Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Study of microclimate parameters
- 2. Devices for measuring air humidity
- 3. Normalized parameters of microclimate
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Recently, we are increasingly thinking about supplying cities with water not only from rivers, lakes, reservoirs, artesian springs, because often such water is supplied to cities from remote water intake sites using pumping stations, such a remote site is the Seversky Donets – Donbass canal. The length of this channel is 133.4 km. What is the probability that an emergency situation is possible on this site that cannot be eliminated for a long time. How to be, how not to be left without water at all. But other non-standard water supply options are also possible.
This method can be the extraction of water from wells directly near a residential building, or industrial production. Is there really no escape without extracting water from the bowels of the earth? It is possible to supply water with a humidity reduction unit, reduce humidity by condensing water and collecting condensate in a container for further pumping and application of the liquid. The advantage of this type of supply is the production of process water with low hardness, thereby simplifying water treatment than when using water from wells. It is necessary to conduct research on whether it is possible to achieve the necessary volume of condensate to ensure the norms of human water consumption.
1. Study of microclimate parameters
Microclimate is the meteorological conditions of the indoor environment in the premises, which are determined by the combinations of temperature, humidity, air velocity and thermal radiation acting on the human body.
Indicators that characterize the microclimate are:
- air temperature;
- relative humidity;
- air velocity;
- intensity of thermal radiation.
The air temperature T, °C (°K), is a physical quantity directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the thermal motion of particles.
Air velocity V, m/s – vector of the average velocity of air flow movement under the action of various driving forces.
Thermal radiation (the same as temperature, infrared radiation, thermal radiation) is electromagnetic radiation emitted by a substance and arising from its internal energy.
The main characteristic is the intensity of thermal radiation. The intensity of thermal radiation I, W/m 2, is the total flow of radiation energy passing per unit time through a unit of surface perpendicular to the direction of radiation.
The parameters of weather conditions should also include atmospheric (barometric) pressure, which is the pressure in the gas envelope surrounding the earth. Atmospheric pressure 1 atm = 1.0332 kg / cm 2 = 101.325 kPa = 760 mmHg = 10332 mmHg
The air humidity can be absolute, maximum and relative. Absolute humidity A, g / m 3, is the mass of water vapor in a unit of air volume.
Humidity is an indicator of the water vapor content in the air. The humidity of the home air varies depending on weather conditions and the processes of human activity. The air humidity can be absolute, maximum and relative. Absolute humidity A, g/m 3, is the mass of water vapor in a unit of air volume.
Maximum humidity F, g / m 3, is the maximum possible (saturating) mass of water vapor located in a unit of air volume at a given temperature (dry thermometer temperature). Relative humidity φ,%, - the ratio of the absolute humidity of the air to the maximum.
For a person, the amount of humidity is a very important parameter of the environment, because our body is very active in responding to its changes. For example, such a mechanism of regulating the functioning of the body as sweating is directly related to the temperature and humidity of the environment. At high humidity, the processes of evaporation of moisture from the surface of the skin are almost compensated by the processes of its condensation and the removal of heat from the body is disrupted, which leads to violations of thermoregulation. At low humidity, the processes of evaporation of moisture prevail over the processes of condensation and the body loses too much fluid, which can lead to dehydration.
The value of humidity is important not only for humans and other living organisms, but also for the flow of technological processes. For example, because of the known property of water to conduct an electric current, its content in the air can seriously affect the correct operation of most electrical appliances. Also, too humid air can spoil furniture and finishing materials, contribute to the development of fungus on the walls and reduce immunity in humans.
A decrease in humidity in the room can occur due to excessive use of heating devices or air conditioning. Cooking without a hood or high-quality ventilation, drying clothes in the house, high humidity on the street lead to a high level of humidity in the apartment.
Dry air in the room can cause drying of furniture and finishing materials, wilting of plants, dry skin and mucous membranes. Often, dry air leads to allergic reactions and the development of colds.
How to prevent an increase or decrease in the relative humidity of the air and how to determine the same humidity of the air? Without special equipment, it is difficult to determine the relative exact level of air humidity. However, the concentration of moisture that does not correspond to the norm can be determined by the dryness of the skin and mucous membranes or the accumulation of condensation (dew point) on windows and mirror surfaces. Today, there are special devices that can be used to determine the balance of humidity in the room with high accuracy.
2. Devices for measuring air humidity
A device for measuring air humidity is called a hygrometer. A hygrometer is a device that measures the humidity in a room. If the percentage of moisture content in the air is too low, various viruses can enter the body, which can significantly weaken the immune system. Thanks to the hygrometer, you can avoid discomfort and protect the mucous membranes and skin from drying out.
The principle of operation of this device is based on the physical characteristics of the materials from which it consists. Materials change their properties depending on the level of moisture in the air: weight, density, length, and others.
There are several types of hygrometer:
- hairline;
- film;
- weight;
- condensation;
- psychrometric;
- electronic.
The effect of the hair hygrometer (Figure 1) is based on the property of non-fat human hair to change the length when the air humidity changes, which allows you to measure the relative humidity from 30 to 100 %. The hair is slightly stretched on an elastic metal frame. The change in the length of the hair is transmitted to the arrow moving along the scale, graduated in units of relative humidity.
