Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Principles of IP Telephony
- 4. MPLS technology
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Currently, there are many different programs that allow you to conduct telephone conversations via the Internet or a local network. Such a possibility does not surprise anyone, it only requires a computer connected to the network, a corresponding program and a microphone with headphones. Of course, such a solution is clearly not suitable for organizing a telephony in a serious company (yet such means are more entertaining in nature), but the idea of ??voice transmission through the data transmission network is very tempting, especially if the firm has many offices in different cities. And in this case, sooner or later the question arises about the introduction of IP-telephony.
IP-telephony, in fact, is a method of organizing telephone communications using a data network for voice transmission. The advantages of such a telephone communication organization are obvious, and the main one is a significant reduction in the cost of calls between offices located in different cities. In addition, this approach allows you to enter a single number plan for the entire organization, when you do not need to remember the telephone codes of the cities in which the company's branches are located. And of course, do not forget about the introduction of additional services.
1. Theme urgency
The development of modern information technologies in telecommunications opens up huge opportunities for the development of telecommunications providers and operators and prospective growth, offering customers not only new services, but also affordable prices for them. However, technical progress is closely related to the problem of ensuring the quality of voice transmission.
At present, there is a tendency for an ever increasing share of voice traffic in the total volume of information transmitted over packet-switched networks. At the same time, due to the loss of speech packets during their processing and transmission, pauses in the speech signal and the appearance of the echo signal effect are possible on the receiving side.
Thus, the problem of increasing the intelligibility of speech transmitted over a packet-switched network is actual. When solving it, the advantages of real-time speech processing should be preserved, as well as the possible delay values [1].
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim of this work is to improve the methods of providing VoIP quality indicators in distributed networks based on the results of theoretical and experimental research of existing algorithms for replacement of lost packets in the transmission of a speech signal.
To achieve this goal, it is necessary to solve the main tasks:
- Conduct an analysis of existing methods to ensure quality indicators (QoS).
- To study the algorithms of queue management.
- Improve the method of weighted fair service.
- Simulate and explore processes on the network.
The result of the research will be recommendations for improving the quality of services in the network to meet customer requirements.
3. Principles of IP Telephony
IP-telephony is a technology that allows you to use the Internet or any other IP-network to conduct telephone conversations in real time.
To make a call, a voice signal is used, which is converted into a compressed data packet (analog signal). Next, packets are transferred over packet-switched networks, in particular IP networks. When the receiver reaches the packets, they are decoded into the original voice signals. These processes are possible due to the large number of auxiliary protocols. This also allows full-duplex communication [2].
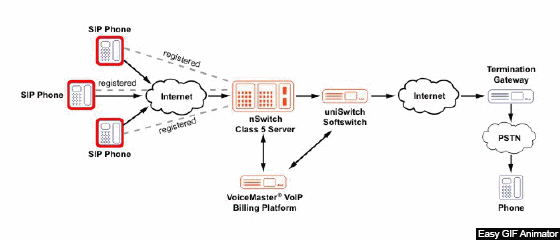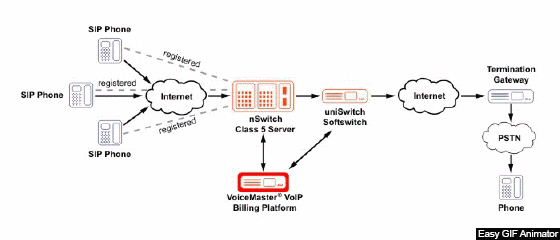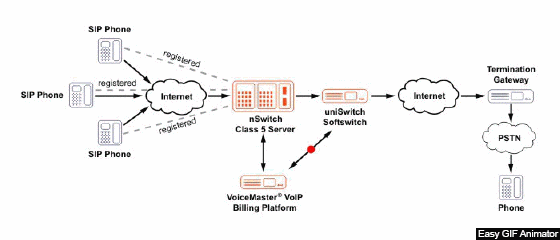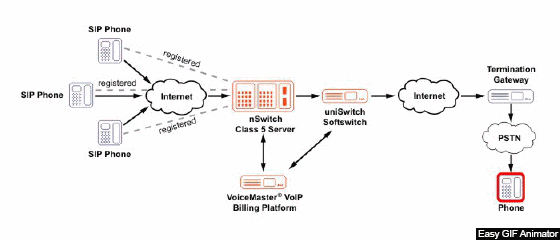
Figure 1 – Example of Voip network operation
(animation: 20 frames, endless repetition cycle, 163 kilobytes)
IP-telephony is based on two operations: converting analog speech to digital form, and vice versa, inside the encoding / decoding device and packaging into packets for transmission over the IP network.
