Abstract
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: January 2015. Full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his adviser after that date.
CONTENT
- 1. General characteristics of work
- 1.1. Theam’stopicality
- 1.2. Link with academic programs, plans, themes
- 1.3. Оbject and objectives of the study
- 1.4. Subject and object of study
- 1.5. Actual material
- 1.6. Research methods
- 1.7. Scientific novelty
- 1.8. Practical value
- 1.9. Personal contribution of the author
- 1.10. Testing results of the work
- 2. A review of research on the theme
- 3. Geological characteristics of the object
- 4. Technique of processing of the experimental informations
- 5. Results of research
- 6. Conclusion
- 7. References
1. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF WORK
1.1. Relevance of the topic
In the Donetsk region is the largest in Europe Elenovskoe deposit of carbonate raw materials, which is being developed Dokuchaevsky flux-dolomite combine. Mined raw materials (limestone and dolomite) are mainly used in metallurgical industry. A much smaller portion of the feed consumed by the gas industry (for desulphurization of gas flows) in the sugar industry, in agriculture (soil treatment) and water supply (purification of water for domestic and industrial needs).
Quality is determined by the content of carbonate raw material components such as: CaO, MgO, SiO2, Al2O3+Fe2O3, S, P. Karst development in the fields of raw materials and reduces the impact on its quality. For a given area of research relevant issue is not confirmed reserves due to the difficulty of estimating the volume and nature of the manifestations of karst processes on the areas of exploration work. On the other hand, the chemical composition of carbonate rocks largely determines the development of karst.
1.2. Link with academic programs, plans, themes
Problems of maintenance of metallurgical enterprises flux raw materials identified in the relevant legal documents geological industry, particularly in the national program for the development of the mineral resource base in Ukraine to 2030 program of development of mineral resources base of Donetsk region until 2020. These issues were repeatedly raised in the scientific literature, which addressed the problem of prospective evaluation of non-metallic raw materials for the steel industry.
1.3. Оbject and objectives of the study
The purpose of the study is to determine the factors of quality changes of carbonate resources for area development Dokuchaevsk’s flux-dolomite combine.
Research objectives:
- To examine the requirements for grade composition fluxing limestone and dolomite gray smelting.
- To analyze the changes in the chemical composition of carbonate rocks on the individual sub-horizon at one site Elenovskogo field.
- An analysis of karst rocks on the site and find out geological factors of karst development that affect the quality of carbonate materials.
- Develop practical recommendations for future mining southern Elenovskogo field.
1.4. Subject and object of study
Object of research on the area of land-development Dokuchaevsk’s flux-dolomite combine. Subject of research - geological factors of quality changes of carbonate resources for subhorizon: CIta2, CItb1, CItb2, CItс .
1.5. Actual material
Material presented data from 66 operational exploration wells Elenovskogo fluxing limestone deposits Donetsk region. The sample data includes the data of chemical analysis of samples of section 1427.
1.6. Research methods
Research methods, such as
- Analysis of graphic material to elucidate the structural features of the object (geological map of the area, cuts, etc.);
- Construct specialized maps of the distribution of quality of carbonate resources;
- Statistical analysis of geochemical data;
- Spatial analysis of the distribution of quality raw materials;
- Analysis of karst rocks;
- Calculations indicators karst rocks.
1.7. Scientific novelty
- The change in quality indicators of carbonate raw materials, depending on the characteristics of the petrographic composition of the rocks of individual horizons.
- Karst development in a given area affects the quality of carbonate materials.
1.8. Practical value
Established patterns of change in the space of quality indicators can improve the efficiency of processing Elenovskogo field.
1.9. Personal contribution of the author
Statistical processing of data and interpretation of results. The character of changes in the chemical composition of carbonate rocks. The maps of the spatial distribution of karst some subhorizon.The peculiarities of the influence of the chemical composition of rocks and rupture dislocations on the development of karst.
1.10. Testing results of the work
According to the results of work done at the VII International report scientific conference DONBASS 2020: DEVELOPMENT PROSPECTS eyes of young scientists.
2. A REVIEW OF RESEARCH ON THE THEME
Analyzed the literature and archival materials on the topic of carbonate raw materials in Ukraine and abroad. Particular attention was paid to the Lower Carboniferous deposits of limestone junction zone Azov mega block Ukrainian shield and folded Donbass. In Ukraine, the study of the Lower Carboniferous deposits of Donbass conducted near geologists since the mid-XIX century.
