Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study
- 3. Calculation of voltage losses in electric networks with pulsed loads
- 4. A value of neutral wire
- 5. The problem of disposing of compact fluorescent lamps
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In the modern world has become very popular to use familiar society appliances with energy-saving technology, but rather widespread energy-saving lamps. In networks there is a gradual replacement of the outdated incandescent light bulbs with more efficient and economical. The master's thesis, research involves compact fluorescent lamps. Lamp is a twisted in a spiral flask, the inside of which is covered with a phosphor layer. In the base of the lamp is placed the electronic ballast, which is a trigger device for the lamp. Lamps of this type of production have a number of advantages and disadvantages. Advantages of lamp: 1) a large enough service life to 10,000 hours; 2) low energy consumption; 3) the factory warranty period of 1 year; 4) high level of efficiency; 5) ground compatible, which allows you to quickly replace the incandescent lamp, without additional investments.
The disadvantages of lamp: 1) high cost (in comparison with incandescent bulbs); 2) contain mercury and phosphor; 3) in the process generates higher harmonics, which leads to increased harmonic distortion in electric distribution networks, and as a consequence, to increased losses of electric power and energy.

Figure 1 – Design СFL
1. Relevance of the topic
In the process of exploitation of electrical networks the most important indicator is the quality of electricity. Indicators of power quality are trying to do in accordance with the nominal values of the Standard normal deviation is fluctuation is ±5 %. Still the problems of power quality related to compact fluorescent lamps were largely ignored, since the number of these lamps was not large and the associated impact was difficult to quantify.
Most modern CFL was built on a typical circuit solutions and not equipped with any systems that optimize the quality parameters of electricity consumed. Higher harmonics in supply networks lead to a number of negative consequences, despite the advantages of CFL, they create pollution frequency components are multiples of the fundamental tone. And their level is high enough, which would affect the operation of electrical equipment and the correctness of the accounting of electricity induction meters. High intensity of higher harmonics can cause radio interference and interference with household electronic devices, and create an additional load on the conductors.
It is supposed to process experimental data on the currents of various types of lamps and to obtain initial data for designing in the form of the phase curves of the currents and their derivatives, as well as to justify increasing the cross-section of neutral conductors. The correct calculation will reduce the development of emergency situations, to improve the quality parameters of electricity and to take measures to prevent their possible reduction.
2. The purpose and objectives of the study
The purpose and objectives of the study was to reduce the load on the wire; to reduce losses in the wires; improving voltage quality; to increase the service life of equipment; reduce voltage dips in the network; increasing the cross-section of neutral conductors.
3.Calculation of voltage losses in electric networks with pulsed loads
Discusses the features of calculation of voltage losses in the power of electrical receivers with pulse load (for example, compact fluorescent lamps CFL).
Typically, voltage losses are calculated using active and reactive power, and active r and reactive x to resistance network. These values relate to the particular case of sinusoidal load for example incandescent lamps. However, CFLs, power supplies, televisions and computers have an impulse load [1]. In this case, the concept x does not exist. In this connection, you need to develop a method of voltage drop calculation for such loads.
The source for the calculations are the curves of the currents iA(t) CFL, connected between phase a and zero if the lamp is connected to phase B or C, the curve obtained by the offset currents iA(t) 240 and 120 degrees. If the phases are connected several lamps, then the total currents of each phase is equal to the sum of the respective currents. A graph of the current in the neutral wire equal to the sum of currents in all phases.
Especially the calculations of the projected for example, a uniform connection of the three lamps. The curves of the voltages uA,B,C(t) are sine waves phase-shifted.
