Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Analysis of sources
- 4. Functional diagram of the electric drive machine of double feed
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Today the development of world energy is based on using traditional fossil fuels. In the long term energy development in this area will be constrained by ecological, resource and social constraints, however, the demand for energy associated with the development of economic and increase in population will be constantly grow. To satisfy this demand is necessary to use the all range of traditional and renewable energy[1].This contributes to large-scale development of alternative energy in industrialized and in developing countries.
One of the most promising directions is wind power. Further development of wind energy will allow solving problems of quality and reliability of power supply, and reducing the harmful effects of energy on the environment. However, the construction of wind power plants associated with some technical difficulties and economic problems, that are slowing down the spread of wind power.
1. Theme urgency
Urgency of the work is determined by the transition of modern industrial production to the use of energy-saving technologies. Using double feed induction generator (DFIG) in modern automated systems allows to raise essentially technical and economic performance of various process units. The Master's work deals with one of the most promising areas - the use of wind power in an asynchronous machine with direct power supply on the part of the stator and the power supply through a reversible converter on the part of the rotor.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim of the research is to describe the principles of the electrical installation on the basis of double feed induction generator for the use of wind energy.
Main tasks of the research:
- Development a mathematical model of the double feed induction generator.
- Development of the control system electrical drive on the basis of machine of double feed.
Object of study: Electric drive machine of double feed.
As part of the master's work is to get the current scientific results in the following areas:
- Optimization of the system for the maximum output power.
- Getting waveform transients in the drive.
3. Analysis of sources
Questions of electromechanical energy conversion of a new type of contact and contactless double feed induction generators considered in the monograph[2].
Description of the general principles of vector control of the machine of double feed, that used as a generator for the wind power, is set out in article[3].
Models of the machine of double feed and analysis of stability of its transient processes are described in the article [4].
However, these articles contain not enough detailed information about control of the machine of double feed at constant grid voltage and about its mathematical description.
4. Functional diagram of the electric drive machine of double feed
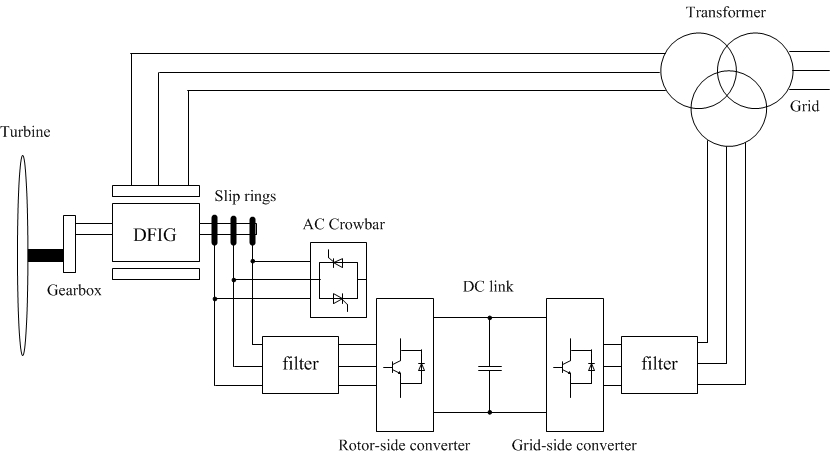
Figure 1 – Functional diagram of the electric drive machine of double feed
The advantage of this scheme are:
- Recoil active power from the stator side at variable rotation speed and constant frequency of the grid.
- Recoil active power from the rotor side when rotation speed higher than the nominal.
- The converter with low installed power.
The rotor-side converter provides the excitation for the induction machine rotor. With this rotor-side converter it is possible to control the torque hence the speed of the DFIG and also the power factor at the stator terminals. The rotor-side converter provides a varying excitation frequency depending on the wind speed conditions. The induction machine is controlled in a synchronously rotating dq-axis frame, with the d-axis oriented along the stator-flux vector position in one common implementation. This is called stator-flux orientation (SFO) vector control. In this way, a decoupled control between the electrical torque and the rotor excitation current is obtained. Consequently, the active power and reactive power are controlled independently from each other. Block diagram of the rotor-side converter is proposed in the article[3].
