Abstract
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Goals and objectives of the study
- 3. Physicochemical and toxic properties of phenols
- 3.1 Physical properties of phenols
- 3.2 Chemical properties
- 3.3 Toxic properties
- 4.Characteristics of phenolic wastewater вод
- 5. Existing methods of wastewater treatment
- 5.1 Mechanical methods
- 5.2 Chemical methods
- 5.3 Physicochemical methods
- The list of sources ь
Вступ
The sewage from coke production is the main source of water pollution. Therefore, the problem of wastewater treatment by coke production is solved by a complex of physico-chemical, mechanical and biochemical methods that are used to purify local wastewater and general phenolic runoff in biochemical plants. The choice of methods and the efficiency of treatment are largely determined by how purified wastewater is used [1].
1. Relevance of the topic
The amount of sewage
at most coke
plants is 0,35–0,4 м3/т
dry batch, or 0,45–0,53 м3/coke.
Most of the runoff is supernumerated water after ammonia columns (more
than 60%).
Table
1 — Wastewater composition of various coke-chemical plants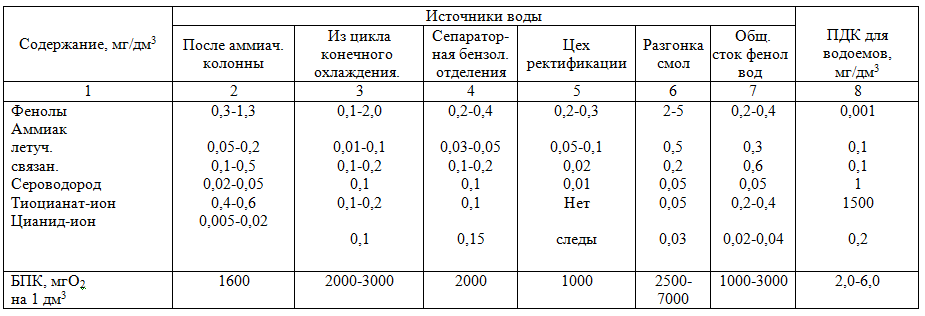
ЯAs can be seen from Table 1, phenolic wastewater is the most polluted and needs to be thoroughly cleaned.
Phenolic wastewater
is:
•excessive supramolecular water formed due to the moisture of
the charge;
•water, formed due to the contact of hot steam and industrial
water with chemical coking products during their capture and processing[2]
2. Goals and objectives of the study
The task is to analyze existing methods of wastewater treatment. In the process of the study, the greatest attention is paid to purification of sewage from phenols, which is due to its toxicity, as well as the ability to form chlorinated phenols, which have increased toxicity and a sharp unpleasant smell even at low concentrations. Identify the most effective methods for wastewater treatment, and develop ways and means to improve its efficiency.
3. Physicochemical and toxic properties of phenols
3.1 Physical properties of phenols.
Phenol C6H5OH (carbolic acid) — a colorless crystalline substance in the air oxidizes and becomes pink, at ordinary temperature it is bounded soluble in water, above 66 ° C it mixes with water in any proportions (fig. 1). Phenol — a toxic substance that causes skin burns, is an antiseptic.

Figure 1 —
Formules of phenol
(animation: 5 frames,
10 cycles of repeating, 182 kilobytes)
3.2 Chemical properties
Acidic properties – are expressed more brightly, than at limiting alcohols (color of indicators do not change):
With active metals:
2C6H5 – OH + 2Na → 2C6H5 – ONa + H2 - sodium phenate
Phenolates — of weak carbolic acid, decompose by carbonic acid кислотою:
C6H5 – ONa + H2O + СO2 → C6H5 – OH + NaHCO3
3.3 Toxic properties
Phenol is toxic. Causes a dysfunction of the nervous system. Dust, vapors and phenol solution irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes, respiratory tract, skin. Getting into the body, phenol very quickly absorbs even through intact skin areas and after a few minutes begins to affect the brain tissue. First, there is a brief excitation, and then a paralysis of the respiratory center. Even with minimal doses of phenol, sneezing, cough, headache, dizziness, pallor, nausea, loss of strength are observed. Severe cases of poisoning are characterized by unconsciousness, cyanosis, difficulty breathing, insensitivity of the cornea, a swift, barely perceptible pulse, a cold sweat, often convulsions. Often phenol is the cause of cancer [3].
