Labour protection in mining industry
Trudovskaya
Occurrence of major accidents in Ukrainian mines caused sudden bursts of dust methane air mixtures in the mountain – you processing requires the search for new effective technical proposed zheny to reduce the likelihood of explosions. The presence of dust in methanol air mixture in the explosion contributes significantly increase NIJ force of the explosion and the formation of a large volume of toxic gases high concentration. Furthermore, aggressively acts on dust equipment surface complex provokes dangerous Zabo ous diseases of the respiratory organs of workers ( principally fan installation airing of coal mines during the day thrown in mine surface complex of more than 1.5 tons of dust aerosol each , creating excess of MPC 2–3 times).
Modern methods of underground coal mining characterized by the formation of significant amounts of dust and its release into the atmosphere of mine workings.
Dust control is a complicated engineering and logistical problem because mine dust worsens sanitary working conditions, reduces the visibility into the workings, clogs and irritates the skin and eyes, causing major diseases, clogs and irritates the airways and lungs during prolonged breathing can cause chronic lung disease. Furthermore, the presence of the mine atmosphere of dry coal and fine dust containing over 15% volatiles, causing a danger of dust explosion.
To solve this problem ie to ensure an acceptable level of safety in a coal mine requires detailed planning for integrated dust removal mining, compulsory and complete their execution, which will prevent incidents and accidents.
The purpose of the master’s work is the analysis of the state and development of science - based activities on integrated dust removal mining mine Trudovskaya
.
The main objectives of the work:
Trudovskaya
Shakhtoupravleniye Trudovskaya
is a separate division of the State Enterprise Donetsk Coal Energy Company
of the Ministry of Coal Industry of Ukraine.
Mine mine field is located in the western part of the Donetsk-Makeyevka coal-bearing area on the territory of the Petrovsky district of Donetsk and Donetsk region Maryino.
Field of mine Trudovskaya
opened by four vertical shafts: two center-twin (the cage and skip), the western and the air vent. All developed mine layers (m3, k8, l1 and l4) are opened through main haulage and conveyor crosscuts mountains. 493 m. 493 m horizon is a major, which will be practiced and practiced to evade all field formations developed.
Opening slant of the field produced by field gradients, which are cut from the field and go for a powerful backbone drifts sandstones located 30 meters below the reservoir k8, and then crosscuts on being uncovered layers.
A method of training currently being developed layers l4 and m3 panel. Testing of the panels is carried out on the development of pillar system with working off of stocks long pillars along strike backflow.
The scheme of ventilation shafts - flanking, method of ventilation & ndash; suction.
Year of commissioning – 1952.
Category Mine Gas – I (methane).
Depth of reference works (Wed maximum) – 650m, 690m.
Design capacity – 1000 thousand year.
Currently being developed layers – m3, l4.
Mean dynamic power developed layers – 1.63 m.
The angle of incidence of layers – 100 – 120.
Marc coal – Dan DGen.
The total length of mining – 51.9 km.
Trudovskaya
РSection Anti–dust in the projects of new and reconstructed mines (horizons), opening and preparation of blocks, panels, excavation of fields should contain:
– a list of measures to combat dust in all processes involving dust emission (with coal extraction, conducting excavations, filling operations, loading, transportation and unloading of the rock mass, including in the pit bottom);
– the parameters of the equipment for dust control and placing it on a network of mine workings;
– the specification of equipment and materials for dust control;
–fire – circuit irrigation pipelines with their diameters, the water pressure, placements irrigation devices, pumping units, etc.;
– recommendations for optimal dust factor on the mode of ventilation faces;
– a list of jobs and manufacturing processes which must be applied dust masks.
The project of building a section of the mine there.
To the Shakhtoupravleniye Trudovskoe
w.Trudovskaya
id are used antidusty such activities.
Preliminary moistening consists in the forcing of water into the massif before its destruction (it is most widespread when developing coal fields). It is carried out through the chinks drilled on a layer in parallel or perpendicularly of a plane of a clearing face, in preparatory faces, as a rule, in a plane of a face.The basic parameters, on which depends the effectiveness of this method – pressure and the rate of forcing, the distance between the bore holes, the depth of hermetic sealing bore holes, the consumption of water and time between the forcing of water and the coulisse of coal. Decrease in a dust content of air when developing the humidified massifs happens as a result of an increase in the overall humidity of the destroyed material, its easing as a result of physical and chemical and hydrodynamical processes of interoperability of water and massif and wetting of the dust, existing in the massif before its destruction [2].
