Abstract
Butsyak Daria ,Artamonov Vladimir, Romanko Victoria — Development of ecological network of Donetsk region by means of inclusion coal mining disturbed lands. The analysis of some special features of spoil heaps location within Donetsk region is given in the article. This has allowed to consider the main opportunities for developing of ecological network formation that gives the chance to expand it including coal mining disturbed lands as restoration elements.
The problem of preserving a biological and landscape diversity is primary for achievement of sustainable development. For the first time at the international level, this principle was formulated at the United Nations Conference, held in Rio de Janeiro 3–14 June 1992. The principle finds the most concrete embodiment in the idea of ecological network.
In Europe this idea was accepted as the main direction of realization of the Pan-European biological and landscape strategy approved at the Third Ministerial Conference ‘Environment for Europe’ held in Sofia (Bulgaria), from 23 to 25 October 1995. According to this strategy, should be establish at the Pan-European Ecological Network (PEEN) which would unite areas of environmental interest with natural or seminatural vegetation in the system of ecological corridors for stimulating resettlement and migration of species, to provide population survival and restoration, as well as preservation and protection of their habitats [1].
The ecological network (econet) is a system functionally and territorially interconnected natural territories (water areas), providing a sustainable condition of the biosphere and the ecological functioning of natural systems. In essence the ecological network represents protected areas and ecological corridors connecting them. Econet includes a complex of the protected natural territories (reserves, national parks, wildlife areas, etc.) which are connected among themselves by the ecological corridors organized due to socio-economic and cultural characteristics of the region. The Ecological Network concept considers the region as a unit with natural interrelations, without administrative borders which are formal from the ecological point of view. The purpose of the Ecological Network concept is maintaining a biological and landscape diversity and achievement of steady environmental management.
The spatial structure, usually consists of the following elements of ecological network (fig. 1):
- Core areas are a natural areas, or the regional ecological centers which are formed on the natural territories having a high biological and landscape diversity, performing the main set of the ecosystem functions / services incorporating objects of nature reserve which share considerably exceeds average values.
- Connection elements (ecological corridors) are sites of natural landscapes of various configuration and the size which are communication elements, providing the corresponding conditions for preservation of ecosystems and exchange of a gene pool between populations of various core areas and regions. Ecological corridors belong to nature protection territories, however unlike key territories in their limits the traditional way of managing (which is essentially not breaking structures and functioning of ecosystems) can remain.
- Buffer zones provide protection of core areas and connection elements against anthropogenic influence. Are transitional strips between natural territories and territories of economic use.
- Restoration areas provide formation of spatial integrity of ecological network for which primary measures concerning reconstruction of their primary natural state have to be executed. These are such territories in which it is necessary and possible to restore a natural vegetation cover and to carry out repatriation of plant species and animals. A certain restored territories after holding the relevant activities for a renaturalization, can be included in structure of the core areas or connected territories, or to turn directly into them [2].
Разработчики моделирующих программ при создании своих продуктов не достаточно ориентируются на современные технологии модуляризации (COM, CORBA) и предпочитают выполнять реализацию самостоятельно. Все модули могут быть не просто автономными, а уже традиционно считаются независимыми программными продуктами. Наиболее простой и легкий в создании модуль - математическое ядро.
Анализ программ для моделирования динамических процессов
В тестируемой модели для разработки системных программ, в т.ч. реального времени, является модель гармонического осциллятора. Она позволит определить частоту и точные характеристики разрабатываемых программ.
