Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal, object and subject of the research
- 3. Modeling of the LTE frame planning subsystem
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The concept and architecture of quality of services (QoS) in 2G, 3G and LTE are defined in the TS 23.107 of the 3GPP consortium [1]. The TS 37.324 describes a new SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol) protocol that controls QoS flows in fifth-generation networks [2]. Within the 3GPP specifications, the following operator features are defined: quality of service control and tariffication control [3]. In addition, the TS 23.207 describes such an aspect as end-to-end quality of services (E2E) [4].
Considering the task of providing Е2Е QoS, it is possible to draw an analogy with links of a single chain [5]. Since the data pass through a number of intermediate network devices, QoS support requires the interaction of all network elements along the traffic path, that is, end-to-end
. QoS guarantees are as true as they are provided by the weakest
element in the chain between the sender and receiver. Thus, the task of sending and receiving data with acceptable quality parameters is common for the operator's network segments – Evolved Packet Core (EPC) and radio interface (E-UTRAN), which will be emphasized in this master's thesis.
1. Theme urgency
Important and urgent problems in the field of quality of service, resource allocation are the problems of planning [6,7]. In the QoS provisioning process, frame scheduling is required in order to determine which packet will be served first in a particular queue [8-11].
Due to the growing popularity of LTE technologies, there is an increasing interest in the development of downlink scheduling algorithms worldwide [12]. The LTE schedulers system base station use the FCFS scheduling algorithm (first come, first served) or its modification RR (Round Robin Scheduler). To further improve the quality and efficiency of data transmission in LTE networks, research and selection of a scheduling algorithm is required, and that will reduce the average waiting time in the queue, average packet processing time, and the number of dropped packets. This, in turn, will increase throughput and will allow organizing access to channel resources to a greater number of subscriber stations. Thus, the task of analyzing and choosing a more efficient frame scheduling algorithm is relevant.
2. Goal, object and subject of the research
Research object: service quality management process in mobile networks.
Research subject: LTE downlink scheduling method of network resources
Research goal: improving mobile networks efficiency by developing a method for distributing network resources.
3. Modeling of the LTE frame planning subsystem
General approaches to modeling the parameters of 3G and LTE mobile networks are described in [13]. The article briefly describes the advantages and disadvantages of actual system-level (SLS) and link-level (LLS) simulators. Taking into account the task set, the OMNeT++ discrete event simulator is selected. This software has a powerful queuing library which is named QueueingLib. In addition, scientists from the University of Pisa have developed an OMNeT++-based LTE/LTE-Advanced network simulator that supports scheduling methods that are used in real LTE eNodeBs.
A brief introduction to OMNeT++ with an emphasis on queuing systems (QS) is described in [14].
The frame scheduling subsystem model developed in the OMNeT ++ environment consists of four sources of incoming traffic, Classifier module, four passive queues, server (scheduler) and sink.
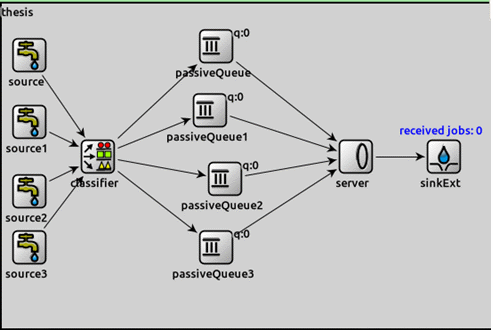
Figure 1 – The frame scheduling subsystem model
Number of jobs generated from each source: 100.
Some results obtained during the simulation:
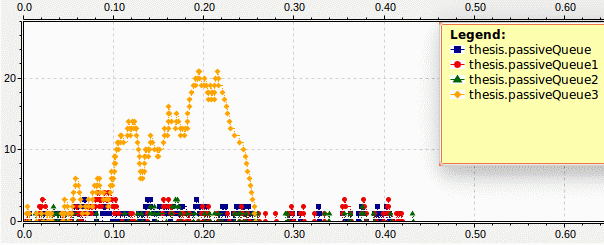
Figure 2 – Filling queues by jobs
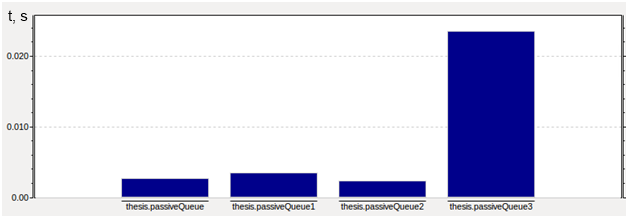
Figure 3 – Average time spent in the queue, s
The average time that jobs spent in the queue ranges from 0.002 s to 0.023 s for different queues. As you can see, with a preset intensity, queue 3 is the fastest-filled.