The grid-side converter controls the flow of real and reactive power to the grid, through the grid interfacing inductance. The objective of the grid-side converter is to keep the dc-link voltage constant regardless of the magnitude and direction of the rotor power. The vector-control method is used as well, with a reference frame oriented along the stator voltage vector position, enabling independent control of the active and reactive power flowing between the grid and the converter. The grid-side converter is current regulated, with the q-axis current used to regulate the active power and the d-axis current component to regulate the reactive power. Schematic structure of the control of grid-side converter provided in article[3].
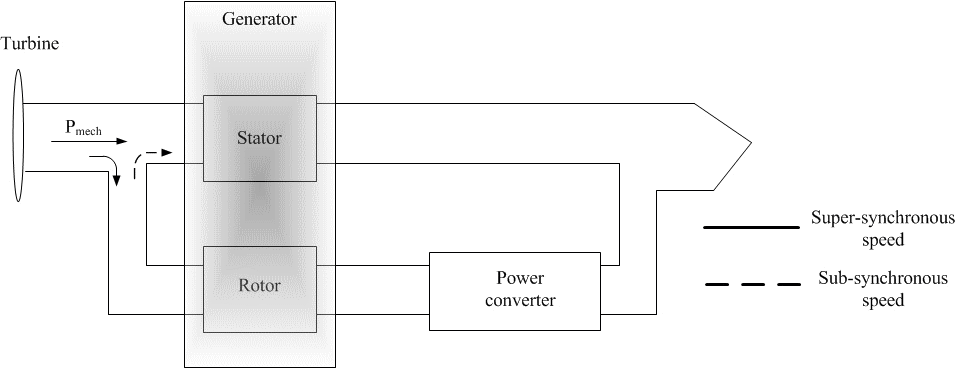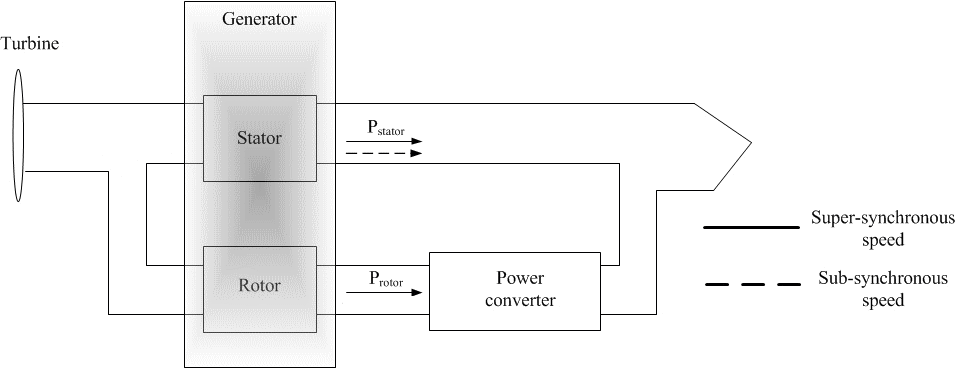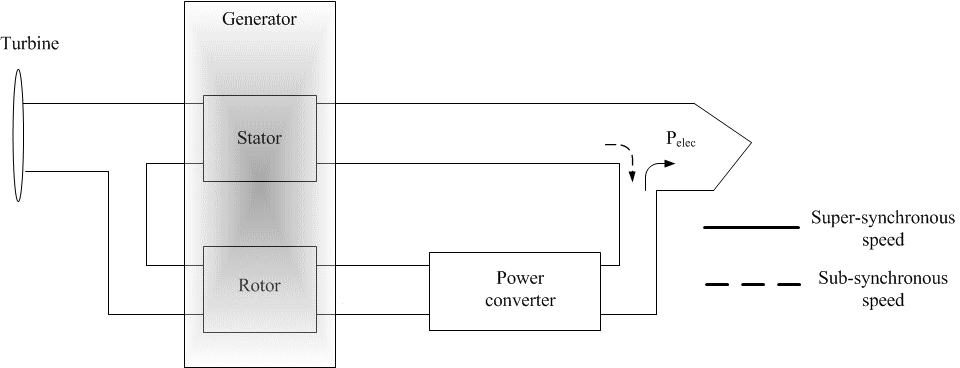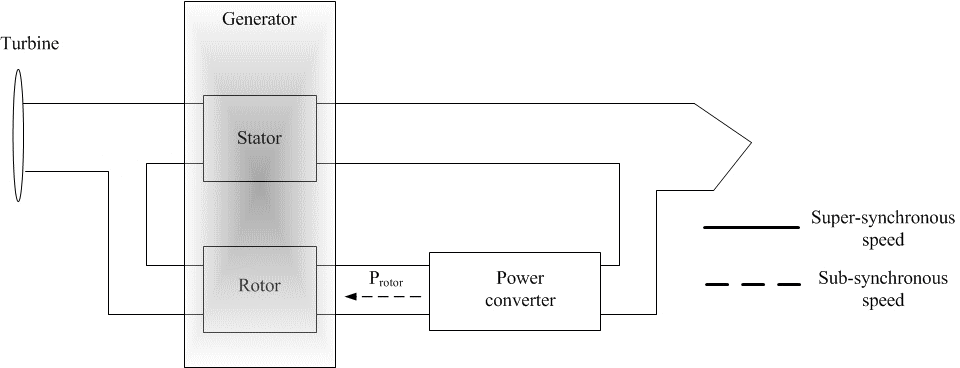
Figure 2 – Active power flow in the DFIG
(animation: 4 frames, 7 cycles of repeating, 27 kilobytes)
When the wind speed increases, the speed of the rotor must change in order to optimize the efficiency of the aerodynamic system. Therefore the rotor speed increases above synchronous speed, resulting in a negative slip and super-synchronous operation. In this operation, power ?ows to the grid from both the stator windings and the rotor windings. As the wind speed decreases, rotor speed decreases, and the machine operates in sub-synchronous mode, with a positive slip. Under these circumstances, the rotor must absorb active power from the grid, essentially borrowing power for rotor winding excitation.
Conclusion
- Have been described the principles of the electrical installation on the basis of double feed induction generator.
- Developed a mathematical model of the double feed induction generator.
