Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Network Planning
- 2. Passive optical networks. GEPON Basic Information
- 3. Modeling
- 4. Conclusions
- Source List
Introduction
The construction of a multi-service high-speed network with the provision of a set of services that meet modern standards of quality requires the use of equipment that supports bandwidth and quality characteristics that are not yet widely and confidently used, at least today. The construction of a multiservice high-speed network with the provision of a set of services that meet modern standards of quality of service requires the use of equipment that supports bandwidth and quality characteristics that are not yet widely and confidently used, at least today.
The tasks of multiservice networks construction projects include providing potential subscribers with services that are interesting to them today and for a certain period of time ahead, and it is beneficial for them to use these services. On the other hand, the payback of the design object determines whether such an option for building a network is possible at all, when it makes sense.
The big problem of most access networks is the impossibility of organizing other services besides access to the Internet, because the technologies for constructing these networks do not support the QoS parameters necessary for the quality provision of real-time services. It also makes the design task based on the use of fiber optic cables and modern FTTx technology relevant.
The purpose of the work is to achieve a certain social, economic effect. The social effect is to provide subscribers with services that satisfy their needs and lead to better living and working conditions. Scope - private sector homes with the presence of two - and five-story houses. The network can be used to transmit any type of information, provides an optical fiber that provides communication lines that will work and be beneficial for years to come. An important feature of the network is also support for the easy transition to new technologies in the future.
1. Network Planning
The object for which the network is being designed consists of two residential areas of the “Red Partisans” of the Proletarsky district and a residential district in the Leninsky district of the city of Donetsk shown in the figure 1.
At the moment, these areas are similar in composition.
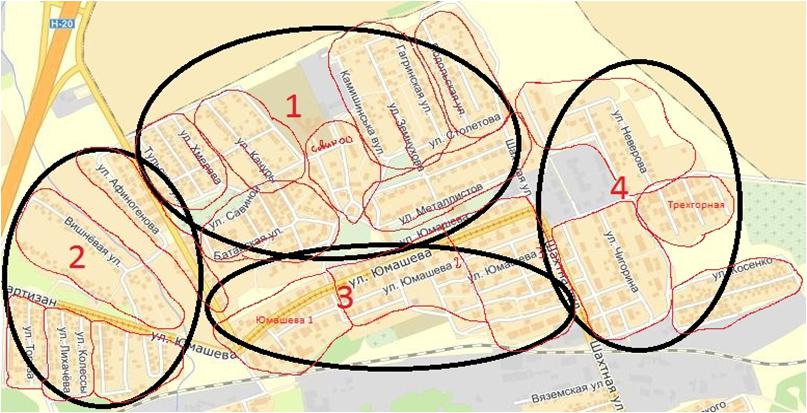
Figure 1 – Building layout
Each district has a school, a hospital, several buildings for private enterprises, retail outlets, government offices and residential buildings (multi-storey and single-storey), a third of all buildings are multi-storey. The population of the Red Partisans districts of the Proletarsky district and the residential district in the Leninsky district of the city of Donetsk has approximately 6,000 and 3,000 residents.
Network infrastructure should be able to provide office subscribers with broadband and telephony services, and for private subscribers – data, voice and video services over one channel - Triple Play - high-speed access to Internet, IPTV and VoIP. It is possible to connect many derivative services based on the above basic types of services. These are services such as organizing private video servers for subscribers.
Depending on the types of services provided to subscribers, the following categories of service can be distinguished:
Subscribers of private firms belong to the first group, two types of tariffing are developed for them, that is, for small and large enterprises. The districts have many government agencies, so they need to make a separate tariff. There are three types of tariffs for individuals.
Based on the selected types of services in certain categories, it is necessary to develop an information network model that will reflect the interaction of key elements with each other and the redistribution of network load.
All groups of subscribers through the data network are combined with the main node, which supplies all the planned types of traffic to the network. Each type of traffic is guided by an appropriate specialized device. To host the archive database of video and other types, servers are also used, which are also located on the main node. The main node receives data through gateways from certain traffic providers.