AP Rota in 1928 - 1929 years.produced by geological mapping of the South-western part of the Donbass, which resulted in the adoption of a new indexing stratigraphic zones[9]. In 1947-1951 the. Ukrgeoltrestom MCM made instrumental scale 1:100000 geological survey in order to clarify the future direction of geological prospecting work capacity balance reserves of flux limestones and dolomite[10] The study of geological and tectonic features of occurrence of carbonate raw materials at the junction of Azov mega block Ukrainian shield and folded Donbass A scientist engaged . I. Nedoshovenko. In his article On the method of exploration of carbonate resources southwestern part of the Donbass
, published in 1977, highlighted the issue of karst study area and the imperfection of the geological exploration of similar sites. In the scientific article SA Machulina and MV Bezuglov On the discovery of large formations stalaktitosimilar pyrite in the limestones of the Lower Carboniferous Stylskogo quarry southwestern part of the Donbass
(2004) indicated the causes of sulphide sulfur in the limestone caverns Tournaisian age[11].
3. GEOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE OBJECT
Area of work includes Elenovskoe deposit fluxing limestone and dolomite is located in the southwestern part of the Donets Basin. Timed to coincide with the band Lower Carboniferous outcrops, stretching from east to west, from p. Razdolnoe through with. Chilled, city Dokuchaievsk with. Novotroitskoe up with.Ol'ginka. The plot is a strata of limestone and TournaisianVisean Lower Carboniferous occurring relatively quiet. From the north-west and south-east portion of the effluent is limited to violations of nature. Hence, the area forms a kind of horst, substandard limited thickness of limestone and marl age C1vd, C1ve, C1vf. As established by many years of experience of exploration and exploitation works in the fields of carbonate materials in the southwestern part of the Donbass, karst rocks and strata in substandard thicker mineral quite irregularly distributed and can not be geometrize in space. This position is in the same measure to the specific and varietal composition of carbonate raw materials, regulated condition. Significant manifestation of tectonic processes in the area of the field led to the widespread development of the Lower Carboniferous rocks fracture. Most of the cracks has no padding and is the leading channels for groundwater, which contributes to the development of a wide karst processes. Oilfield is characterized by a complex geological structure, the presence of a large number of differentoriented faulting, magmatism Devonian and Permian age [1]. Unstable, changing situation depositional carbonate material, subsequent tectonic processes and epigenetic alteration of rocks affected the variability of their composition.
4. TECHNIQUE OF PROCESSING OF THE EXPERIMENTAL INFORMATIONS
To obtain accurate information about the causes and patterns of variability in the quality of limestone, was conducted spatially statistical research data southeastern part Elenovsk’s field. Data are spatially referenced values of chemical analyzes of samples from plastoperesecheniyam exploration wells. The sample includes data sampling 66 wells (1427 sectional sample, the average length of 2.0 m sections). To study the spatial variability of quality specialized maps were constructed changes in quality indicators for individual horizons. Varieties and hybrids on the map of the complex index. Qualitative changes compared with petrographic composition changes of carbonate rocks, tectonic disturbances, with karst. Statistical calculations were performed quantitative data set, the correlation coefficient between the individual indicators.
5. RESEARCH RESULTS
Calculation of correlation coefficients revealed that within the investigated field between CaO and MgO indicators there is a significant negative correlation.
Subhorizon CIta2 dramatically different content of SiO2 and MgO overlying subhorizons. Here the content of MgO, with rare exceptions, does not exceed 10% (Fig.1), and SiO2 ranges from 1 to 2% (Fig.2). At the same time subhorizon CItb1 characterized by high contents of MgO (10 - 20%) (Fig.3), but sharply lowered concentration SiO2 (less than 1%) (Fig. 4) and CaO.