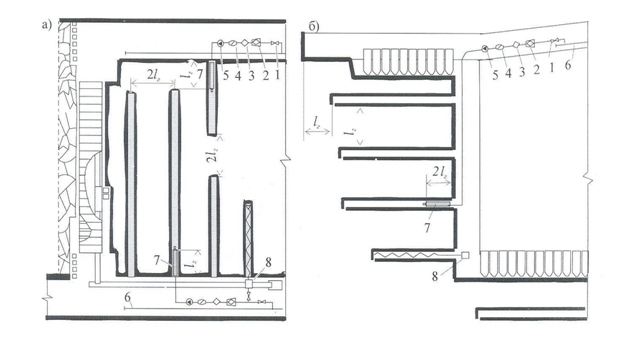
1 – a valve; 2 – a filter a drift; 3 – a metering device of smachivatelya; 4 – a flowmeter; 5 – the pumping setting high–pressure; 6 – a drift pipeline; 7 – germetizator; 8 – a boring machine–tools
Figure 1 – Flowsheets of festering of water from the preparatory making in the cleansing backwalls of declivous layers (a) and at a shield coulisse on steep layers (b)
In the mechanized stope of declivous and steep layers the dust - suppression with the groove of coal is achieved with the draft on funds of irrigation, with which are equipped the excavated combines mechanized timberings, frontal and shield aggregates. On a figure 2 flowsheets are resulted the dust - suppression the irrigation at the coulisse of declivous layers by the mechanized complex [4].
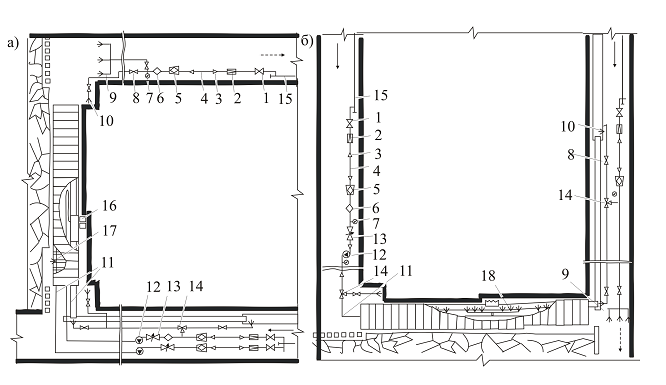
1 – flanged valve, 2– pressure reducing valve, 3 – adapter, 4 – pressure hose, 5 – filter shtrekovy 6 – wetting agent dispenser, 7 – gauge, 8 – box–pass valve, 9 – Water Curtain, 10 – Nozzle, 11 – plumbing mud, 12 – pumping station, 13 – solenoid valve, 14 – a three–way valve box–, 15 – shtrekovy pipeline, 16 and 17 – irrigation systems combine and lining, 18 – automatic sectional irrigation.
Figure 2 – Flow charts irrigation dust control during excavation of shallow reservoirs mechanized complex a) and with the plow groove b)
During the excavation processor or application loading and drilling machines used means of dust suppression, which are equipped with these processors and machines. On formations with high dustiness category tunneling machines on request mines can additionally be equipped with dust collectors for irrigation or autonomous dust extraction units (Fig. 3) [6].
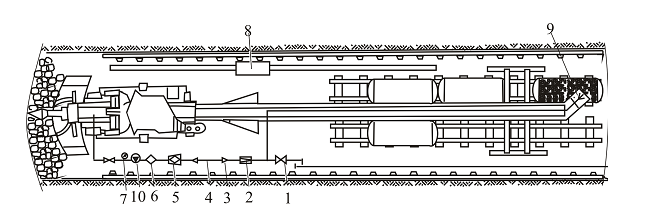
1 – valve flange; 2 – a pressure reducing valve; 3 – adapter; 4 – pressure hose; 5 - Filter shtrekovy; 6 – wetting agent dispenser; 7 – pressure gauge; 8 – dust collector; 9 – water curtain; 10 – nozzle
Figure 3 – Technological scheme dedusting in the mine with the sinking of a combine
When using independent ventilation dust removal facilities deadlock advance working can be injection-suction and suction. A suction ventilation is supposed to apply to mines not gassy mines, pressure-suction ventilation with independent dust collection units can be used in the mines of any category of methane, in addition to developments that are dangerous to sudden outbursts of coal and gas and piper.
The residual dust content of air on a network of mountain developments, as a rule, is at rather high level and the airflows which are starting with clearing and preparatory developments, as well as passing on a network of developments, require in additional the dust removal. For the dust removal of the air flow we use water -air (fog -forming) curtains.
For creating the water curtains of the type [VZ]-1 are used the flat - ink - jet atomizer.