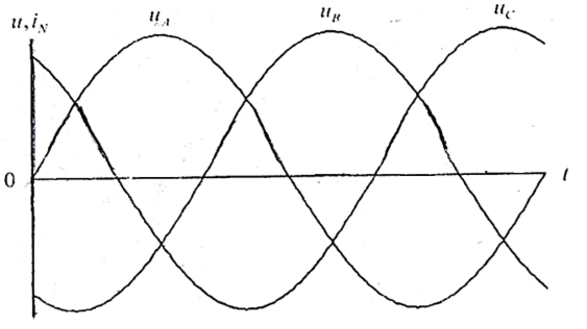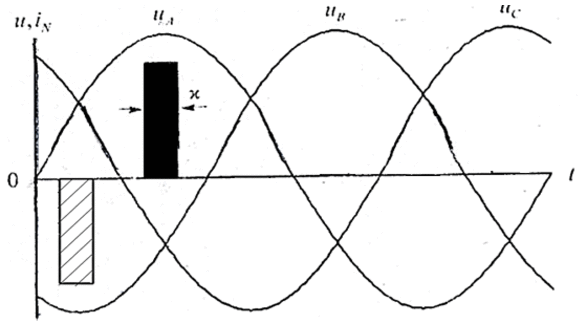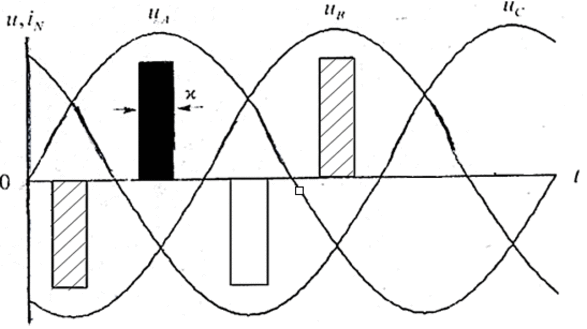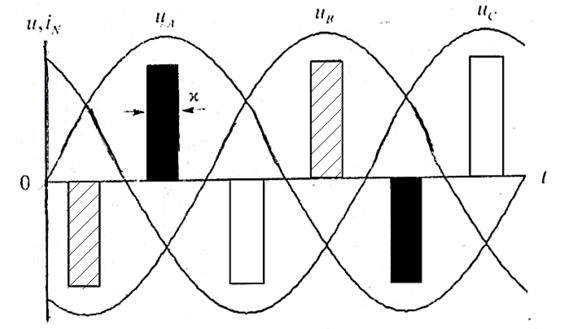
Figure 2 – Curves stress uA,B,C(t)
(animation: 4 frame, 99.4 kb)
In the case of incandescent lamps, the curves of the currents iA,B,C(t) repeat the curves of the voltage at any point in time, the sum of these currents is zero, so the neutral wire current is absent. This is not the case with CFL, for simplicity, consider the idealized curve of the current as a sequence of bipolar rectangular pulses with a width of EV, and a value of ± B. In Figure 2, the pulse current waveform of phase A shaded pulses phase B is shaded, and the pulse of phase C is shown without hatching.
In each phase observed in two pulse, so effective values of currents of the same:
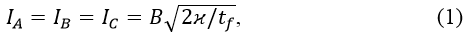
где tf = 0,02с– cycle duration at a frequency of 50 Hz.
In the summation of impulses of currents of the phases do not overlap, in this connection in the neutral wire current iN (t) has six different dimensions of pulses. In this case, the current value of the current

up to 3 times any phase current. In fact, the current pulses of the lamps partially search through, therefore the excess current in the neutral wire will be at least.
Voltage loss uA curves is determined by the current iA(t):
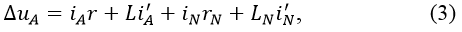
Here rN the resistance of the neutral wire, L и LN – the inductance of the phase and neutral wires.
The purpose of the calculation is the definition of the actual value UA voltage loss. But it can't be determined by RMS averaging of the graph of uA(t), and is required to first find the voltage across the lamp.
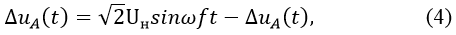
where Uн– phase rated voltage , wf = rad/s – the angular frequency.
The current value of the
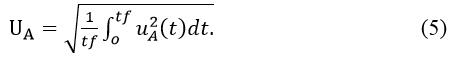
The desired voltage loss

Found the curves of the currents of the phases and neutral wires allow to estimate loading of wires.
4.A value of neutral wire
In distribution networks 0.4 kV, there is a significant problem that is associated with significant distortions of voltages in phases. When connecting power consumers in apartment buildings, it is impossible to track which of the phases is loaded more and which are less loaded. On the loaded phase voltage drops to 200...210 V and to less loaded due to the shift of zero
may increase to 240 or more. Overvoltage may result in damage to equipment consumers. While in the neutral wire four-wire a current flows, equal to the geometric sum of the phase currents.
The distortions of the stresses have a strong influence on the operation of electrical equipment. By increasing the voltage on the bulbs to 5% the luminous flux increases by 20 %, and the lifetime of such a lamp is reduced twice.
To compensate for the bias voltage, it is advisable to redistribute the load currents in phases, aligning with their values. Since there is currently no global measures to limit the current in the neutral wire, there is the idea of increasing the cross-section of neutral wire to the value of the cross section of the phase wires.
