Abstract
When writing this essay, the masterʼs work is not yet completed. Final completion: June 2020. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his leader after the specified date.
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Research and Development Overview
- 3.1 Overview of international sources
- 3.2 Overview of national sources
- 4. IPTV network structure
- 5. IPTV network construction method for telecom operators
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
More recently, the dense forest of antennas on the roofs of high-rise buildings was replaced by cables with hundreds of imported channels, and if the operators did not reach out, satellite dishes. Now a new transition is expected – in the era of interactive television IPTV. This is explained not only by the advantages of technology, but also by a factor that at first may seem unobvious – in the case of IPTV, it is not television that controls the viewer, as the century went on, but the viewer – television. IPTV is not broadcast over the Internet, it only uses the Internet data transfer protocol, the technology does not depend on the global network, but on the provider that provides the service. IPTV can be transmitted over closed networks supported by a telecommunications company. This is the most modern and optimal option in terms of “quality+capabilities”. It comes to the house via the same cable as the Internet, it can potentially supply an unlimited number of channels, always high quality pictures, a large selection of additional services (IPTV contains a certain set of functions and is available only to subscribers of the service).
1. Theme urgency
Modern telecommunication technologies practically do not limit Operators and users in the field of services provided. At the moment, the greatest interest for most services is caused by the properties of interactivity (when the user becomes an active participant in the process of providing the service), personalization (when the user receives individual content for him) and mobility (when access to the service is possible not only over fixed networks). At the same time, the properties of new services may present such disproportionate (compared with the properties of traditional services) requirements for telecommunication resources that they may become unprofitable for the Telecommunications Operator. For this reason, a comprehensive study of the properties of modern telecommunication services is extremely relevant. The object of research in this work is the family of services of IPTV systems, the number of subscribers of which is steadily growing. According to the research firms Digital TV Research and TeleGeography, the number of subscribers of IPTV systems in the world exceeded 155 million, which is about 25 percent of the client base of the broadband Internet. Among all the methods for delivering television content, it is digital television technology over IP (IPTV) that maximally satisfies the new properties of services, which makes it more and more popular in the telecommunications services market and therefore relevant from the point of view of scientific research.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim of this work is to increase the efficiency of the provision of interactive services by IPTV systems in ISP networks by caching data.
Main tasks of the research:
- To analyze the structure of the multiservice network that provides the IPTV service.
- Describe the model of the process of organizing the interactive service “Video on Demand”.
- To develop a caching algorithm for the implementation of the interactive video-on-demand service that allows calculating the incoming proxy server bandwidth.
- Carry out a simulation of the network with the provision of IPTV services.
- Conduct a feasibility study.
Research object: IPTV family of services.
Research subject: caching data in an IPTV network video server.
3. Research and Development Overview
Since interactive television is one of the most important telecommunication systems, the problems of their construction and implementation have been widely studied by both American, European, Japanese scientists, and domestic experts.
3.1 Overview of international sources
Book of foreign authors Fathi Suleiman Mohamed, Azad Sayfula, Pathan Al Sakib Khan IPTV delivery networks: a new generation architecture for Live and Video-on-Demand services
[1] is a guide to modern technologies related to the process of providing services both in real time and on demand within IPTV delivery networks. The authors of an international expert group are introducing a framework for a delivery network applicable to live and video-on-demand services. They address the fundamental problems of IPTV delivery networks and study the quality of service (QoS) problem for IPTV delivery networks, which emphasizes security and anomaly detection in relation to quality.
Since IPTV is an ever – evolving system, it is often the subject of research papers for various degrees. Gerges Mansour Salama Mansour in his dissertation Study of IPTV network models
[2] offers a study of the network aspects of IPTV and analysis of the numerical characteristics of IPTV traffic and quality of services through IPTV-network.
3.2 Overview of national sources
Issues related to IPTV technology can be found in many international and national sources, such as study guides, scientific articles and dissertations. Kireeva N.V. and Buranova M.A. in their work Ensuring the quality of service in multiservice networks
[3] provide information on building an IPTV network, IP-telephony, calculate the characteristics of voice packet transmission and methodology for evaluating the quality parameters of packet speech transmission.
The dissertation by M. Makolkina Development and research of models for assessing the quality of video transmission in IP networks
[4] provides an analysis of architecture and capabilities existing systems using IPTV services as an example, developing a set of quality of service parameters that have a significant impact on assessing the quality of video transmission over IP networks, developing a model for assessing the quality of video transmission over IP networks, taking into account network characteristics and parameters specific to video applications, conducting simulation model anija to validate the assumptions that were made in the model to simplify the calculation, as well as to assess the suitability of the model. In scientific work, Ph.D. Borodinsky A.A. Models and methods of managing IPTV services in NGN networks
[5] such scientific problems as the development of an analytical model for organizing the service Television shifted by time
, development of a caching algorithm for the implementation of the Time-shifted Television
service, which allows calculating the incoming bandwidth in the proxy server, formulating the task of optimizing the incoming bandwidth of the IPTV proxy server by controlling the size buffers, research of possibilities of wireless technologies of broadband for access for the provision of IPTV services, an experiment in the provision of interactive IPTV services with an assessment of the effectiveness of using shared caching in proxies, which have also gained practical distribution.