В качестве исследуемой функции возьмем уравнение Ван дер Поля, амплитуда колебаний которого затухает во времени:
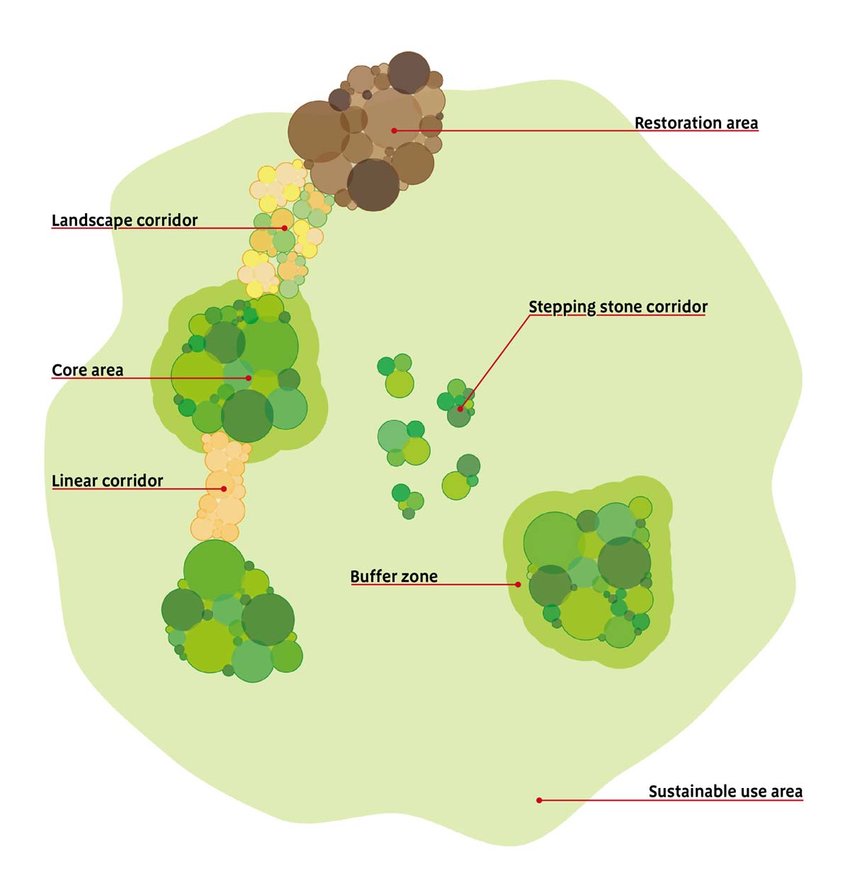
Figure 1 - The components of ecological networks
The Donetsk region is characterized by a large number of coal–mine disturbed lands because of the highly developed coal mining industry. Owing to such development natural landscapes of the region are strongly fragmented and are under strong technogenic and anthropogenic pressure that sets for society urgent tasks of their protection, rational use, reproduction and inclusion in biotic circulation of earlier unused resources.
It has strong negative impact on a problem of maintaining landscape and biological diversity of the region which state do not conform to modern requirements of the balanced environmental management. Formation of ecological network as complete complex of ecosystems, habitats, types and landscapes can become a basis for the solution of this environmental problem in the region. But formation of ecological network in industrial regions is impossible without attraction of additional post-technogenic elements.
Feature of the Donetsk region is a large number of spoil heaps which are territorially located in the form of an extended strip from the west to the east. Such location gives the possibility to use these technogenic landscapes as restoration areas of regional ecological network which is consided to be a part of ecological corridors which are broken owing to anthropogenic human activity.
According to the State Committee for Environmental Policy and Natural Resources, now the territory of the Donetsk People’s Republic are officially documented 521 spoil heaps, 83 of which burning, 54 — rehabilitated and planted trees and shrubs. Only in Donetsk there are 154 spoil heaps. All these waste heaps occupy the space about 4 thousand hectares and there are about 900 million cubic meters of waste.
Terricones have negative effect on the environment (fig. 2). They occupy the huge spaces of valuable lands, reduce productivity of adjacent lands, pollute the atmosphere gases and dust, break the hydrogeological mode of the area. Besides, the waters which are flowing down from dumps destroy vegetation in the adjacent territory. Therefore, the terricones located near settlements worsen sanitary and hygienic living conditions of people.
