Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Research purpose, objectives and expectations
- 3. Survey of ways for securing the roof bolt
- 4. Securing roof bolt by the means of natural deformation of anchor hole walls
- Summary
- References
Introduction
The economic system and energetic safety of Ukraine depends on coal industry as the fundament for the country’s industrial potential. The prospects for increasing coal production rates are closely connected with complicated geological environment and great mining depth, which average value accounts for 700 m, and the highest value — 1400m, where rather high overburden pressure is present. In this respect, the problem of providing support for mine openings is extremely important.
The efficiency of coal mines is first and foremost determined by coal prime cost, by which 45% go for preparation, securing and supporting development openings. At the same time 90–95% of openings are secured with an arch support made of special SVP section (special replacement section). The annual length of rehabilitated openings comprises 49–57%. One of the most promising ways to decrease costs by the means of an overburden bearing capacity is the application of a roof bolt. In this case the costs for rolled steel decrease 5–10 times, the efficiency of an opening support increases 2–5 times and opening development rates increase 2–3 times. The application of the roof bolt is promising; however in Ukraine it is used only in 1–2% of cases. One of the main reasons obstructing the application of the roof bolt in mines is insufficient understanding of its role in providing opening support as well as the lack of regulatory system, which allows due to particular geomechanical system and application experience to provide parameters for roof bolts.
1. Relevance of the topic
The installation cost for one roof bolt accounts for 100–120 UAH, 40% of which go for a securing compound. That is why the development and research of new ways for securing roof bolt by the means of natural wall deformation is a relevant scientific-technical objective.
2. Research purpose, objectives and expectations
The research purpose is to provide parameters for a new way of securing roof bolt by the means of natural deformation of anchor hole walls.
Main research objectives are:
- To perform an analysis of ways and means for securing roof bolt;
- To make analytical, laboratory and underground researches to provide:
- rational directions along section perimeter for implementing new ways of securing roof bolt;
- to analyze a shifting range of anchor hole walls in laboratory and underground conditions to provide advisable diameters for an anchor hole and roof bolt.
According to the research results it will be possible to specify geological and technical conditions (rock stiffness, mining depth, correlation of anchor hole and roof bolt diameters), under which a resource-efficient technology of securing the roof bolt will be used.
3.Survey of ways for securing the roof bolt
There are different ways for securing the roof bolt.
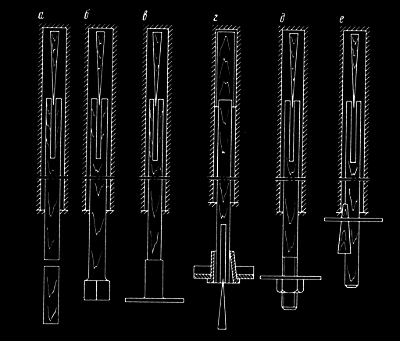
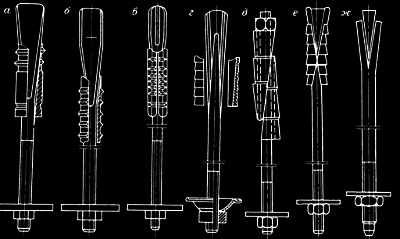
First way includes securing using locks of different designs, which are strut off in the anchor hole with a wedge or by rotating the bolt. Here come slot-and-wedge anchors with following support elements: а — wooden wedge; б — square head; в — pressurized plug with a sheet; г — cone plug with a wooden wedge; д — pressurized threaded coupling with washer and nut; е — washers with steel wedge; (fig. 1), locking steel anchors: а — ШК-1м; б — АК-8у; в — АКМ; г — ЭС-2Э; д — АД-1; е — АП-2м; ж — slot-and-wedge (fig. 2). Bearing capacity comprises 18–120 kN, the installation process takes 2–5 min [1].
Figure
1 –Slot-and-wedge anchors
Figure
2 –Locking steel anchors
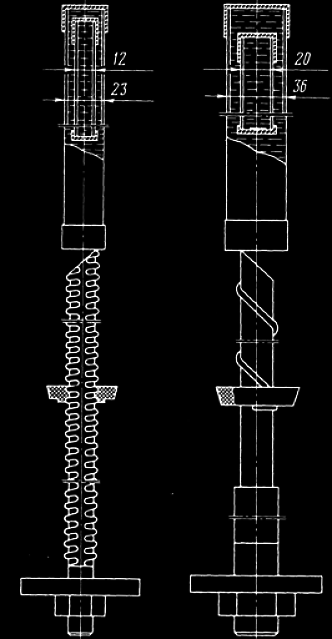
The second type of securing roof bolt includes means using binding materials. In this case the anchor is secured at a particular point or throughout the length. The holding force here is 50-130 kN. The installation takes 2-5 min, but the commissioning is provided only after the period of hardening of binding material (fig.3).
