Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Development of
optimum solutions
search module - Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Any leader has to take various daily management decisions. In most everyday situations decisions are made based on the situation, but sooner or
later before any problem arises leader informed decision-making. Therefore master's work is devoted to actual scientific task of finding the best
solutions based on the software product 1C: The company
.
1C: The company
— software company 1C
, intended for automation of activities of the enterprise. Initially, 1C: The
company
has been designed to automate accounting and management accounting (including payroll and human resources management), but today this
product finds application in areas distant from the actual accounting tasks [1]. 1C: The company
— is(both)
and technology platform, and user mode. Technology Platform provides objects (data and metadata) and facility management mechanisms. Objects
(data and metadata) as described configurations. When you automate any activity compiled its own configuration object, which is a complete
application solution.
1. Relevance of the topic
One is the economic planning of the most important aspects of business management. Effective forecasting, even in times of crisis can improve the financial sustainability, productivity, profitability and other indicators. As shown by various studies, it is a major key to business success. For anyone, even a small company in the preparation of plans there are so many alternatives. One way to solve such problems is to optimize the management. Optimization — purposeful activity, is to obtain the best results under certain conditions. The quest for the optimal solution of — the natural state of man who has to save resources and reserves of the belt.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim of the research is the development of the module search for optimal solutions
in the system 1C: The company
.
Key issues to be addressed:
- Evaluation of the functionality of the program
1C: The company
. - Selection of typical optimization of different classes of scheduling problems.
- Development of algorithms and software.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the use of the developed subsystem.
To achieve this goal it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
- To learn mathematical methods of modeling of economic systems.
- Perform analysis purposes used to evaluate the performance of the enterprise.
- A review of optimization problems in enterprise management.
- Analyze opportunities subsystem
Finding solutions.
Research object: Finding Solutions
subsystem development process.
Research subject: methods and algorithms of mathematical and economic models and systems.
The novelty of the is to develop software that can be included in the configuration of 1C
for the purpose of to
optimize the use of calculations in 1C
.
The practical significance of is that the developed software can be included in the standard configuration
3. Development of optimum solutions
search module
The program 1C: The company
is widely used for accounting, management and other types of accounting in small and medium business,
as a kind of standard in these areas. Update configuration tools to find optimal solutions decision support tasks will significantly increase
the efficiency of the use of this software. Now 1C is possible to find effective solutions due to the accumulation of data in the software
product and play a variety of situations, at the expense of the choice of the most rational decisions. It is definitely a big plus, but as you
know, to get the best, or rather the best solution, we can only be constructed a mathematical model of the problem (or situation) and applying
for finding the optimal solution is one of computational optimization methods. Inclusion in the configuration 1C such opportunities
significantly enhance the effectiveness of the solutions. The result should be the development of software that will allow to find optimal
solutions decision support tasks.
In order to understand the principle of the developed product is necessary to understand how the search for solutions
in the MS Excel.
For this we consider a typical linear programming problem. The circle of problems solved using linear programming methods is quite wide:
- The problem of the optimal use of resources in production planning;
- The problem of the mixtures (product planning staff);
- The problem of finding the optimal combination of different types of products for the warehousing (inventory management — inventory
or
knapsack problem
); - Transportation problem (analysis of plant location, the movement of goods).
Economic–mathematical model of linear programming tasks include: the objective function, the optimal value of which (maximum or minimum) [6] is required to find the limit in the form of a system of linear equations or inequalities, the non–negativity requirement variables [4]. In general, the model is written as follows:
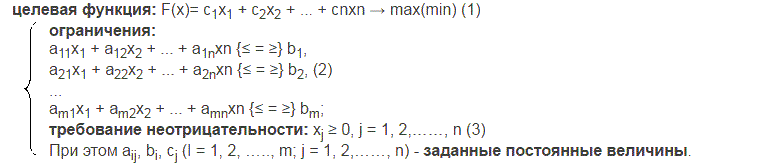
The task is to find the optimal values of the function (1), subject to constraints (2) and (3). System constraints (2) is called functional limitations problems and limitations (3) — straight. Vector satisfying the constraints (2) and (3) is called a feasible solution (plan) of a linear programming problem. The plan, for which the function (1) is at its maximum (minimum) value, called optimal.Linear programming problem can be solved manually; algebraically and graphically, and it is possible with the help of MS Excel.
Types of linear programming problems [5]:
- the problem of optimal allocation of resources in the planning of production at the company (the problem of the range);
- task for maximum output for a given range;
- the problem of mixtures (diet, diet);
- transport problem;
- the problem of rational use of existing facilities;
- assignment problem.
To solve the problem of linear programming is necessary to build the economic–mathematical model of the test of the economic process.
The model belongs to the class of economic–mathematical linear programming models. The tasks described economic – mathematical model of linear programming is usually carried out universal simplex method. It is quite time–onsuming. Therefore, the implementation of payments recommended in the medium MS Excel. This program allows you to quickly and easily solve the problem of linear programming.