4.IPTV network structure
IPTV technology is a technology for the delivery of multimedia services (TV, audio/video, text, graphics, data) based on IP networks in broadcast mode and in interactive mode.
IPTV belongs to the class of closed private television broadcasting systems. It is similar to cable television systems existing today and differs from them in that television programs are delivered to subscribers via secure IP channels. This can significantly improve content delivery management. At the same time, the main advantage of IPTV services is the availability of a permanent return channel.
A feature of IPTV is that content is delivered to the subscriber’s house through a partially closed network infrastructure, which cannot be accessed via the Internet. This infrastructure is managed by a telecommunications operator or Internet service provider (ISP). When providing services, IPTV operators use advanced compression technologies, which leads to improved image quality.
In general, an IPTV network is built on the basis of distributed information resources. As a rule, the operator assumes placing several video servers “charged” with different content on the IPTV network.
IPTV Benefits:
- online video stores with multiple choice of diverse programs.
- the ability to order delivery of a hard disk for digital recording.
- the ability to view programs that have already been shown on television.
- improved high-resolution image quality.
- interactive use for shopping, mail, music.
Disadvantages of IPTV:
- the need for access to a DSL and IPTV provider that can serve you.
- need for IPTV – Set-Top-Box.
- Internet bandwidth should be sufficient for IPTV service.
- The unresolved issue of protecting information, providing IPTV users with their data to various companies is not regulated by law.
To implement IPTV, a Head-End station is required – this is a server software and hardware complex that receives, stores and records content, manages services and subscribers.
Also required client equipment – Set-Top-Box set-top boxes for televisions, which are clients for the headend.
Components of the backbone (backbone) transport network, including:
- the actual backbone optical network based on IP technology or ATM technology;
- high-performance switches (routers) with optical interfaces;
The head station consists of a number of components:
- IP streamer is a device that receives a satellite, cable or terrestrial TV signal and transmits it to a local IP network in multicast mode.
- Middleware is an IPTV management middleware. This is the main component of the IPTV complex, as it determines the set of services available to the user, sets the user interface.
- Billing system (user management system) – deals with accounting and billing of services consumed by users.
- The VoD/nVoD server is a separate device that stores a database of films that can be provided upon request from subscribers.
- Content concealment system (CAS) – using this system, the operator can control access to content for individual subscribers who subscribe to certain services. The system encrypts flows on the network and manages the distribution of access keys to these flows.
Client equipment:
- IPTV PC client – a software client exists to access IPTV services through a personal computer. With it, the subscriber will be able to watch TV channels and use all the additional IPTV services on his PC.
- Set-top boxes – for using IPTV services by subscribers, special Set-Top-Box (STB) set-top boxes are required. They are the link between the Middleware system, the content sources on the network and the subscriber’s television[6].
A typical IPTV network diagram is shown in Fig. 1.
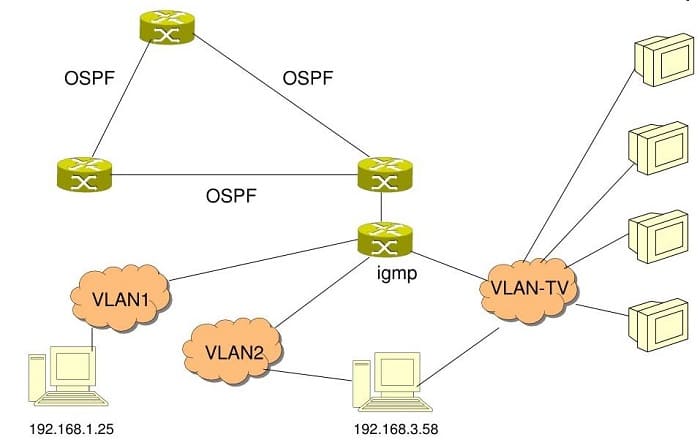
Figure 1 – Typical IPTV Network Diagram
5. IPTV network construction method for telecom operators
Today, a new transition is expected in the world in the era of interactive television IPTV. And one of the main requirements of the user, for any service, is the quality of the content they receive, which directly depends on the transmission speed. To balance these indicators in the IPTV service system, you need to skillfully place content on your existing servers, with a minimum number of them.
In this paper, we propose to consider a method of building a network with two server levels (Fig. 2).
