Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2.The aim of the study
- 3. Processes of digital imaging
- 4. The process of interpolation
- 5. The procedure is mathematical
- 6. Contrast
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In recent years, interest in electronic, digital and optical imaging techniques has grown significantly in order to improve their quality. Widespread coverage was given to work related to space and biomedical research. [1, 2, 3].
To improve the image, a set of operations is used to improve the image perception [ 3 ] by the observer (for example, when the size of the image changes the matrix's dimension and there are false contours) or to convert it in another image, more convenient for machining.
The procedure for improving the image is reduced to a set of operations in order to either improve the visual perception of the image, or transform it into a form more convenient for visual or machine analysis.
However, the uncertainty of the general theory of image enhancement should be noted. This is due not to the generally accepted standard of image quality.
1. Theme urgency
Digital image processing is widely used in virtually all areas of the industry. Often, its application makes it possible to get into the highest-quality latest scientific and technical level of production. At the same time, the most difficult are the issues related to the automatic removal of images and interpretation of information that is the basis for decision making in the process of managing production processes.
2. The aim of the stud
The aim of the study is to improve image quality.
In order to achieve the goals, the following tasks must be solved:
- carry out an analysis of existing systems;
- execute mathematical statement of the task;
- analyze possible solutions;
- develop a model and algorithm for solving the problem;
- carry out experimental research of the developed model;
- process and analyze the resulting primary results.
3.Processes of digital imaging
Most form systems in the first approximation can be regarded as linear and invariant to the displacement. The images shaped by such systems undergo linear spatially invariant distortions, characterized by the fact that the mechanism of their occurrence is the same for all points (x, y). Linear distortions appear in the attenuation of the upper frequencies of the original image. Visually this leads to a deterioration of its sharpness. In the process of recording the image is also distorted by the noise present in any real physical device. In a number of practically important cases, noise can be considered additive and independent of the original image.[9]
Given the foregoing, we can not see a sharp image.
Problems arise because digital images store a picture in discrete units: pixels. Any attempt to magnify the image accordingly increases these pixels.
Taking as a basis the image taken earlier by a digital video camera with a limited size of the matrix, counting the number of pixels, interpolating them to improve the quality. Image interpolation works in two dimensions and tries to achieve the best approximation in color and brightness of the pixel, based on the values of surrounding pixels.
4. The process of interpolation
Interpolating the image horizontally, vertically and using diagonal interpolation, assign the resulting values of the new matrix. As a result, we obtain a new (modified) matrix with a smaller sampling rate and a large number of pixels.
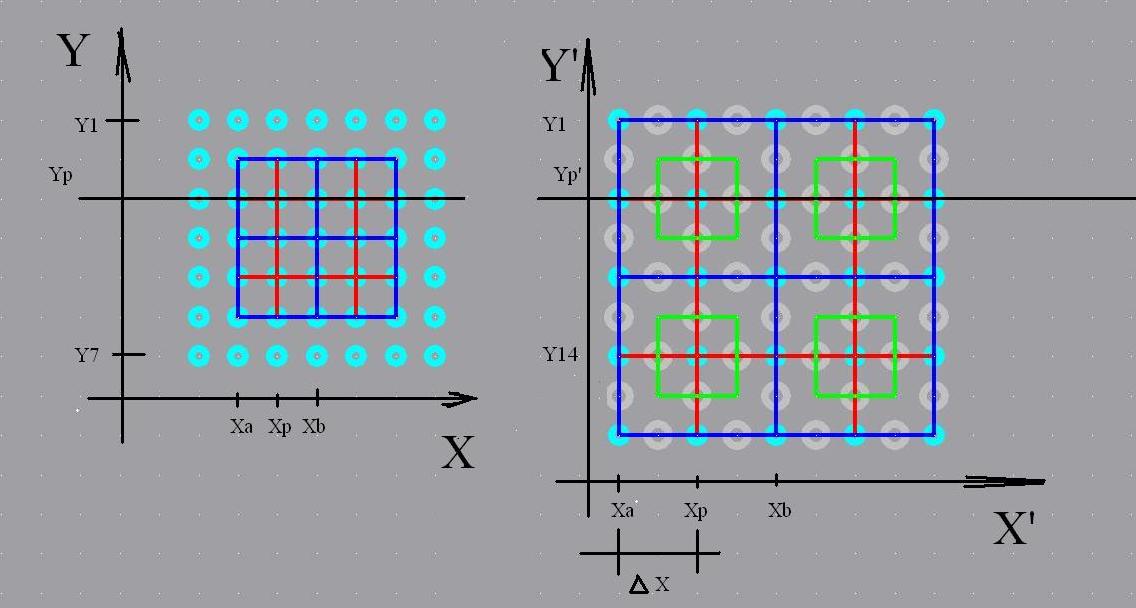
Figure 1 – Recalculate the number of pixels. Sample rate.