The information model is a scheme that maps network services and logical groups of subscribers into correspondence, and that is why this access can be organized by a solution. That is, first of all, this is the logical network diagram shown in Figure 1.2
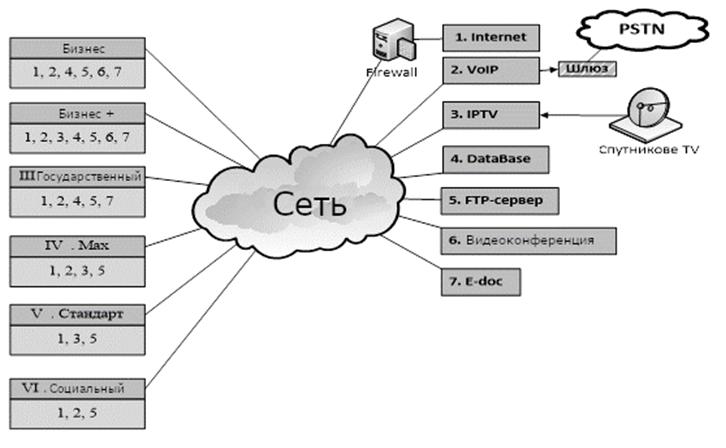
Figure 2 – Data Network Information Model
The subscriber structure is divided into 6 categories of services according to the types of services requiring specific subscribers. The design of the network information model has been carried out, reflects the interaction of subscribers and service categories. Typical location of buildings on the territory, typical layout options of the buildings themselves, typical service requests for this time make this project typical of the telecommunications services market.
2. Passive optical networks. GEPON Basic Information
PON (Passive Optical Network – passive optical network) involves the creation of a branched network (mainly tree topology) without active components – on passive optical splitters.
PON technology is ideal for covering a vast territory with various building densities: from multi-storey areas to cottage towns, where the advantages of the technology are fully revealed.
Transmission and reception in both directions are performed, as a rule, along one optical fiber, but at different wavelengths (1310 and 1490 nm).
Information for all users is transmitted simultaneously with the temporary separation of channels from the headend – optical line terminal (OLT, Optical Line Terminal) - to the terminal optical network units (ONU, Optical Network Unit).
The optical power from the OLT output at the network nodes is divided (evenly or unevenly) so that the signal level at the input of all ONUs is approximately the same.
GEPON structure To construct an optical passive network, in addition to optical fiber, the following are used:
– OLT (Optical Line Terminal) - optical linear terminals that provide communication between the PON network and external networks;
– SFP OLT Modules for PON, with Enhanced Power and Signal Encoding;
– ONU (Optical Network Unit) - final network unit (modem) at the subscriber;
– splitters - passive splitters in network nodes.
GEPON (Gigabit Ethernet Passive Optical Network) one of the varieties of technology of passive optical PON networks, which allows transmitting and receiving data at speeds (up to 1.2 Gbit / s), with a maximum division ratio of 1: 64. This technology uses 1490nm to transmit information 1310nm for reception and 1550 is also registered for cable TV. All packets go from the central node, at the end point each ONU "picks up" only its own one, indicated by the identifier of the MAC address containing the data about the ONU time slot and its error correction method, the structural diagram of this process in Figure 2.1.
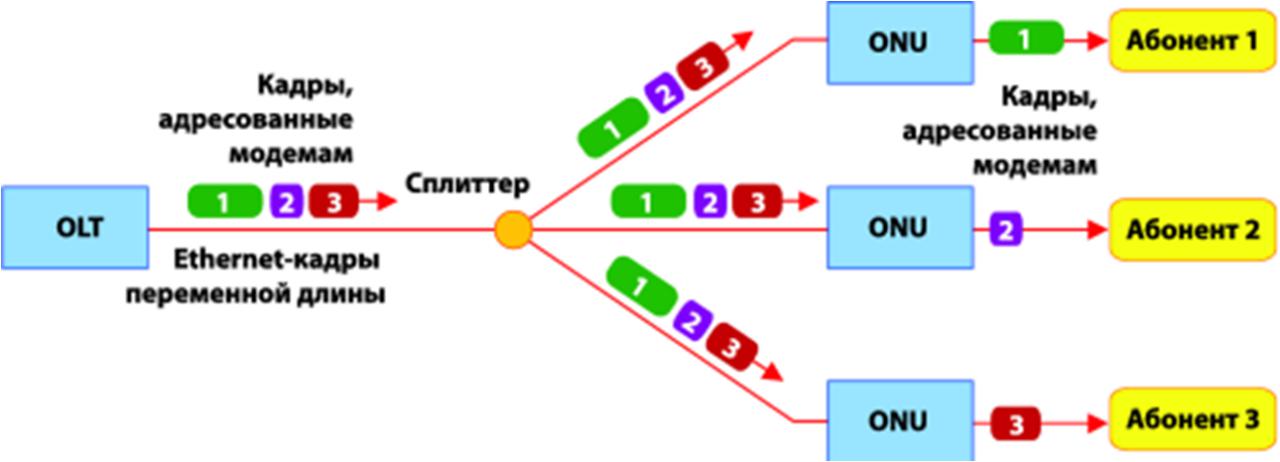
Figure 3 – Traffic distribution scheme
An OLT (Optical Linear Terminal) is installed on the provider side.– Optical Line Terminal) – L2 switch with all the functionality that follows from here, having Uplink ports (for connecting your loved one to the L3 router) and Downlink ports (for client needs). OLT from the order-bearing Chinese manufacturer BDCOM, for example, has 2 optical gigabit Uplink ports, 2 “combo” gigabit Uplink ports (2 optical + 2 copper), and 4 gigabit Downlink PON ports. OLT is managed both through the terminal port and using all your favorite protocols such as SNMP, SSH and TELNET.