The technology for solving linear programming environment MS Excel will show in the following example.
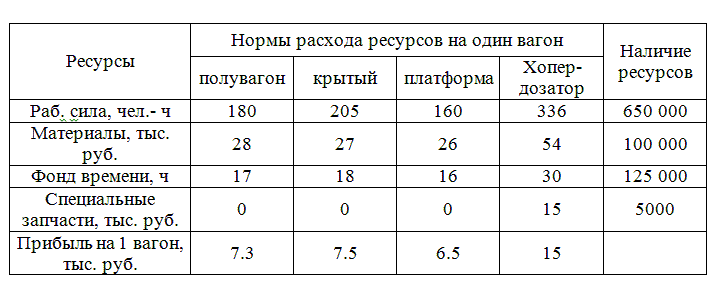
I wanted to find a plan for the repair of cars in which to maximize the total profit of the enterprise. Let x1, x2, x3, x4 number of cars of each type. Formulate economic–mathematical model of the problem:
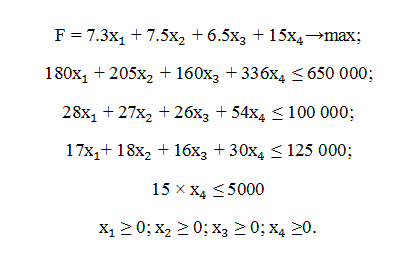
Solution of linear programming tasks in the medium MS Excel add-in by using Search solution
. For this example we demonstrate the
technology for solving the problem of optimal use of resources. The problem of the optimal values of the vector X = (x1, x2 x3, x4) will
beplaced in the cells of the B3: E3, the optimal value of the objective function — in cell F4. Introduce the input data into
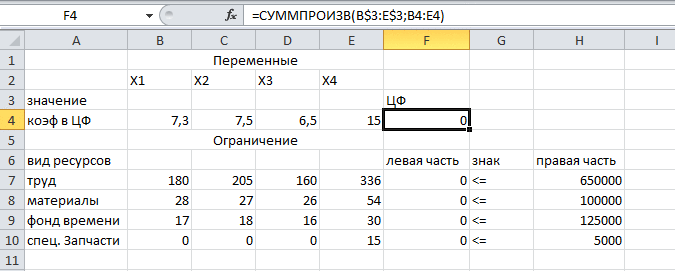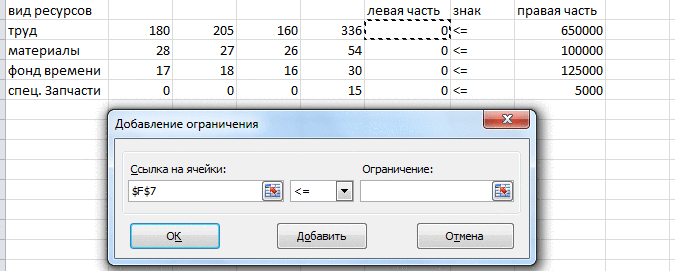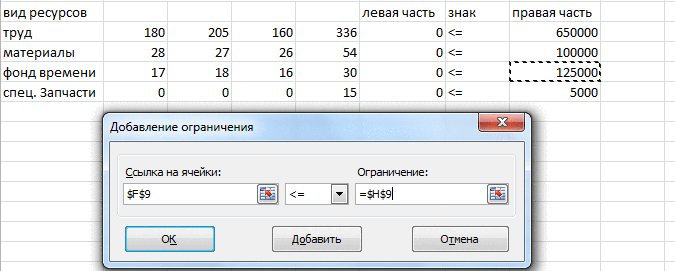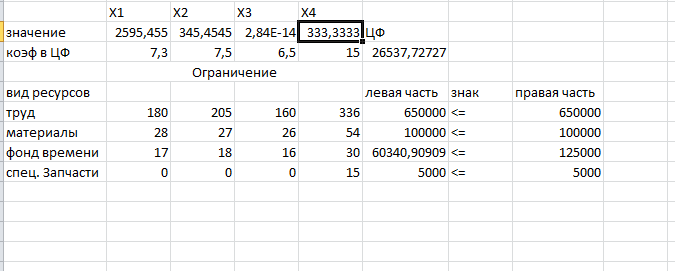
the created shape. We get the result shown in figure 4.
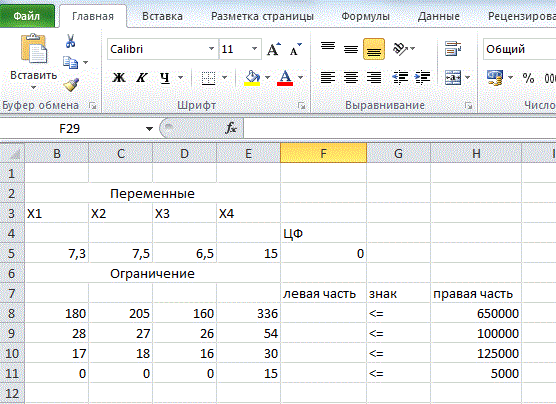
After all the constraints and parameters, we obtain the required solution of the problem
Size: 464 KB; Shots 20; Repeat: Unlimited; Delay: 0.5 sec.