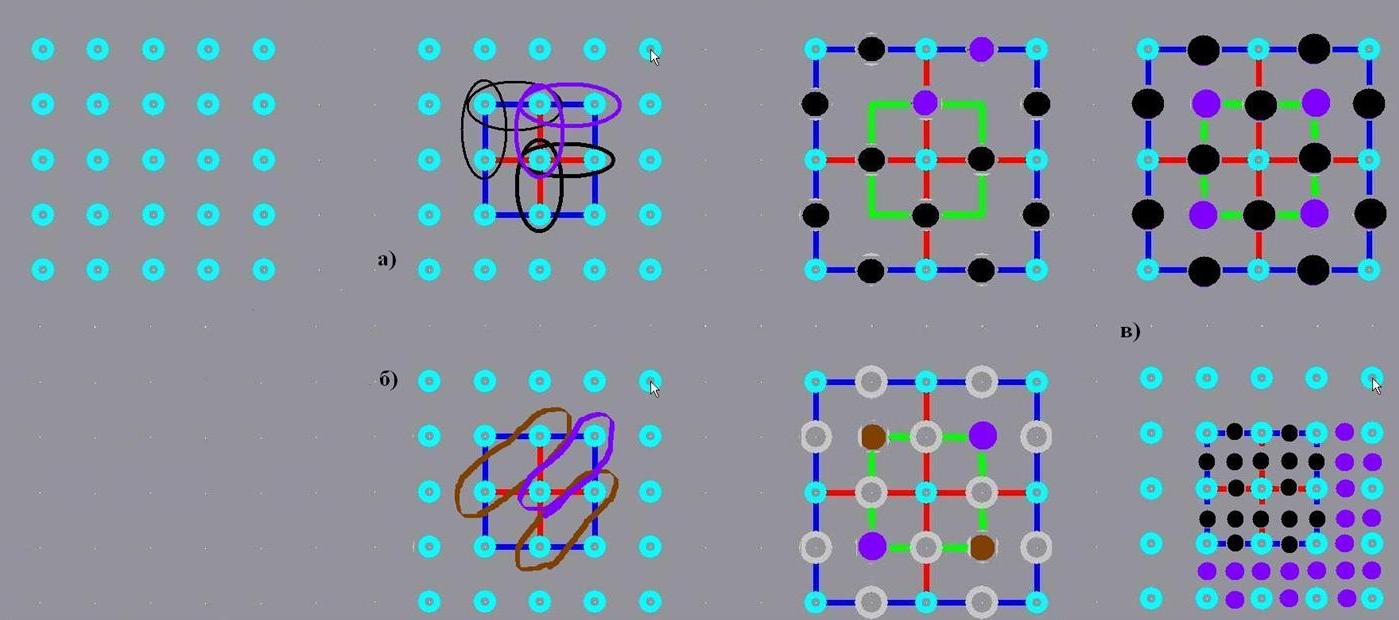
Figure 2 – Interpolation of the matrix of the original image to form a new matrix for improving the image of a larger format. a) - interpolation vertically and horizontally, b) - diagonal interpolation, c) - original image).
5. The procedure is mathematical
Mathematically, this procedure procedure looks like this:
For horizontal interpolation:
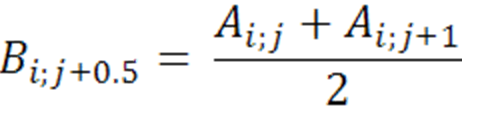
(1)
For vertical interpolation:
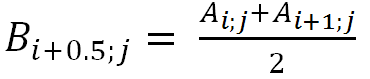
(2)
For diagonal interpolation:
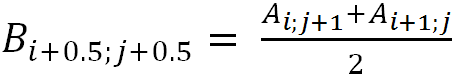
(3)
To obtain a physically natural result, we need to change the formulas:
For horizontal interpolation:
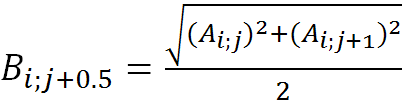
(4)
For vertical interpolation:
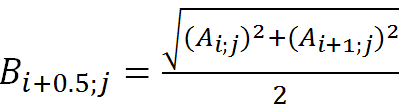
(5)
For diagonal interpolation:
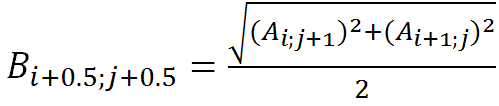
(6)
When you zoom in on an image, you can see that the image becomes less clear, pixels merge into a square matrix. What is the cause of image distortion.