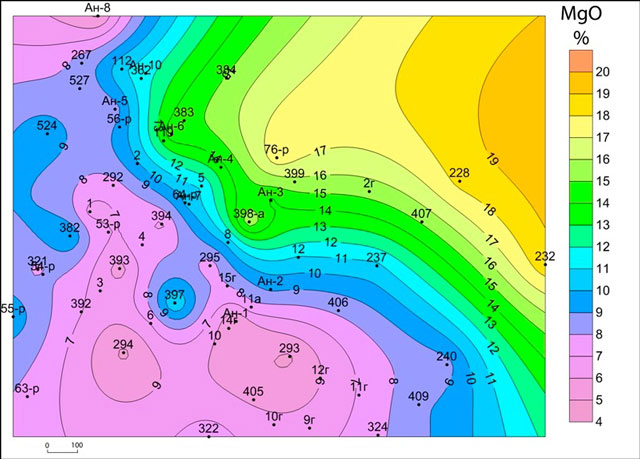
Figure 1 – Map of the MgO horizon CIta2
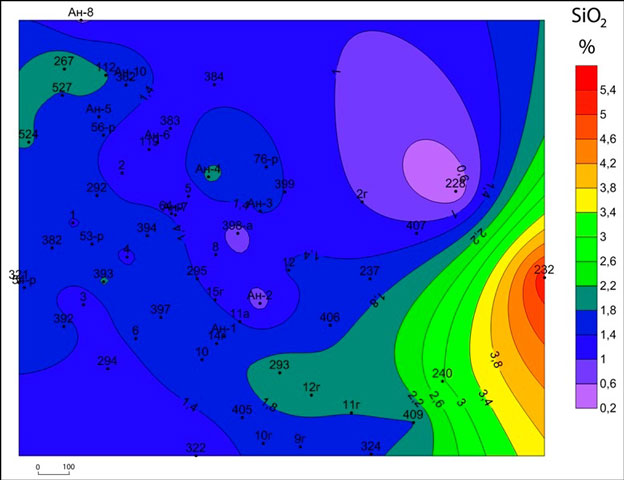
Figure 2 – Map of SiO2 content horizon CIta2
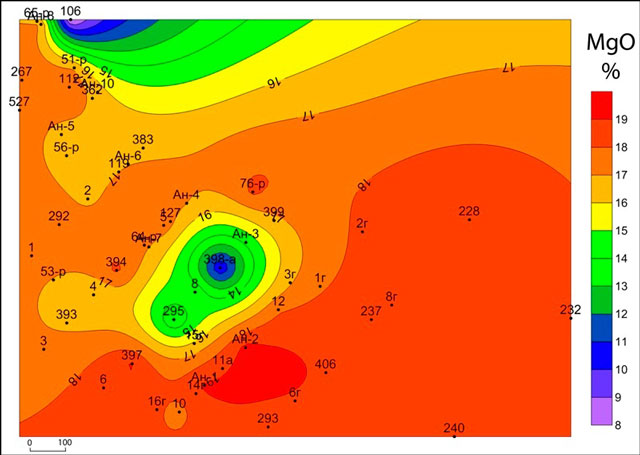
Figure 3 – Map of the MgO horizon CItb1
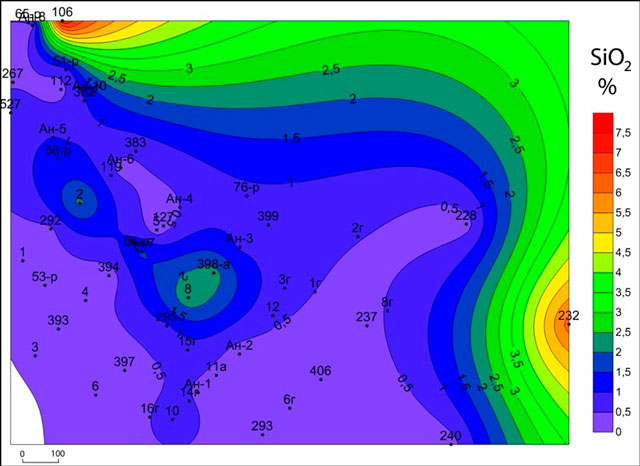
Figure 4 – Map SiO2 content horizon CItb1
Comparison of the results of chemical analysis for each power karst horizon revealed some dependence on karst development of chemical components. Thus in rocks with abnormally high MgO and SiO2 in the majority of cases, decreases power Karst.
It is well known that the composition of the rocks is one of the factors in the formation of karst. Researchers in the study of karst in carbonate rocks identify several factors influencing its formation. These factors include [2, 3, 4]: climate (precipitation, composition, etc.), geological structure (composition of the rocks, their fracture, etc.), geomorphological conditions (topography, its degree of compartmentalization) and hydrogeological conditions ( dynamics, chemical composition and the groundwater regime).
The analysis of karst rocks in the area and its relation to the faults and fracture zones. Due to the fact that a significant part of the square is the technologically altered landscape (career piles of rocks), and the rest of the territory is covered by young loose sediments (Neogene-Quaternary) we studied the eastern part of the site using remote method research. Analysis of satellite imagery territory with the release of linear landscape elements - lineaments (Fig.5).