On the client side, an ONU (Optical Network Unit) is installed.– Optical Network Terminal, also sometimes referred to as ONT (Optical Network Terminal) – Optical Line Terminal) – full-fledged VLAN switch of small size. ONU from the same BDCOM standardly has one optical gigabit port and 4 copper (100Mbps or 1Gbps). There are ONU models with a combined optical port for television and data, with ports for telephony (SIP), with a different number of copper ports, with a Wi-Fi adapter, as well as a combination of all of the above. Each ONU has a built-in MAC address filter; upon receipt of the packet, the ONU checks that the packet belongs and, if the packet does not belong to it, discards it. The ONU is managed directly from the OLT, while the OLT considers the ONU a “subport” of its port with its own ports, that is, the following hierarchy is observed: OLT port -> ONU number -> ONU port.
Thus, when using this technology, we get the following advantages:
– fiber saving in optical cables;
– significant savings of optical emitters at the headend;
– the ability to provide three types of information (according to the Triple Play concept) – voice, video and data;
– there is no need for power supply of network elements (except for terminal);
– low maintenance costs;
– easy ability to connect subscribers;
– further increase in transmission speed (up to 10 Gb / s and higher) without replacing the equipment of the linear path (optical cables, splitters, connectors).
3. Modeling
Modeling is hosted by Cisco Packet Tracer. Packet transfer on the network in Figure 3 (animation).
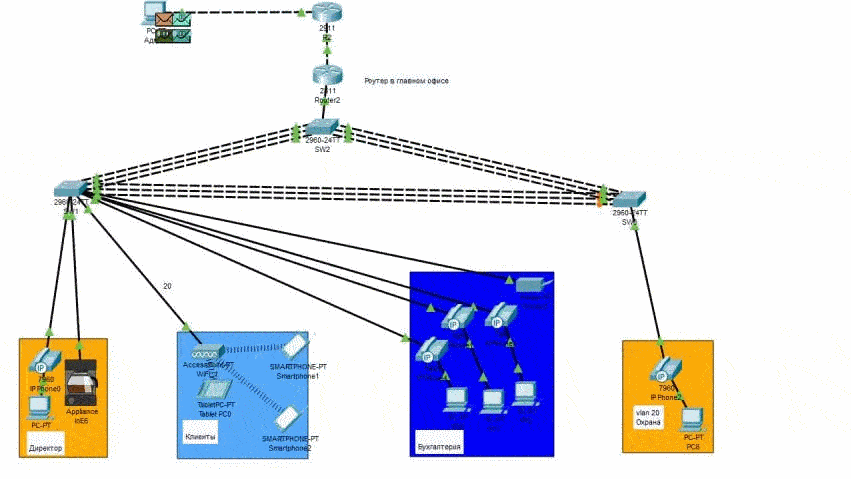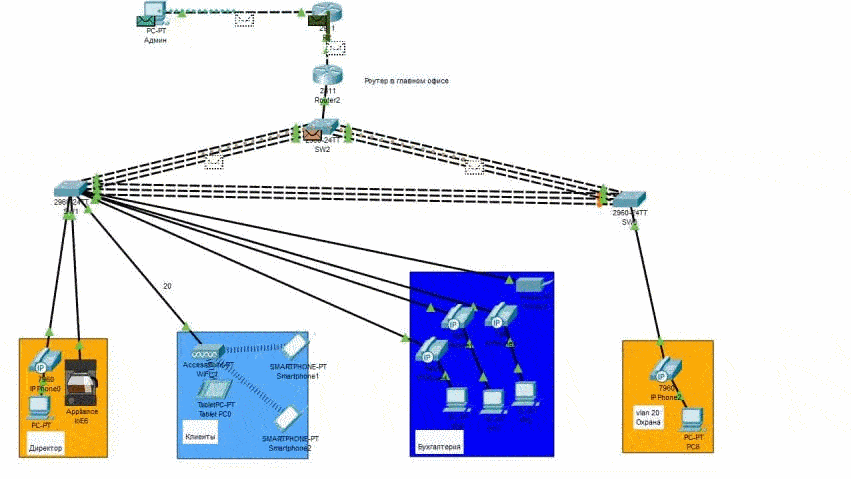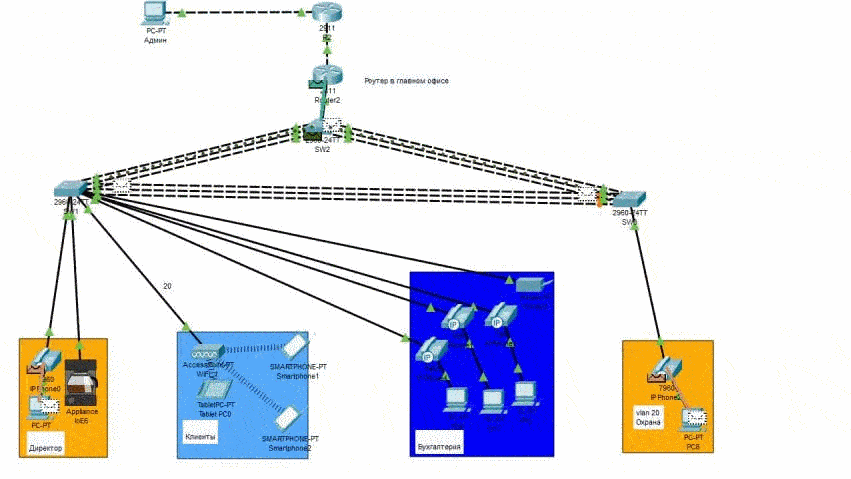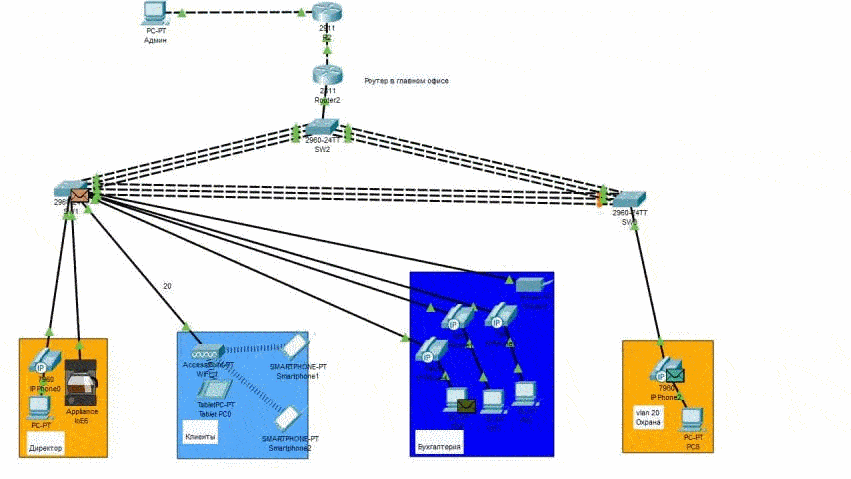
Figure 4 – Network Packet Transfer