In a time when all consumers are linear and the loads on the phases are equal, then zero Explorer was not loading. Therefore, for reasons of economy, metal zero Explorer was made thinner, but now the situation has radically changed and the zero conductors are required equal phase.
Having modeled the uniform load on the phases, was received curves currents in the phases and in the neutral wire (figure. 3)
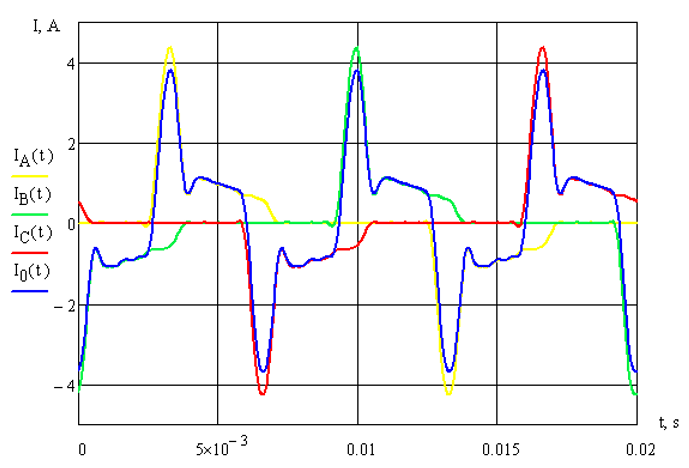
Figure 3 – The curves of the currents flowing in the phases and the neutral wire.
As can be seen from figure 3, the current in the neutral wire at evenly distributed load over the phases formed as a consequence of higher harmonics of multiples of three.
Curves of current compact fluorescent lamps are periodic, in this case, the value of even harmonics can be equated to zero, and in the neutral wire will be the sum of the currents of odd harmonics multiple of three such as 3, 9, 15, etc.
It can be concluded that the effective value of current in the neutral wire of 1.5 times the current that flows through the phase conductors.
Recalling the recommendations of the (p.1.3.8)[10] which says that zero working conductors in four-wire three-phase current system must have a conductivity of at least 50% of the conductivity of the phase conductors and, if necessary, the cross section should be increased to 100% of the conductivity of the phase conductors. In the case of data obtained from the experiment, where the load in the neutral wire exceeds 1.5 times the permissible load for the phase conductors, the inevitable overloading of the neutral wire, so even equal cross section phase and neutral wires will not change the picture. It is also necessary to note that in the experiment, the load was evenly distributed, which is impossible to do in the operation of distribution networks, given the fact that consumers everywhere are computers, which create noise in the mains. The current value will be even greater and in fact, any accident will lead to a huge failure of the electrical equipment consumers. Proceeding from the above one can clearly argue that the norms and rules of design regarding the choice of the cross-section of neutral conductor has become obsolete and require immediate adaptation and implementation.
5. The problem of disposing of compact fluorescent lamps
Discharge lamps low pressure, which include common fluorescent and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are one of the main contemporary sources of household mercury-containing wastes. Unique physical and physico-chemical properties of mercury and its compounds has caused their wide application in various fields of production and life. At the same time, mercury and its compounds are extremely hazardous substances for humans and the environment. The world health organization they are affiliated to one of the most primary pollutants.[2] the question Arises of whether to continue the ban of turnover LN the power below 100 watts, as this will push the population and state-owned enterprises to purchase CFLs contrary to economic feasibility. In addition, the absence of cities of disposal of burned-out CFLs will lead to a deterioration of the environmental situation in the country. This problem requires a systemic solution.
The total amount of mercury polluting the environment objects within the residential areas that in Russia is more than 1.5 tons per year. The average CFL contains 3-5 mg of mercury (for comparison, a thermometer contains about 0.5-3 g), and in the most perfect lamps - 1 mg. [2] About half of the Hg eventually absorbed into glass, phosphor, combines with a metal spiral, which does not evaporate in case the lamp breaks. According to the forecast, the disposal of CFLs from 175 million units in 2018 will increase to 478 million units in 2020. The proportion of recyclable lamps should be increased from 7 to 36%, which will require the creation in Russia of 34 disposal plant with a capacity of 3 million lamps per year.[2]

Figure 4 – The process of recycling waste lamps.