Figure 5 – Territory with the release of the animated lineaments according to satellite imagery analysis(volume of 265 kb, 6 frames, delay between shots 0.5s)
It is assumed that these structures reflect the position of rupture dislocations in carbonate strata, and can control the spatial distribution of karst. As can be seen from the figure at the site is dominated by lineaments NW and NE trending, which is very typical for discontinuous dislocations young age.Po materials geological maps of various scales analyzed trending fold and rupture dislocations on the area adjacent to the site of research. Found that some of the previously established large faults have similar stretch along its entire length, or in some areas. Axis is folded structures (anticlinal and synclinal) in the square are trending. In three horizons (CIta2, CItb1, CItb2) we studied the degree of karst carbonate rocks. Used data from exploration work conducted in different years. According to the analysis drawn schematic map of the spatial distribution of karst, which shows the karst areas in excess of 30% power subhorizon. Showing combined three karst areas subhorizons (Fig. 6)
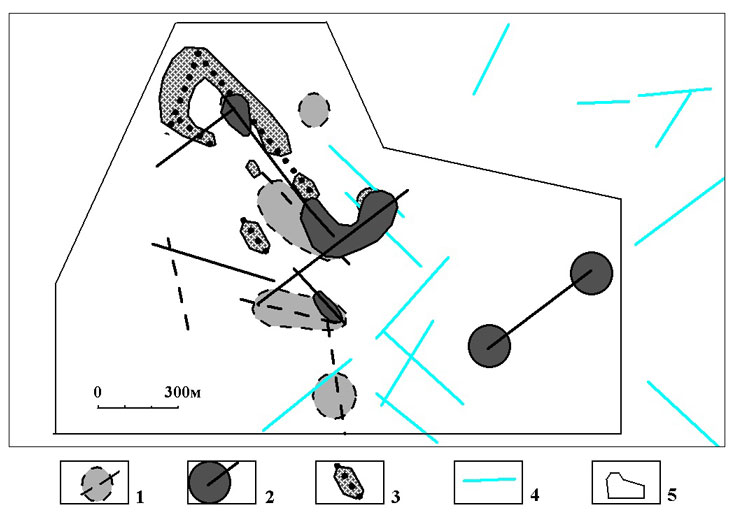
Figure 6 – Distribution of karst in the area of research:
1, 2, 3 - zone of karst development in excess of 30% percent of capacity subhorizon and their axes: 1 - subhorizon CIta2, 2 - subhorizon CItb1, 3 - subhorizon CItb2; 4 - lineaments; 5 - contour plot studies
As can be seen from the figure, the main area of karst development controlled by NW-trending lineaments system and located in the central part of the plot.
6. CONCLUSION
On the basis of research on the topic of work, as well as statistical data processing and interpretation of testing concluded the most significant factor affecting the spatial distribution of quality. Set sharp differences in the chemical composition subhorizons carbonate rocks. Revealed the association of karst areas to abnormally low levels of MgO and SiO2 in carbonate rocks and zones of NW-trending rupture dislocations in them.Practical conclusions and recommendations to simulate the test field.
7. REFERENCES
- Лазаренко Е. К., Панов Б. С., Груба В. И. Минералогия Донецкого бассейна. Киев:
Наукова Думка
, 1975. – Т. 1. – 253 с. - Соколов Д. С. Основные условия развития карста. М.: Госгеолиздат, 1962, – 321 с.
- Максимович Г.А. Основы карстоведения. – Т.1. Пермь, 1963. – 444 с.
- Карст Башкорстана. Уфа, 2002. – 382 с.
- Ляхов Г. М. Нерудные ископаемые – известняки, глины, обломочные горные породы – М., 1948.– 116 с.
- Лыгина Т.З. [Электронный ресурс] / Т.З. Лыгина Комплексная переработка неметаллических полезных ископаемых как основа инновационных проектов – 2008 – Загл. с титул. экрана. – Свободный доступ из сети Интернет. – http://www.krc.karelia.ru/...
- Митинский А. В. Флюс, в металлургии//Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона. – Санкт-Петербург, 1890—1907.
- Пономарев В.В. Известняк – Д.,2005.-220
- Науково-технічна бібліотека – [Електронний ресурс]. – Режим доступу: http://lib.nmu.org.ua/...
- Глуховский карьер кварцитов – [Електронний ресурс]. – Режим доступу: http://metodportal.net/...
- Геологические условия формирования
черного курильщика
в Донбассе – [Електронний ресурс]. – Режим доступу: http://dspace.nbuv.gov.ua/... - Глуховский карьер кварцитов – [Електронний ресурс]. – Режим доступу: http://metodportal.net/...
