Abstract
- 1. Actuality of theme
- 2. Aim and research problems
- 3. Expected results
- 4. Description of the wave algorithm
- 5. The concept of using a digital algorithm in modeling wave propagation of an impurity
- Conclusions
- References
1. Actuality of theme
Recently the problem of environmental safety began to be felt acutely. The major reason is the growth of industry and transport worldwide. There may be up to a million sources of emissions within the average industrial city. Harmful substances are being released into the air, water, soil, and then in living organisms, including human.
Used models based on numerical or analytical solutions of the diffusion equation To estimate or predict the spread of contaminants in time and space are used the models based on numerical or analytical solutions of the diffusion equation. These models are also known as atmospheric dispersion model, dispersion air model and air quality models.
Predicting the spread of harmful substances is very important challenge for ecologists. There are several methods to assess the spread of pollutants in the atmosphere today: analytical and empirical, numerical and statistical. Their detailed description is given in a source.
To increase the speed of mathematical calculations, as well as a visual representation of the air masses are being used special computer software products based on these models. However, all of them have a number of disadvantages. These disadvantages can be avoided by applying the method of digital wave.
2. Aim and research problems
The purpose of research is to improve the digital method for solving wave propagation impurities in the atmosphere.
The main objectives of the study:
1) to analyze methods for predicting the spread of pollutants in the atmosphere;
2) to analyze software predicting the spread of pollutants in the atmosphere;
3) to develop modifications of the algorithm for the digital wave propagation modeling impurities in the atmosphere.
Object of research: distribution of pollutant substances in the atmosphere.
Subject of research: algorithm for simulating the propagation of impurities using the digital wave.
3. Expected results
As part of the master's work is planned to develop a mathematical model of the spread of harmful impurities, which will simulate the distribution in the surface layers of the atmosphere at the level of the industrial city.
4. Description of the wave algorithm
Wave algorithm — an algorithm to find the shortest path on a planar graph.
This algorithm works on a closed field of arbitrary shape and consists of three stages.
- Initialization. The whole field is split into a multitude of rectangular cells, including two cells — the start and finish. All other cells are divided into two subsets: the subset passable and not passable subset (obstacles) cells.
- Wave propagation. The step is generated from the starting cell in all adjacent cells, unless they do not belong to the subset passable or previously labeled cells. If conditions are fulfilled ,the cell recorded the number of steps (so called the wave front) to it from the start (it is equal to 1 at the initial stage). Each cell is labeled with the number of steps from the homepage itself becomes the starting for a time. Activities are to be repeated as long as any step will be impossible.
- Restoring the shortest path. This step is necessary for finding the shortest direct path between the pair of cells. It occurs in the opposite direction, i.e. from the finish to the start. A cell having an attribute of the distance from the starting one less than the current cell is being selected here at each step.
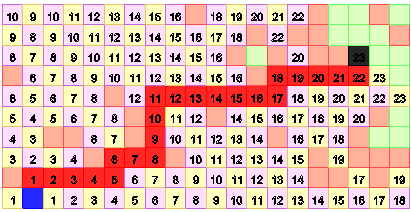
Figure 1 — Visualization wave algorithm
As a result of using this algorithm there are two possible situations:
1) extradition the shortest path;
2) extradition reports of obstruction.
5. The concept of using a digital algorithm in modeling wave propagation of an impurity
The concept of applying the algorithm of the digital wave assumes.
- The presence of a regular lattice with a certain step, the value of which is specified at development model. The geo-referencing should be performed for the specified lattice during the territory of the object under review.
- All cells of the lattice, which are fully or partially overlap the building (or other impassable objects) form a set of impenetrable cells.
- Starting cell is the source of emissions. If the emission source is not a point (e.g, linear or areal), starting cells can be multiple.
- Finish cell in this modification of the algorithm is not used, the process modeling flows endlessly from the start, which corresponds to a real propagation conditions impurities. The modeling process can be suspended, only if the concentration of impurities in all the cells of the lattice do not change for a long time.
- To calculate the wave front for 8 adjacent cells used coefficients that derived from the base of the diffusion equation. These coefficients are partial solutions of turbulent diffusion coefficient. These coefficients depend on the one hand from the current values of meteorological parameters — wind speed and direction, temperature, humidity, pressure etc. On the other hand, the values of these coefficients depend on individual features distributed impurities — molar mass, composition and impurities etc.