- Developed of the control system electrical drive on the basis of machine of double feed.
At the time when this abstact was writing the dissertation wasn't completely done. The full text of it can be recived from author in december of 2015.
References
- Быков Е. Н. Обоснование параметров ветроэнергетической установки со спиральными лопастями на основе экспериментальных исследований/ Дис. канд. тех. наук/ Санкт-Петербургский государственный политехнический университет - Санкт-Петербург, 2007. – 141 с.
- Гуляев И.В. Системы векторного управления электроприводом на основе асинхронизированного вентильного двигателя/ И. В. Гуляев, Г. М. Тутаев // Монография. Саранск: изд-во Мордов. ун-та. - 2010. - 200с.
- Dr John Fletcher and Jin Yang "Introduction to Doubly-Fed Induction Generator for Wind Power Applications", - электронный ресурс. Режим доступа:http://www.intechopen.com/books/paths-to-sustainable-energy/introduction-to-the-doubly-fed-induction-generator-for-wind-power-applications
- Michael A.Snyder "Development of Simplied Models of Doubly-Fed Induction Generators (DFIG)", - электронный ресурс. Режим доступа:http://publications.lib.chalmers.se/records/fulltext/166648.pdf
- Безденежных Д. В. Разработка и исследование электропривода на базе машины двойного питания с подключением обмоток статора и ротора к преобразователям частоты/ Автореферат дис. канд. тех. наук/ Липецкий государственный технический университет - Липецк, 2011. - 18 с.
- Глазырин М. В. Построение систем векторного управления электроприводов на базе машины двойного питания/ Автореферат дис. канд. тех. наук/ Новосибирский государственный технический университет - Новосибирск, 1997. - 19 с.
- S. Muller,M. Deicke, Rik W.de Doncker "Doubly fed induction generator system", - электронный ресурс. Режим доступа:http://web.mit.edu/kirtley/binlustuff/literature/wind%20turbine%20sys/DFIGinWindTurbine.pdf