4. Characteristics of phenolic wastewater
Phenolic wastewater has a pronounced smell of resin, phenol, naphthalene, hydrogen sulphide, burned peat, acetic acid. It has zero transparency and high temperature (up to 70 ° C). Contains environmentally hazardous organic and inorganic components. Among it are phenols, naphthalene, benzene, fatty acids, alcohols, aldehydes, polycyclic aromatic carbohydrates. Phenolic wastewater also contains volatile and bound ammonia, rhodanides, cyanides, hydrogen sulphide, sulfates, chlorides, etc., which concentration fluctuates in a wide range.
In addition, surface water bodies contaminated with phenolic wastewater contribute to the deterioration of the quality of groundwater sources (рис.1).

Figure 2 — Upcast of phenic effluents
Phenolic wastewater degrades the organoleptic properties of water. The unpleasant smell and aftertaste, appearing in the water at the concentration of phenol 15-20 mg / l, and cresols - 0,002-0,005 mg / l, make the water unsuitable for use. In drinking water, as a result of its chlorination, a drug smell appears at phenol concentrations of 0.001 mg / L and 0.001-0.002 mg / L of creosols. Phenolic waters are dangerous for fishery reservoirs. It cannot be used for cultural and recreational needs and for household needs. In addition, surface water bodies contaminated with phenolic wastewater contribute to the deterioration of the quality of groundwater sources [4].
5. Existing methods of wastewater treatment
5.1 Mechanical methods
Mechanical cleaning is made to separate insoluble mineral and organic impurities from the waste water.
The purpose of mechanical cleaning is to prepare industrial wastewater for deeper cleaning. Mechanical cleaning at modern sewage treatment plants consists of straining through gratings, sand trapping, sedimentation and filtration.
As a rule, mechanical cleaning provides separation of suspended solids from these waters to 90-95% and reduction of organic contaminants to 20-25%.
5.2 Chemical methods
The main methods of chemical treatment of industrial wastewater are neutralization; oxidation and precipitation. Among the methods of neutralization, the most common method of liming; Oxidizing methods include mainly chlorination and ozonation.
Chemical cleaning can be used as an independent method before the supply of sewage into the circulating water supply system, as well as before it is discharged into water bodies. The application of chemical purification in some cases is advisable (as a preliminary) before biological, mechanical or other methods of purification.
5.3 Physicochemical methods
Physicochemical methods play a significant role in the purification of industrial wastewater. It is used both independently and in combination with mechanical, chemical and biotechnological methods.
Physicochemical methods include coagulation, flocculation, flotation, sorption, including ion exchange, reverse osmosis, extraction, evaporation, electrochemical methods.
Conclusion
As can be seen from the above, sewage from coke plants is the main cause of pollution of water bodies. Judging by the composition of wastewater, the component most exceeding the MPC for ponds is phenol. Phenolic wastewater is the most polluted and needs to be thoroughly cleaned.
Currently, various methods of wastewater treatment by coking plants are used. Themost effective of the methods of deep cleaning considered are the methods of chemical and electrochemical sewage treatment. Further research will be devoted to the research of these methods of wastewater treatment and development of ways and means to increase their effectiveness.
During writing this essay, the master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: March 2018. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his scientific directorafter the specified date.
The list of sources
- Очистка сточных вод в коксохимическом производстве [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: Очистка сточных вод
- Лекция 2. Безотходные технологические процессы и охрана окружающей среды в химической технологии твердых и горючих ископаемых [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: Безотходные технологические процессы
- Урок № 33. Строение, свойства и применение фенола [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: Применение фенола
- Фенольные сточные воды. Коммунальная гигиена [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: Фенольные сточные воды
