possible to determine the flux density - the number of cars per unit length of the road (eg, 1 km). [4] Communication between the main characteristics of the flow of vehicles is as follows:
N = VQ,
where N-traffic, Q - flux density, V - the average speed.
If the flux density on the highway will be very large, the calculation should be carried out recommended values of motion parameters.
You need to know how to determine the duration of traffic lights and vehicle speed. [2] Manage traffic light for exposure of the object with respect to one direction of movement, parameters may be:
- Т - total cycle time, s;
- tз - duration of the green signal, s;
- tж - the duration of the yellow signal, s;
- t0,i - i-cycle delay of the traffic in relation to the chosen controller to zero (traffic light), t0,i< Т.
Duration of red signal from the relation
tк = Т - tз - tж,
We assume values of Т, tз and tж same for all traffic signals and highway find meaning Dt0,i - start incorporating green signal of the i-traffic traffic relative to the point 0, providing unimpeded passage cortege cars across highways in the "green wave".
Imagine a one-way highway in the form of a piece, which is divided into separate sections in some known points.
Let L - total length of the backbone, and li - the distance between the adjacent (i +1) and i intersections (i = 0, 1, 2, 3,…, n). For this decomposition
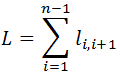
Movement of the head of a vehicle on a highway in the tuple formed at 0, described by the equation
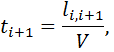
where V - the recommended speed of vehicles, km / h
For the first traffic light object at the point 1, the value t1 l0,1 / V, defines the value Dt0,1 - start incorporating green traffic light signal with respect to the point 0.
In the general case (k +1)-th traffic light (k where k = 1, 2, 3,…, n-1. Thus it is evident that the duration of traffic lights depends on the recommended rate of passage of a vehicle and the road
segment is possible to control both the speed and duration of the signal. To find effective strategies for traffic management in the big city and traffic should be considered a wide range of traffic
characteristics, patterns of influence of external and internal factors on the dynamic characteristics of traffic flow. Currently,
one of the most used methods to solve the problems of the organization and traffic management is the method of simulation, the implementation
of which requires an adequate model of traffic flow, taking into account the complexity of the configuration of transport interchanges, external
influences, and random factors affecting the whole structure of the interaction of moving flows. As a result of the research was the necessity of developing a computerized management system
traffic of the city, its main functions are identified, analyzed the existing methods of calculating rational
traffic flow parameters, principle of the method is a "green wave", destined to use simulation
to find the recommended parameters of motion control based on the complexity of the system configuration of the transport and the impact of the whole
a number of random factors.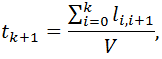
Conclusion
References