Accordingly, knowing the source matrix and position of each pixel, changing the scale of visualization of the image, can significantly improve the quality of the image. Each pixel of the original image matrix must be represented (after the above interpolation of adjacent pixels) in a matrix of greater dimension (adequate output image), but with large geometric permissions.In order to improve the image quality, it is necessary that the sampling step improves the image by interpolating the values of adjacent pixels, which is smaller than the original matrix. That is, the bit for the discrete representation of the coordinates of the pixel (x, y) should be large (large bit, provide a smaller step size).
6.Contrast
To increase the contrast of the output digital image of the matrix (m, n) with an increase in the geometric dimensions of the 2 nd time of the processed image (Figure 3), it must be represented by a matrix (2m, 2, n).
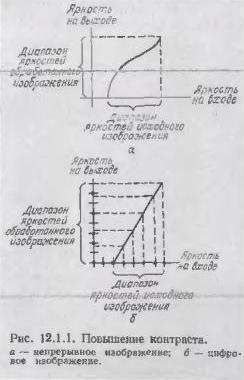
Figure 3 – Increasing contrast.[3]
To reduce the error of quantization noise according to [3] (Figure 4) when increasing the geometric dimensions of a digital image, it is necessary to form values of another 4 pixels, the neighboring elements of the matrix in relation to the output.
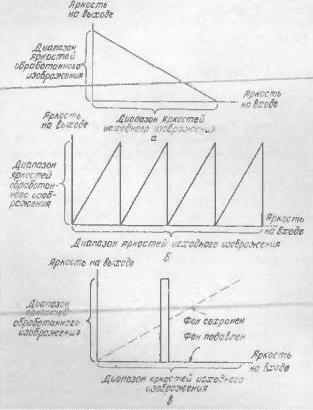
Figure 4 – Special Contrast Conversions. a - Contrast Scaling; b-saw-like contrast zoom; in-brightness of the cut.[ 3 ].
In the source [1] the method of forming the values of the processed image (where the value of the pixel is determined by the integral of convolution) is described.
Conclusions
In the master's work the actual scientific and technical task is devoted to the improvement of the quality of the digital image. The algorithms of transformation of the initial digital (matrix) image into a larger image are considered. In order to enhance the resolution of the image. The algorithms of forming new elements of a matrix of greater dimension are realized, by increasing the dimension of the output matrix (due to the interpolation of neighboring pixels).
The formation of new values of contrast and brightness, new elements of the matrix of adjacent with the output occurs by the discrete convolution of two functions.
When writing this essay the master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: June 2018. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after the specified date.
References
- Гонсалес Р., Вудс Р. Цифровая обработка изображений.- Москва: Техносфера, 2005.- 1072с.
- Грузман И.С., Киричук В.С., Косых В.П., Перетягин Г.И., Спектор А.А.Цифровая обработа изображений в информационных системах: Учебное пособие.- Новосибисрк: Изд-во НГТУ, 2000. - 168.
- Прэт Э. Цифровая обработка изображений: В 2-х книгах, Пер. с англ,- М.: Мир, 1982.
- Суранов А. Я. LabVIEW 8.20: Справочник по функциям. – М.: ДМК Пресс, 2007. – 536 с.
- Романюк О.Н., Обідник М.Д. Один із підходів до підвищення швидкодії зафарбування. Наукові праці ДонНТУ випуск 21 (183) -116.
- Ю.В. Визильтер, С.Ю. Желтов, В.А. Князь, А.Н. Ходорев, А.В. Моржин. Обработка и анализ цифровых изображений с примерами на LabVIEW IMAQ Vision - М. ДМК Пресс. 2007.- 464 с.
- Грузман И. С. Цифровая обработка изображений в информационных системах: Учебное пособие. / И. С. Грузман, В. С. Киричук, В. П. Косых, Г. И. Перетягин, А. А. Спектор. – Новосибирск: Изд-во НГТУ, 2000. – 168 с.
- Фурман Я. А. Цифровые методы обработки и распознавания бинарных изображений. / Я. А. Фурман, А. Н. Юрьев, В. В. Яншин. – Красноярск: Изд-во Краснояр. ун-та, 1992. – 248 с.
- Богнер Р., Введение в цифровую фильтрацию. / Р. Богнер, А. Константинидис. – Москва.: Мир, 1976. – 216 с.
- J.F. Asmus, et al., «Computer enhancement of the Mona Lisa,» Perspectives in Computing, vol. 7, pp. 11-22 (1987).
