Abstract
Research of modern radio communication standards for the provision of multiservice services in infocommunication networks
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Review of research and development
- 3.1 Analysis of existing radiocommunication standards
- 3.2 Basic Elements. Advantages and disadvantages of special purpose wireless networks
- 4. Object Analysis
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
At present, various security systems based on wired and wireless communication lines are used to protect and protect various important objects. Recently, wireless security systems have developed a great deal.
Ensuring the reliability and noise immunity of the radio channel is one of the priority tasks in building new and improving existing security systems. One of the main areas of emphasis is the need to increase the security of the radio channel of security systems against destabilizing factors. We can distinguish the following types of destabilizing factors: interception, viewing, substitution, radio electronic suppression.[1]
1. Theme urgency
As a wireless security system, we will take a wireless network of a special purpose (WNSP), namely fire alarm and burglar alarm.
Classical special purpose networks require the laying of significant length of cable networks: communication lines, signal loops, power cables that provide power to individual detectors and actuators. In fact, the whole structure is covered by a cable network in terms of the volume comparable to the building's power supply network, and in some cases surpassing it.
If the system needs to monitor an object of a large area or a complex structure, the cost of building a network will increase substantially. In addition, the installation of cable networks can not always be performed for technical or aesthetic reasons. In buildings of historical value, the use of wireless systems is sometimes the only possible way out.
The transmission of information and alarm messages to such a system occurs over the radio link. Thus manufacturers select such frequencies on which do not influence work of household devices, state of health of people and domestic animals. To protect against the influence of external interference and emissions, the transmitted signal is encrypted or modulated.[2]-[3]
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim of the work is the development of a wireless channel model for a special purpose wireless network, which ensures its reliability and noise immunity in real operating conditions.
The main objectives of the study:
1. Analyze existing radio standards and technologies;
2. Develop a mathematical model of WNSP;
3. Make the modeling of WNSP;
4. Economically calculate the cost of the model;
5. Allocate occupational safety measures.
3. Review of research and development
3.1 Analysis of existing radiocommunication standards
Over the past twenty years, a number of standards for reliable wireless communications have been developed. Of the latter, most provide sufficient for wide-scale use of information protection. To date, the introduction of standardized radiocommunication solutions has become an economically effective and safe means for monitoring and control devices operating in remote environments or at an industrial enterprise. There is a question of an optimum choice of the standard of wireless communication from set of accessible.
All standards and technologies for wireless data transmission can be classified according to a number of formal parameters. Table 1 provides a general classification of the most current wireless data transmission standards.[4]
Table 1 – General classification of basic standards for wireless data transmission
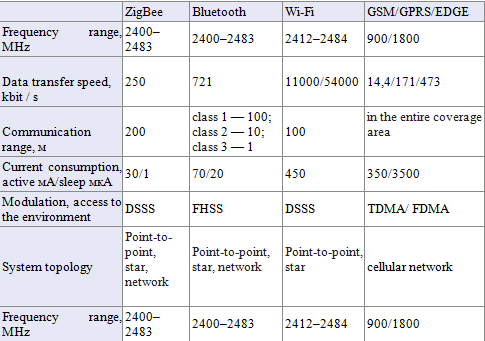
There are three technical parameters that most often determine the scope of a particular standard in a specific user application: power consumption (or current consumption), communication range and data rate. By the value of these parameters, we can conditionally select the following leaders:
Bluetooth
The basic idea of Bluetooth was to create a universal, reliable and very cheap wireless interface for wireless access. Bluetooth technology allows you to interface with various professional and consumer equipment in the modes of voice, data and multimedia, while ensuring its electromagnetic compatibility with other home or office equipment. As it was indicated in the table, there are only three classes of Bluetooth devices, if they are graded according to the radiated power: the 1st – up to 100 meters (up to 100 mW); 2nd – up to 10 meters (up to 2.5 mW); 3rd – up to 1 meter (up to 1 mW).
Wi-Fi
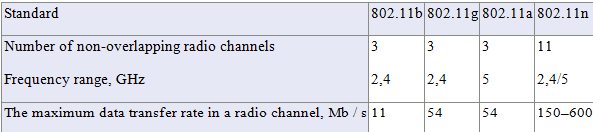
The standard of wireless data transfer Wi-Fi was created specifically to combine several computers into a single local network. Conventional wired networks require the laying of multiple cables through walls, ceilings and partitions inside the premises. Also, there are certain restrictions on the location of devices in space. Wireless Wi-Fi networks do not have these drawbacks: you can add computers and other wireless devices with minimal physical, time and material costs. To transfer information, wireless Wi-Fi devices use radio waves from the frequency spectrum defined by the IEEE 802.11 standard. There are four types of Wi-Fi standard (Table 2). 802.11n supports simultaneous operation in two frequency bands simultaneously on four antennas. The total data transfer rate is reached 150-600 Mbit / s.