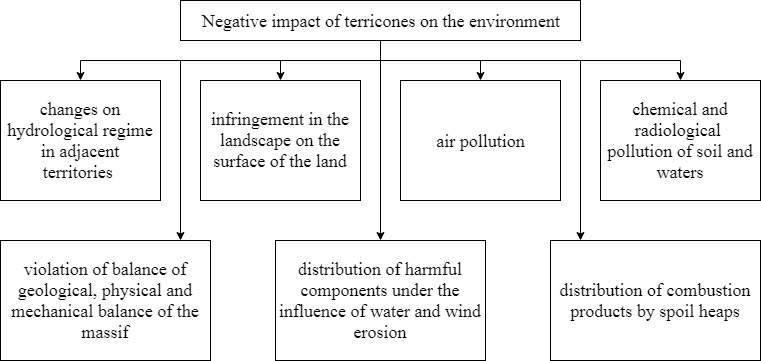
Figure 2 – Negative impact of terricones on the environments
The main directions of prevention and elimination of negative impact of spoil heaps have to be provided with a package of practical measures aimed at meeting the requirements concerning protection of the surrounding environment, the current legislation, sanitary standards and rules, hygienic norms, fire-prevention standards, local ecological conditions and restrictions. Operation of the existing spoil heaps and also their extinguishing and exploitation have to be carried out on special projects or sections of construction projects (reconstruction) of mines, concentrating factories and passports of a spoil heap which have to contain the following requirements [3]:
- prevention of self-ignition;
- technologies of extinguishing and exploitation;
- ensuring stability at operation, extinguishing and exploitation;
- recultivation.
At an optimum outcome of recultivation of spoil heaps it is possible to involve them in formation of ecological network as they become perspective recovery elements for the message of ecological corridors.
Considerable part of ruptures of ecological corridors in the Donetsk region is caused by anthropogenic (technogenic) activity. Use the rehabilitated of technogenic landscapes as restoration elements of ecological network will allow to break barriers to migration of a biota.
Use of inactive and not–firing planting spoil heaps when forming ecological network is one of a possibility to control its development conditions. Improving management process of formation of ecological network thus we not only we will provide full value of its structure, but also we will solve one of the main problems of the region: a problem of spoil heaps of mines which occupy the huge spaces of land resources and do harm to the environment and health of the population.
Main objective of formation of ecological network is maintaining a biological and landscape diversity for achievement of sustainable development of the region. Therefore global benefit of creation of econet of the Donetsk region is providing a favorable ecological situation in the region, creation and maintenance of necessary conditions for maintaining a specific variety.
At successful gardening and inclusion of spoil heaps in ecological network they can have the following positive ecological effects:
- restoration of ruptures of ecological corridors for migration of a biota;
- providing safe ecological conditions for life and health of the population;
- increase areas for the rest and health care;
- growth of nature protection capacity of the region;
- ensuring restoration of biogeochemical circulations in the environment, reduction of threat of degradation and loss of fertility of lands;
- solution of the problem of deficiency of green plantings;
- decrease in pollution of atmospheric air dust and harmful substances from a surface of spoil heaps.
At this stage it is difficult to estimate economic effect of creation of ecological network of the region as introduction of nature protection actions always demands big expenses, and can be productive only in the long term. However increase in tourist capacity of the territory and decrease in economic damage owing to decrease in pollution of environment are positive economic effects of formation of ecological network. And considering the high nature protection importance of this project it is possible to consider its introduction expedient.
The main social effects are:
- preservation of esthetic value of natural landscapes;
- decrease in incidence of the population and increase in life expectancy;
- improvement of working conditions and rest.
Thus, creation of ecological network of the Donetsk region with inclusion of spoil heaps as the additional restoration areas conducts to the solution of a number of environmental and social problems.
References
1. Глухов А. З., Сафонов А. И. Экосеть: обоснование, концепции, опыт. Донецк: ДонНУ, 2011. — 320 с.
2. Шапарь А. Г. Ландшафтно–гидрографические подходы к созданию экологической сети. Днепропетровск: Монолит, 2002. — 71 с.
3. Шматько В. Г. Экология и организация природоохранной деятельности : учеб. для вузов. Киев: КНТ, 2008. — 304 с.