The preliminary network architecture was modeled, on which four objects were provided with Internet traffic:
– director's office;
– provider clients;
– accounting department;
Conclusions
When designing the fiber-optic communication line using GEPON technology, a simulation was carried out at the Department of Radio Engineering and Information Protection, which confirms the possibility of implementing this technology in the physical environment, in accordance with the specified parameters.
Source List
1. Анализ живучести мультисервисных сетей связи, построенных по технологии PON [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа:https://cyberleninka.ru
2. Коваль І .Б. Защита информации в волоконно-оптических линиях связи [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа:http://intkonf.org
3. Михеев В. А. Основы постороения подсистемы защиты информации многофункциональной информационной системы [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа:https://cyberleninka.ru
4. Защита информации на волоконно-оптических линиях связи от несанкционированного доступа [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа:http://pnzzi.kpi.ua
5. Проблемы защиты информации, передаваемой по волоконно-оптическим линиям связи, от несанкционированного доступа [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа:http://emag.iis.ru
6. Изучение способов съема информации с волоконно-оптических линий [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа:https://bibliofond.ru
7. Вопросы информационной безопасности сетей PON [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа: http://www.tssonline.ru
8. Каналы и методы несанкционированного доступа к информации [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа: https://studfiles.net
9. Технические средства защиты информации [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа: https://doklady.bsuir