More effective are fog–forming the veils created fogger of type ОП-1 or ТЗ-1В. The diameter of the drops of the generatrix of fog does not exceed 10–50[mk]; therefore the atomized water long time is retained in air. For formation of a water fog in foggers tricked the water and compressed air. At the serve of the compressed air and moving of slide - valve water and compressed air enter the mixing chamber, in which is formed water–air mixture. Spraying of the latter occurs through the annular slot, with the aid of which is regulated the degree of dispersion of the water fog [1].
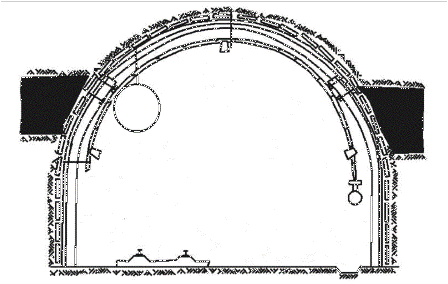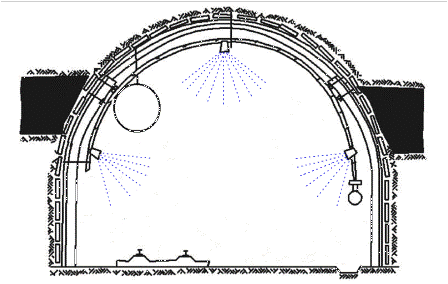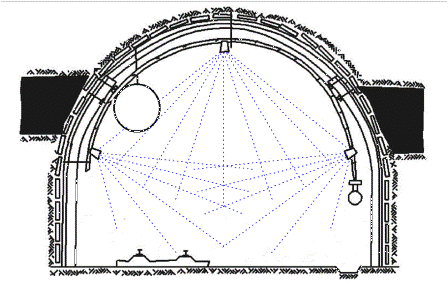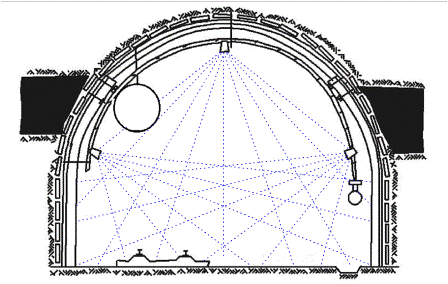
Figure 4 – Cleaning the air flow from the dust water curtain type VZ-1
(Animation: 7 shots, 5 cycles of 196 kilobytes)
The essence of dust–suppression by irrigation consists in the fact that with interaction of the drop of liquid with the particle of dust occurs, its moistening, seizure by drop and the precipitation of the received aggregate - dust particle - water.
In irrigation systems as sprinklers are used nozzle giving a compact and versatile jet nozzle, the torch of different shapes: cone (CF) - as a solid cone, umbrella -(DF) in the form of a hollow cone, FLAT (PF) - in the form of a flat fan. The designation indicates the shape of the nozzles of the torch, the coefficient of water flow and angle of the torch. For example, KF 1,6&ndsh;75 nozzle cone nozzle with a flow rate ratio of 1.6 and angle of the torch 750.
Irrigation efficiency depends on the specific consumption of the liquid dispersion of droplets drops dust capture conditions (relative velocity of the particles and droplets elektrozaryazhennosti drops), dust wetting and uniformity of irrigation.
In all irrigation systems is obligatory to use water purification filters shtrekovyh FS-1M, FS-200, or PCF FC [3].
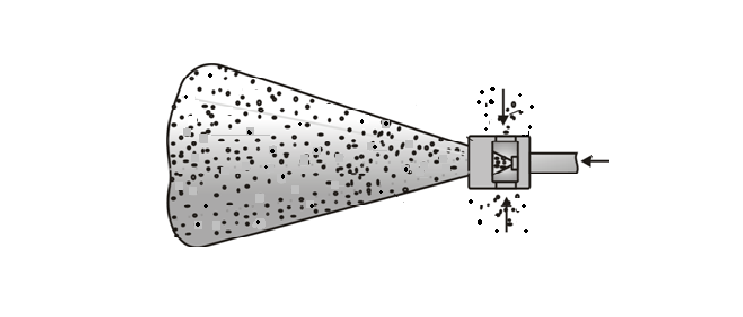
Figure 5 – The principle of operation of the air ejector
Respiratory protection of miners from the coal and rock dust by using dust mask type F-62SH which provide clean air inhaled from dust to the maximum allowable concentrations.
Respiratory protection miners will be reliable and efficient only if the respirator is properly selected size. Properly selected and fitted respirator should fit snugly and evenly to the face [5].
In the course of the master's work were collected and analyzed materials on w. Trudovskya
, was produced by the analysis methods used at the mine dust suppression, it was given to assessment of the effectiveness of measures employed at the mine based on the above set of effective measures for dust control in mines.