In practice, many economic parameters (prices for products and raw materials, stocks of raw materials, market demand, wages, etc.) over time, change their values. Therefore, the optimal solution of the problem of linear programming, resulting in a particular economic situation, after the change may not be suitable or optimal. In this regard, the problem arises the problem of the sensitivity analysis of linear programming, namely, how possible changes of the original parameters of the model will affect the optimal solution obtained previously. The binding constraints pass through the optimum point. Nonbinding restrictions do not go through the optimum point. A resource that represents a binding constraint, called the deficit and the resource submitted nonbonding limitation, non–deficient. Restriction referred to redundancy if its deletion does not affect the feasible region and, consequently, the optimal solution. There are the following three tasks assay sensitivity.
- Analysis of the reduction or increase in resources:
- how much you can increase or decrease the supply of a scarce resource for improving optimum value of the objective function?
- how much you can increase or decrease the supply of a readily available resource, while maintaining the obtained optimum value of the objective function?
- Increase (decrease) in reserve some of the resources in the most profitable?
- Analysis of changes in the target factors: what is the range of variation of the coefficients of the objective function, which does not change the optimal solution?
The only drawback solving linear programming problems using MS Excel can be: the absence of a complete solution, ie, search for solutions immediately gives a ready answer, without showing all the calculations, but based on the fact that not always important process solutions and the most important result — it is a minor drawback. But there is another disadvantage of MS Excel (which is a disadvantage for us, based on the theme of work) — a manual reference source data model. That is, if data is generated in the 1S, how to use their program MS Excel, is not easy. Therefore, by analogy with MS Excel it makes sense to have such a tool 1C.
Conclusion
The examples of economic problems, in all their diversity have one thing in common — they presuppose the existence of optimal solutions. Different tasks require different approaches and modeling of economic objects. In turn, depending on the mathematical model for finding optimal solutions to be chosen and the corresponding algorithms and techniques for solving such problems. As a whole the process of finding optimal solutions can be represented in the form of the following stages:
- Mathematical model of the entity:
- definition of the main output index (optimization criterion) operation of the facility;
- the definition of all relevant factors and parameters affecting the value of the output parameter;
- definition of the parameters that can be optimized by changing the output parameter (variable optimization);
- construction of the objective function (criterion) optimization;
- constructing mathematical expressions reflecting restrictions on optimization settings.
- Selecting the search method for optimal solutions and related software.
- Perform optimization calculations and finding optimal solutions.
- Validation solutions.
During the analyzed methods and means of building a find a solution
module. Since a large number of tasks from various fields of economics
and management can be described by linear mathematical models, the modules find a solution
will always be in demand, especially
considering that the program 1C: The company
is widely used for accounting, management and other accounting small and medium business.
The practical value of the development is that the current methods of mathematical modeling in economics and optimization techniques based on linear models are widely used in the practice of economists and managers [7]. Modeling of economic objects and further optimization allow us to study objects and predict their key indicators for different values of external and internal factors.
Therefore, in this study will be designed not to play the situation, in the likeness of that which is implemented in the system 1C: The company
and full optimalnog finding solution of the desired objectives, based on the mathematical model described above.
In writing this essay master's work is not yet complete.
Final completion: May 2017. The full text of work and materials on the
topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after that date.
References
- «1С: Предприятие» [Электронный ресурс]: Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии: Последнее изменение этой страницы: 09:34, 25 мая 2016 // Википедия, свободная энциклопедия — Режим доступа: wikipedia.org/wiki/1С:Предприятие
- Поиск решений [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа: necomod.narod.ru/Materials/
- Линейное программирование [Электронный ресурс]: Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии: Последнее изменение этой страницы: 13:43, 8 мая 2016 // Википедия, свободная энциклопедия — Режим доступа: wikipedia.org/wiki/Линейное_програм...
- Научный электронный архив [Электронный ресурс]: Лыкова Н.П., Князева А Постановка Задач линейного программирования и их решение с помощью msexcel/Научный электронный архив — Режим доступа: ПОСТАНОВКА ЗАДАЧ ЛИНЕЙНОГО...
- Задачи линейного программирования [Электронный ресурс]: Режим доступа:ЗАДАЧИ ЛИНЕЙНОГО П...
- Microsoft [Электронный ресурс]: Постановка задачи и решение проблемы с помощью надстройки "Поиск решения" — Режим доступа: support.office.com/ru-ru/article/Постановка...
- Учебно – методический комплекс по курсу "Методы оптимальных решений" [Электронная библиотека]: Раздел 2. Методы поиска оптимального решения в задаче линейного программирования — Режим доступа: Методы оптимальных решений