Visualization of an operation of this algorithm is following:
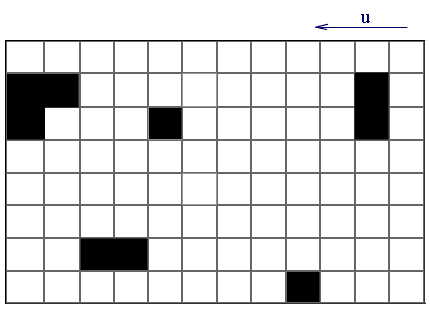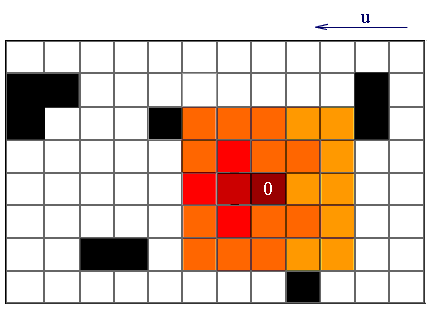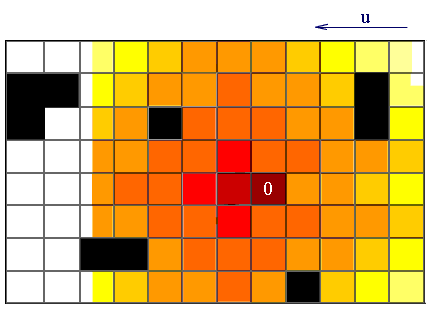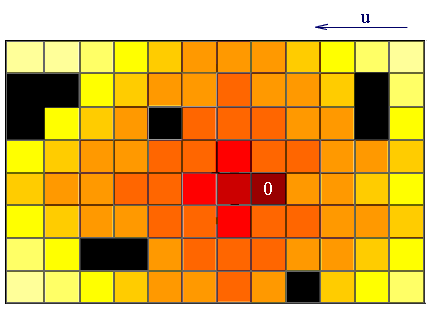
Figure 2 — Visualization of an algorithm for solving wave propagation impurities in the atmosphere
(animation: 30 frames, 6 cycles of repetition, 32.4 KB)
In this example, u — wind direction, black figures — this building, and the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere occurs at 0.
Conclusions
This material can be used as a basis to develop a method of modeling of pollutants atmosphere using a modification of the digital wave. This modeling method can be fundamentally new in terms of the similarity of his behavior compared to the real environment.
References
- Milton Beychok. Air pollution dispersion modeling [Электронный ресурс] / Milton Beychok. – Режим доступа: http://www.eoearth.org/view/article/51...
- Павлий В.А. Построение информационной модели расчета распространения примеси в приземном слое атмосферы над территориально-распределенными объектами [Текст] : научн. журн. / Виталий Александрович Павлий // Наук. праці Донецького Національного технічного університету. – [під ред. Є. О. Башкова]. – Сер.
Системний аналіз та інформаційні технології у науках про природу та суспільство
. – (САІТ-2011). – Вип. 1(133) – Донецьк: ДонНТУ, 2011. – С. 71–81. - Long description of model 'ADMS 5' / Режим доступа: http://pandora.meng.auth.gr...
- Long description of model 'GASTAR' / Режим доступа: http://pandora.meng.auth.gr...
- Long description of model 'NAME' / Режим доступа: http://pandora.meng.auth.gr...
- Long description of model 'AUSTAL2000' / Режим доступа: http://pandora.meng.auth.gr...
- Long description of model 'TCAM' / Режим доступа: http://pandora.meng.auth.gr...
- Long description of model 'GRAL' / Режим доступа: http://pandora.meng.auth.gr...
- Ильина Ю.В. Моделирование процессов распространения вредных примесей в атмосфере [Электронный ресурс] / Ю.В. Ильина – Режим доступа: http://masters.donntu.ru/2012...
- Дейкун О.В. Исследование процессов загрязнения атмосферного воздуха по данным автоматизированных контрольных постов Донецко-Макеевского региона [Электронный ресурс] / О.В. Дейкун – Режим доступа: http://masters.donntu.ru/2009...
- Волновой алгоритм поиска пути / Режим доступа: http://100byte.ru/100btwrks...