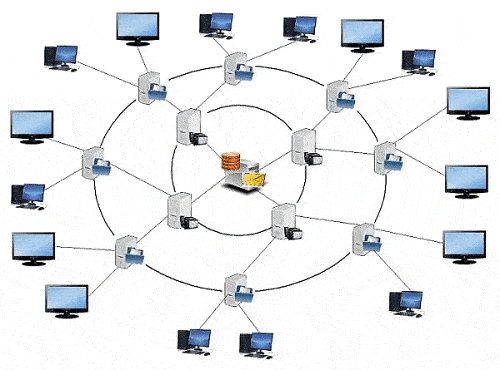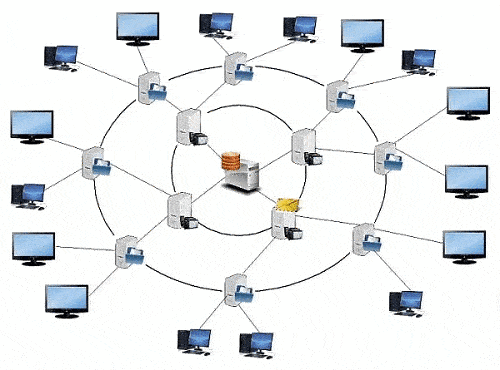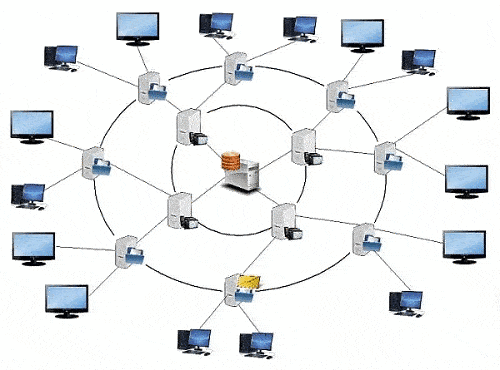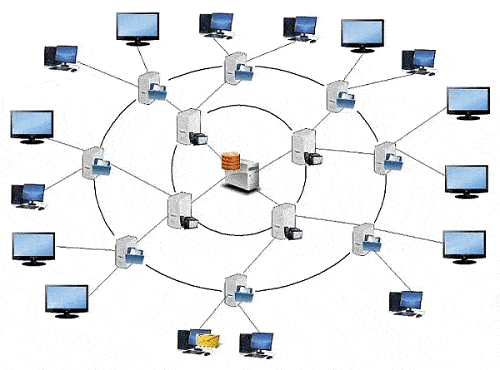
Figure 2 – IPTV network built on two server tiers (animation: 7 frames, 8 cycles, 144 KB)
In the IPTV network, built on the basis of two server levels, first-level servers are used to store the first 15 minutes of television programs, which allows to increase the amount of stored content, as well as the subscriber’s access time to the TV programs he needs. The second level of servers stores, directly, television programs without the initial 15 minutes. The network is based on the topologies ring
[7] and star
[8], which increase the fault tolerance of this network.
Consider the caching algorithm for Video on Demand services. Since it is advisable to store only segments of the TV program, the volume of servers can be limited to a few gigabytes, which will, in turn, reduce the resources of the central IPTV server, and as a result reduce the cost of deploying the service.
Shows the basic principles of the caching algorithm. During the interval t3, requests for viewing the program by subscribers are sent to the servers. If the beginning of the program is not stored on the server closest to the subscriber, the request is made to the neighboring server. In the case when the program is not yet in the neighboring server, the broadcast starts from the central IPTV server (for example, the movie premiere just took place, and the video has not yet been cached to the server). Each time, the popularity indicator P is updated on the server for the tvi program. This indicator will be used to determine the popularity of the program, taking into account the value of the remoteness of the server on which it is stored. This means that a popular program will not be cached because a neighboring server has already saved this program.
Conclusion
Based on the data obtained, it can be concluded that the construction of the IPTV network, considered in the article, is beneficial for both providers and subscribers. Since the provider in this case minimizes the load on the central IPTV server, since the number of requests from subscribers is significantly reduced, it also gets the opportunity to increase the amount of content stored in the servers. The subscriber, in turn, receives a large selection of television programs and a short time for their request.
References
- Fati Suliman Mohamed, Azad Saiful, Pathan Al-Sakib Khan (eds.) IPTV Delivery Networks: Next Generation Architectures for Live and Video-on-Demand Services. Wiley, 2017. – 372 p.
- Гергес Мансоур Салама Мансоур. Исследование сетевых моделей IPTV. Автореферат диссертации на соискание ученой степени кандидата технических наук. – Санкт-Петербург. 2012. – 19 стр.
- Киреева Н. В., Буранова М. А. Обеспечение качества обслуживания в мультисервисных сетях. – ПГУТиИ, Кафедра МСИБ, Самара, 2013. – 35 с.
- Маколкина М. А. Разработка и исследование моделей оценки качества передачи видео в IP-сетях. Автореферат диссертации на соискание ученой степени кандидата технических наук. – Санкт-Петербург. 2014. – 18 стр.
- Бородинский А. А. Модели и методы управления услугами IPTV в сетях NGN.: Автореферат диссертации на соискание ученой степени кандидата технических наук. Санкт-Петербург. 2013. – 16 стр.
- Барсков А. Г. ТВ в сетях IP. Сети и системы связи. 2004. № 11.
- Олифер В. Г., Олифер Н. А. Компьютерные сети. Принципы, технологии, протоколы: Учебник для вузов. 5-е изд. – СПб.: Питер, 2016. – 992 с.: ил. – (Серия
Учебник для вузов
). - Куроуз Джеймс Ф., Росс Кит В. Компьютерные сети. Настольная книга системного администратора. 6-е изд. –
Эскимо
, 2016. – 912 с.