Table 2 – Varieties of the standard Wi-Fi
ZigBee
In cases where the range of radio communication in line of sight is not large enough and there is a need to increase it while maintaining power consumption at a low level, it is worthwhile to pay attention to the standard of wireless communication ZigBee. The characteristic features of this standard allow:
– Create complex network solutions with automatic routing, retransmission of data packets and automatic network recovery in the event of failure of individual nodes.
– Provide a high level of protection for transmitted data.
– Flexibly configure the network nodes.
– Support in one network from several hundred to several thousand nodes.
– Get the speed of data exchange 250 kbps on the radio channel. [5]
GSM
The GSM wireless network, in its purpose, is designed not only to detect fires, but also to control access to the object. The installation of ignition sensors and optical electronic access sensors takes place in parallel and closes to one device, which is the event recorder and the transmitter of the danger signal.
It can be connected to several lines of a constantly working channel and report to centralized security control panels, to telephones or computers of owners and all stakeholders, wherever they are. All the broadcast is online. The GSM wireless network is equipped with autonomous power sources and does not depend on the connection of the object to the power supply networks.
When disconnected from the network as a result of an accident or malicious intent, the controller, together with the module and the communicator, switches to the battery mode. At the same time, continuity of observation and communication is maintained.
Having considered all possible options, WiFi has the best bandwidth and the most advanced protocol stack, but Bluetooth, GSM and Zigbee will be an ideal choice for certain tasks. Zigbee is best suited for monitoring a variety of self-powered sensors that are distributed over a large area. Bluetooth is well suited for replacing point-to-point cable connections or monitoring sensors in a small area.
Although technical standards may vary, there is still no reason to doubt the ever-increasing availability of wireless communications in the near future. With the advent of the industrial Internet of things, millions of devices will connect to the worldwide network and many of them through wireless communication. [6]
3.2 Basic Elements. Advantages and disadvantages of special purpose wireless networks
The main elements of the wireless network include:
1.Izveteteli (fire detectors)
2.Priemno – control device
3. Fire alarms
Advantages and disadvantages of special purpose wireless networks
Advantages
1. The installation can be done after finishing the finishing works in the room, since there is no need to wall-cover for concealed cabling;
2. The system has a simpler and at the same time flexible configuration;
3. Financial costs for the cable are eliminated, the cost of the installation itself is much lower, the time for performance of work is significantly reduced;
4. More reliable operation of the system as a whole. There are no breakages due to loss of contact or damage to the cables. Especially during a fire, which makes it possible to track the actual situation of the spread of fire in the building.
Disadvantages:
1. Limitations of the range of data transmission over the radio channel and the instability of its operation. Despite the protection, false alarms are detected from the electromagnetic fields of the operating equipment. The use of wireless systems in buildings the main carriers and enclosing structures, which are made of reinforced concrete or metal, is severely restricted due to the shielding effect.
2. Some tracking devices and sirens require power supplies, which limits their placement.
3. It is necessary to monitor the charge level of the autonomous power supplies for the detectors.[2] - [3]
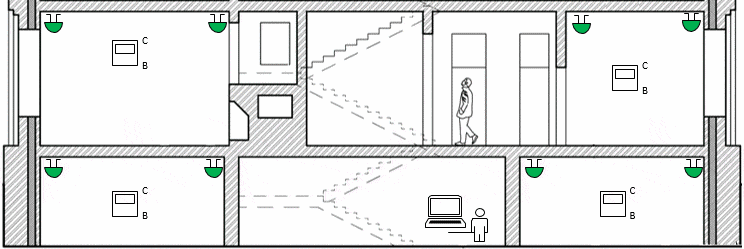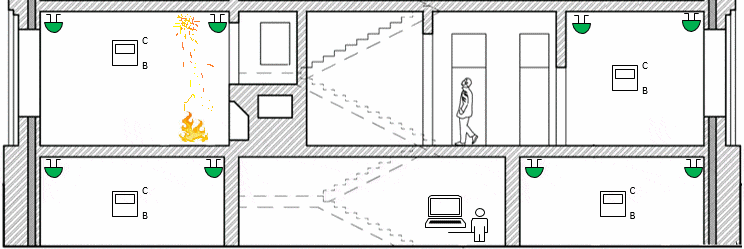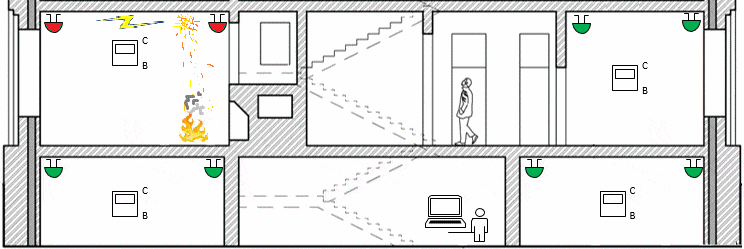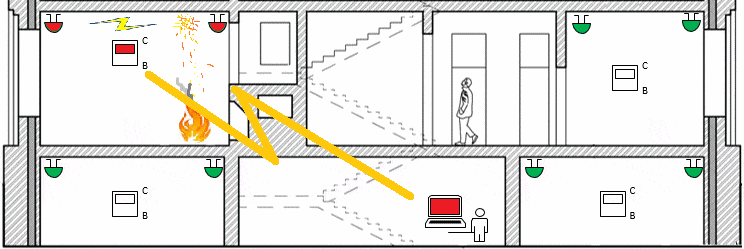
Figure 1 – The operation of a special purpose wireless network(animation: 19 frames, endless cycles of repetition, 54 KB)
4. Object Analysis
Recently, the radio channel is increasingly being used as the main medium for the transmission of information signals. The radio channel has both advantages over wired communication lines, as well as disadvantages.