Conclusion
Thus, the planning subsystem which is located at the MAC level in the LTE protocol stack plays an important role in ensuring quality of service. The correct choice of the scheduler determines the speed with which the frames will be processed, which in turn affects the QoS perception by end users.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: June 2019. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Specification # 23.107 [Электронный ресурс]: 3GPP Portal. URL: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/.. (дата обращения: 27.12.2018).
- Specification # 37.324 [Электронный ресурс]: 3GPP Portal. URL: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/.. (дата обращения: 27.12.2018).
- Степутин А.Н. Мобильная связь на пути к 6G. / А.Н. Степутин, А.Д. Николаев. – Москва-Вологда: Инфра-Инженерия, 2017. – 796 с.
- Specification # 23.207 [Электронный ресурс]: 3GPP Portal. URL: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/.. (дата обращения: 27.12.2018).
- Якименко С.И. Анализ подходов к обеспечению QoS в сетях LTE для сервисов IoT [Текст] / С.И. Якименко, И.А. Молоковский // Труды Северо-Кавказского филиала Московского технического университета связи и информатики – Ростов-на-Дону.: ПЦ «Университет» СКФ МТУСИ, 2018. – С. 447-452.
- Аунг Мьо Маунг. Дисциплины обслуживания очередей для планировщика кадра в QoS сети WiMAX. // Актуальные проблемы информатизации. Развитие информационной инфраструктуры, технологий и систем – 2007. Всероссийская межвузовская научно-практическая конференция: Материалы конференции. – М.: МИЭТ, 2007 г. – С. 70.
- Аунг Мьо Маунг. Планирование кадра в режиме TDD для сети WiMAX. // Актуальные проблемы информатизации. Развитие информационной инфраструктуры, технологий и систем – 2008. 2-ая Всероссийская межвузовская научно-практическая конференция: Материалы конференции. – М.: МИЭТ, 2008 г. – с. 98.
- Cao Y., Li V / Scheduling Algorithms in Broad-Band Wireless Networks // IEEE PROCEEDINGS OF THE IEEE, VOL. 89, N 1, JANUARY 2001. p. 76-87.
- Le L. B. Queuing analysis and admission control for multi-rate wireless networks with opportunistic scheduling and ARQ-based error control / L. B. Le, E. Hossain, A S. Alfa // in Proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC’05), Seoul, Korea, 16-20 May 2005: proceedings. – Seoul: IEEE. – 2005 – р.3329-3333. DOI: 10.1109/ICC.2005.1495038.
- Bonald T. A queuing analysis of max-min fairness, proportional fairness and balanced fairness / T. Bonald, L. Massoulie, A. Proutiero, J. Virtamo // Queueing Systems. – 2006. vol. 53. – р. 65–84.
- Sousa E.S. Cognitive radio: A path in the evolution of public wireless networks / E.S. Sousa, B.M. Sadler, E. Hossain, S. A. Jafar // Communications and Networks, Journal of. – 2009. – vol.11, № 2. - р.99-103.
- Niyato D. Call-level and packet-level quality of service and user utility in rate-adaptive cellular CDMA networks: a queuing analysis / D. Niyato, E. Hossain // Mobile Computing, IEEE Transactions on. – 2006. – vol. 5, №. 12. - р. 1749-1763.
- Якименко С.И. Использование возможностей MatLAB для моделирования и исследования физических каналов LTE [Текст] / С.И. Якименко, И.А. Молоковский // Автоматизация технологических объектов и процессов. Поиск молодых: сборник научных трудов XVIII научно-технической конференции аспирантов и студентов в г. Донецке 22-24 мая 2018 г. – Донецк, ДонНТУ – 2018. – C. 135-138.
- LTE User Plane Simulation Model for INET & OMNeT++ [Электронный ресурс]: simulte.com. URL: http://simulte.com/ (дата обращения: 27.12.2018).