4. MPLS technology
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is a technology for fast packet switching in multiprotocol networks based on the use of labels. MPLS is designed and positioned as a way to build high-speed IP backbones, but the scope of the technology is not limited to IP, but extends to the traffic of any routed network protocol. Traditionally, the main requirements for the technology of the backbone network were high throughput, low latency and good scalability.
The MPLS architecture provides the construction of backbone networks with virtually unlimited scalability, increased traffic processing speed and high flexibility in terms of additional services. In addition, MPLS technology allows the integration of IP and ATM networks, whereby service providers will not only be able to save funds invested in asynchronous transfer equipment, but also benefit from sharing these protocols [10].
Advantages of MPLS technology:
- Separation of route selection from IP address analysis.
- Accelerated commutation.
- Flexible support for QoS, integrated services and virtual private networks.
- Effective use of an explicit route.
- Preservation of investments in installed ATM equipment.
- Separation of functionality between the core and the boundary area of the network.
The introduction and maintenance of MPLS networks is more unified and simplified compared to conventional IP networks due to the use of LDP and RSVP protocols. The first of them is intended for automatic routing of new paths in MPLS-domain. The RSVP protocol allows you to manage the distribution of bandwidth between virtual channels on the network, providing a guaranteed required level of quality of service.
MPLS technology is characterized by high scalability and is considered as the most promising for the transmission of IP traffic. It is standardized by the IETF, therefore, as in the case of IntServ, in the event of a deviation from the specifications, there may be problems with the compatibility of equipment from different manufacturers [11].
Conclusion
The most promising technologies for QoS are MPLS and Int-DiffServ due to the fact that they combine the best aspects of both models. Thus, in MPLS, routing by labels allows for a more flexible allocation of network resources, which allows using several alternative traffic delivery paths for creating high-speed backbones, and interconnecting local networks. In turn, Int-DiffServ represents the golden mean of the price / quality ratio. But for these technologies, there are restrictions that do not allow the use of these methods. MPLS is still poorly distributed and is an expensive technology for corporate networks, and Int-DiffServ requires certain implementation costs and can not provide high compatibility rates.
When writing this essay, the master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: June 2018. Full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after the indicated date.
References
Список источников
- Dissercat – Электронная библиотека [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.dissercat.com....
- Телефония по Voip протоколу [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://globalhome.su....
- Тарасов В. Ю., Дроздов К. И. Качество речи в IP-сетях [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.ccc.ru/magazine....
- Макарова О. С. Способ оценки зависимости качества связи в системах IP-телефонии от критических параметров IP–сети // Молодой ученый. – 2011. – №12. Т.1. С. 83–86.
- Мониторинг и отладка VoIP–сетей с помощью сетевого анализатора [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://www.tamos.ru....
- Яновский Г. Г. Оценка качества передачи речи в сетях IP [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://niits.ru....
- Пролетарский А. В., Баскаков И. В., Федотов Р. А., Мельников С. А. IP-телефония в компьютерных сетях [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://www.intuit.ru....
- Материал из Национальной библиотеки им. Н. Э. Баумана [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://ru.bmstu.wiki....
- Гилазов М. Н. Влияние качества обслуживания на коммутацию IP-пакетов // Молодой ученый. – 2015. – №11. – С. 282–285.
- Гольдштейн А. Б., Гольдштейн Б. С. Технология и протоколы MPLS/ А. Б. Гольдштейн, Б. С. Гольдштейн – СПб.: БХВ, 2005. – С. 304.
- Климов Д. А. Построение сетей MPLS VPN. T-Comm: Телекоммуникации и транспорт/ Д. А. Климов – №51 – 2009. – С. 57–59.