Figure
3 –Fiberpolymer anchors
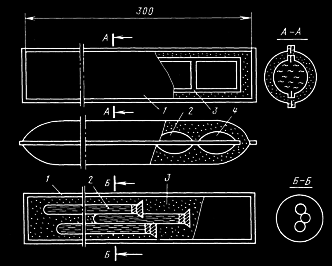
Such installation type, which applies polymortar (fig. 4), is widely spread in Ukraine and abroad.
Figure
4 –Capsule with fast-hardening chemical mixtures
Along with high workability the realization of such type of securing roof bolt is connected with expensive mortar, which goes for 20–40% of the whole installation price, which is 200–250 UAH, the binding component only costs 100–200 UAH. Total expenses for securing 1 linear meter of a mine opening accounts for 1000–2500 UAH [7].
The third way for securing roof bolt does not require binding materials or locks — it is an integral joint securing, which is performed by the means of blast energy (fig. 5) [1], i.e. unbending a previously bent thin tube with the diameter of 41 mm in the hole of 30–39 mm, under the water pressure of 30 MPa [2].

Figure
5 –of roof bolts anchored by an explosive charge
There is another way for securing thin-walled tube bolt with vertical section by the means of elastic characteristics as the roof bolt with diameter of 38mm is inserted into the anchor hole of 35mm diameter. The securing force accounts for 25–50 kN/m. The installation process takes 2 min.One of resource-efficient ways for securing roof bolt is an American technology using no anchor hole
The roof bolt is forced into the ground with the help of a hydraulic unit [3]. An anchor rod of 20.6 mm diameter is forced deep into the ground with stiffness of 30–40 MPa for 0.5–0.8 m. One of realization problems using this type of securing roof bolt is to provide correct direction [4].
4. Securing roof bolt by the means of natural deformation of anchor hole walls
This way is based on natural deformation of anchor hole walls. According to the fact that influence zone covers 3–4 radii [6], the bolt with the length of 2–3m drilled into the ground get into the area of high tenses. Such an area also forms around the bolt. While tenses around the bolt are higher than all around the overburden, it is possible that deformation process around the bolt will be faster than in the overburden. Figure 6 represents the diagram, which explains the principle of securing roof bolt[5].

Figure
6 – Diagram explaining the principle of securing roof bolt
.
(Diagram: 10 frame, 6 repetition cycles, 60 kilobytes)
The realization of this way is provided in two steps. During the first step the bolt is inserted into the drilled anchor hole and then secured with a plastic plug in the hole back. Then the support plate is installed and a pretension process is held with a screw. During the second step the bolt is secured by the means of natural deformations of anchor hole walls, which is possible only if convergent area of the walls is higher than the difference between bolt and anchor hole diameters.
Summary
A short review of existing types of securing roof bolting processes shows that they require particular costs, connected with drilling anchor holes, making special bolts, necessary use of expensive binding materials, use of special equipment. That is why development and searching for resource efficient ways and means of securing roof bolts is a relevant objective. To improve such ways it is necessary to include efficient and simple means into the development process. Thus, a suggested way for securing roof bolts will significantly (1.5–2 times) reduce costs for installation of a roof bolt.
References
- Анкерная крепь: Справочник / А.П. Широков, В.А. Лидер, М.А. Дзауров и др.– М: Недра 1990. – С.34–205
- Юхимов Я.И. Анкерные крепи и средства контроля за состоянием кровли (зарубежная информация)/ Я.И. Юхимов, В.Г. Галыперий // Уголь Украины, 1983. – №10. – С.44–46
- Харрелл М.В. Новый гидравлический способ установки анкерных болтов/ М.В. Харрелл// Mining Congress Journal/ – 1971. – №6.
- Патент на корисну модель №55763 Україна. МКИ E21D 20/00. Спосыб встановлення анкера/ Касьян М.М., Новіков О.О., Петренко Ю.А., Дрипан П.С., Шестопалов І.М., Гладкий С.Ю., Виговський Д.Д. – Заявл. 04.06.2010; опубл. 27.12.2010; бюл. №24. – 6с.
- Мельников Н.И. Анкерная крепь. – М.: Недра,1980. – 252 с.
- Гетце В. Основы применения анкерной крепи в горизонтальных выработках арочного сечения// Глюкауф. – 1977. – №15 – С.25–27
- Штаноговая крепь/ В.Н. Семевский, В.М. Волжский, О.В. Темофеев, А.П. Широков – М.: Недра, 1965. –328с.