Advantages include ease of organization of the communication channel, a lower cost of construction and maintenance costs.
The disadvantages are the need to address the issue of allocating a frequency resource, ensuring the reliability and noise immunity of a radio channel in conditions of a complex electromagnetic environment.
The radio channel is used in in house signaling systems, as well as in radio channel notification transmission systems. The generalized block diagram of the radio channel in the security systems is shown in Figure 2, where OK – control object, И – detector, ПКП – receiving and monitoring device, the РТР – repeater, ПЦО – centralized security guard, f - пкп, fпкп-ртр and fпкп - пцо – transmit and receive frequencies.
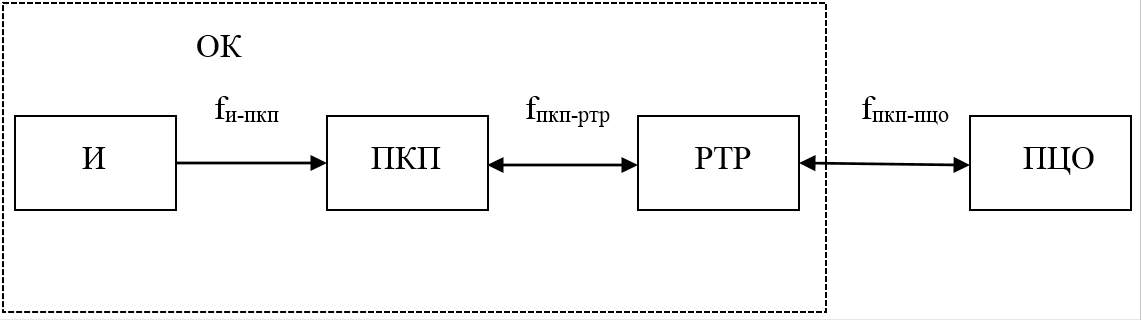
Figure 2 – Generalized structural scheme of radio channel in security systems
The radio channel is an element of the security system. An element is understood as part of a system that is distinguished by a certain degree of independence with respect to the entire system.
In this sense, in the construction of security systems using a radio channel, it is necessary to determine the location of this element in the general system and the requirements for the element for performing functional tasks.
Requirements for the radio channel in such systems may be different. So, in single level and two level systems the radio channel is characterized by:
1. The distance between the transceiver equipment from several to hundreds of meters.
2. Low output power of the transmitting devices.
3. Necessity of organization of two way communication (acknowledgment of exchange signals).
4. The possibility of automatic change of operating frequencies in the event of interference.
5. High speed data transfer.[7]
Conclusion
The master's work is devoted to the current scientific task of the study of modern radio communication standards for providing multiservice services in infocommunication networks.
Within the framework of the conducted researches the analysis of existing standards is carried out and the most suitable for design of a wireless network of special purpose is chosen, the radio channel is also investigated.
Further research is directed to the following aspects:
1. Construction of the radio channel model of a multilevel network;
2. Modeling such a network;
3.Economic calculation of the cost of the network model;
4.Measure on labor protection.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: June 2018. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Гавришев А. А. Повышение защищенности беспроводных систем безопасности: аналитический обзор публикаций // Вестн. НГУ. Серия: Информационные технологии. 2017. Т. 15, № 1. С. 5–14.
- Беспроводные линии связи [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа: http://www.klaster-plus.ua/besprovodnye-linii-svyazi/ – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
- Беспроводная пожарная сигнализация [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа: https://umniedoma.ru/besprovodnaya-pozharnaya-signalizaciya-strelec-ili-bolid/ – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
- WiFi, Bluetooth или Zigbee – какой стандарт лучше? [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа: http://ua.automation.com/content/wifi-bluetooth-ili-zigbee-kakoj-standart-luchshe – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
- Обзор современных технологий беспроводной передачи данных в частотных диапазонах ISM (Bluetooth, ZigBee, Wi-Fi) и 434/868 МГц [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа:http://www.wireless-e.ru/articles/technologies/2011_4_6.php – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
- Беспроводная охранно-пожарная сигнализация [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа: http://proffidom.ru/23-ohranno-pozharnaya-signalizaciya-gsm.html – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
- Эсауленко А.В. Моделирование и обеспечение надежности радиоканала в системах безопасности: Автореф. дис. … канд. техн. наук. Воронеж, 2015. 19 с.