In Russia at the moment does not exist a centralized system of collection and recycling of mercury lamps, while in all developed countries already have special programs. For example, in Germany the use of electrical and electronic equipment is regulated by the "Law on electrical and electronic equipment" (ElektroG) of 16 March 2005, a centralized reception CFLs are carried out by LR&SG . By regulation, 90% used bulbs from legal entities and 10% from physical utilized.
In France, going 36% of compact and linear fluorescent lamps. 55% of the collection is carried out by waste collectors, 23% – distributors of lamps, a 15% installation organizations and 7% by municipalities and directly by the buyers. The activity of points of reception and processing is regulated at the state level (Decree No. 2005-829 from July 2005). Recycling is financed by an eco-tax, which amounts to a few cents per bulb. It is included in the cost. Buyers have the opportunity to take to the store the old lamp when you purchase a new one. Wholesale buyers can collect yourself, and then send to the processing company.
In the Czech Republic in 2002, the organization was created to collect Ekolamp electric equipment group 5 (lighting equipment). The company takes the lamp, regardless of brand and year of manufacture. She has a network of points of reception. Currently, there are about 1,300 nationwide. Overall, covers about 83% of the population. It should be noted that customers also have the opportunity to take the faulty bulb when buying a new. Programs in other countries, tend to have similarities with the above examples: organizations and private consumers have the opportunity to return used lamps to the seller or a special company who then transport the waste to the recycling firms.
In the Russian points of reception of spent energy saving lamps 1276 and they are located in 43 major cities. Moreover, 95% of offices work in Moscow. The number of reception points in Moscow and MO is achieved by housing maintenance offices which should be equipped with special containers and be free reception of fluorescent lamps.
A good example of hazardous waste disposal in Russia can be the results of works for the disposal of mercury-containing wastes at the plant in Veliky Novgorod, Moscow. Currently, Russia is processed no more than 40% failing mercury vapor lamps, due to the lack in many regions of their collection systems and high-performance and environmentally friendly technologies of neutralization. The exception is the Moscow region where a city-wide system for the collection and recycling of mercury lamps is not only from industrial enterprises but also from the housing sector, schools, hospitals. Thus, in Moscow every year is recycled up to 85% of mercury-containing wastes (metallic mercury is a hazard of class 1, MPC = 0.0003 mg/m3).
With further development of the CFL market in Russia power for their utilisation should reach 100 million units by 2010 year.
Conclusion
To obtain a quality supply of consumers, it has been proven that due to the high non-sinusoidal current compact lamps is a violation of voltage quality, and that this factor leads to aging of equipment and the creation of emergency situations. According to the results, it was found that it is necessary to define a new approach to the selection of the cross-section of neutral conductors of four-wire network.
When writing this abstract master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: June 2018. Full text works and materials on the subject can be obtained from Kalchenko Vitaliy Vladimirovich, or at the head of the graduation project class Edward Kurennyy.
References
- Аронов Л. В., Васильева Т. Н. Исследование влияния компактных люминесцентных ламп на несинусоидальность токов и напряжений электрической распределительной сети. — Пермь: Меркурий, 2013. — С. 31-35.
- Антипинский А.О., Алексеев Р.П. Компактные люминесцентные лампы и проблемы их утилизации в Бурятии.— 6 с.
- Измерение и оценка качества электроэнергии при несимметричной и нелинейной нагрузке / Р. Дрехслер; пер. с чешск. — М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1985.—112 с.
- Баланс энергий в электрических цепях / В.Е. Тонкаль, А.В. Новосельцев, С.П. Денисюк и др. — К.: Наук. думка, 1992.—312 с.
- Высшие гармоники в сетях электроснабжения 0,4 кВ // Новости ЭлектроТехники. 2002–2003. № 6(18) – 1(19).
- Шидловский А.К., Кузнецов В.Г. «Повышение качества энергии в электрических сетях», Киев, «Наукова думка», 1985.—268 с.
- Климов В.П., Москалев А.Д. Проблемы высших гармоник в современных системах электропитания. Практическая силовая электроника. Науч.-техн.сб. под ред. Малышкова Г.М., Лукина А.В.- М.: АОЗТ "ММП-Ирбис", 2002. Вып 5.— 14 с.
- Жежеленко И.В. Высшие гармоники в системах электроснабжения промышленных предприятий.– М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1984.—160с.
Показатели качества электроэнергии в электрических сетях
// Школа для электрика. Электронный источник:http://electricalschool.info....Правила устройства электроустановок (ПУЭ)
// Правила устройства электроустановок и связанные с ними документы. Новости энергетики. Электронный источник:http://pue7.ru....