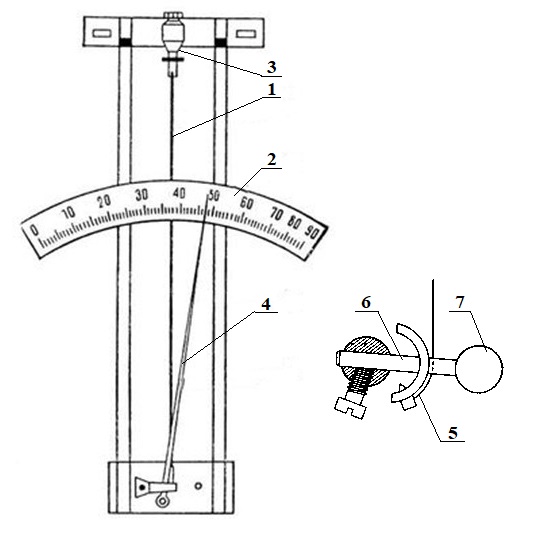
Figure 1-Hair hygrometer
The main part of the device is fat-free human hair 1. The action of the hygrometer is based on the property of such a hair to change its length depending on the relative humidity of the air.
The hair is fixed on a frame with a scale of 2. In the upper part, it is fixed to the regulator with a nut 3. The regulator serves to move the arrow 4 when the corrections to the hygrometer become too large (i.e., the device shows humidity more than in reality). In the lower part, the hair is attached to the cam 5. The cam, in turn, is attached to the rod 6, at one end of which the weight 7 is attached, and the arrow is attached to the other. The weight keeps the hair in constant tension.
When humidity increases, the hair lengthens, and when it decreases, it shortens. These changes are transmitted to the arrow, which stops at the scale divisions corresponding to the air humidity. It is worth noting that the divisions on the scale are located unevenly. At low humidity values, the distance between the divisions is greater than at high values. This means that at low humidity, the hair length changes more than at high humidity.
The film hygrometer (Figure 2) has a sensitive element made of organic film, which stretches when humidity increases and contracts when it decreases. The change in the position of the center of the film membrane is transmitted to the arrow. Hair and film hygrometer in winter are the main devices for measuring air humidity. The readings of the hair and film hygrometer are periodically compared with the readings of a more accurate device — a psychrometer, which is also used to measure air humidity.
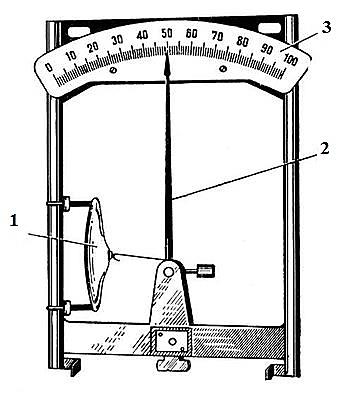
Figure 2-Film hygrometer
In an electrolytic hygrometer (Figure 3), a plate made of an electrically insulating material (glass, polystyrene) is covered with a hygroscopic layer of electrolyte — lithium chloride — with a binding material. When the humidity of the air changes, the concentration of the electrolyte changes, and therefore its resistance; the disadvantage of this hygrometer is the dependence of the readings on temperature.
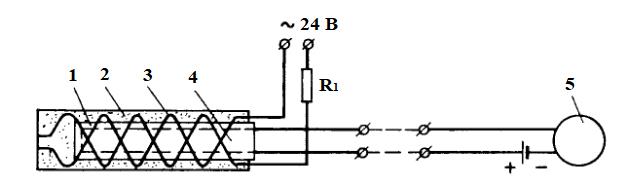
1-tube; 2-glass wool; 3-spirals; 4-resistance thermometer;
5-measuring device
Figure 3-Diagram of an electrolytic hygrometer with a heating sensor
In an electrolytic hygrometer, lithium chloride is used as a moisture-sensitive element. A saturated solution of lithium chloride is heated to a temperature at which the partial pressure of water vapor above the solution is equal to the partial pressure of vapor in the surrounding atmosphere. Therefore, according to the principle of operation, electrolytic hygrometers with a heated converter are similar to dew point hygrometers, but they have the advantage that it is much easier and easier to heat the converter than to cool the mirror in dew point devices.
In some electrolytic hygrometers, the moisture-sensitive surface is a fiberglass thread wound in a spiral with a small pitch around parallel platinized wires. For any relative humidity and temperature values, the electrical resistance of the hygrometer can be measured by an AC bridge.
Therefore, the principle of operation of electrolytic hygrometers with a preheated sensor is similar to dew point hygrometers. The advantage of these hygrometers is that heating the sensor is much easier and easier than cooling the mirror in dew point hygrometers.
The principle of operation of the condensation hygrometer is based on measuring the amount of condensate that accumulates on glass surfaces. A narrow beam of light is directed at a special cooled mirror. Due to the influence of light, water droplets or ice crystals begin to appear on it. An electronic thermometer mounted under the mirror measures the readings, and then converts them to the value of relative humidity.
The simplest of the capacitor-type hygrometers is the Lambrecht hygrometer (Figure 4). The main part of this device is a metal cylindrical chamber with a nickel-plated front wall surrounded by the same ring, the axis of which occupies a horizontal position. One base of the cylinder is made shiny on the outside. In the cylindrical chamber there are holes, a thermometer is inserted into one of them and through it, with the help of a pipette, ether is poured in such an amount that the liquid covers the ball of the thermometer; another hole is used for air outlet, and a metal tube is soldered into the third, reaching almost to the bottom. With the help of a rubber pear, air is slowly blown into this tube, which passes through the ether layer. With the rapid evaporation of ether, the chamber wall is cooled and at a certain temperature, below room temperature, the water vapor located in the air layer adjacent to the wall becomes saturated and begins to condense on the chamber surface.
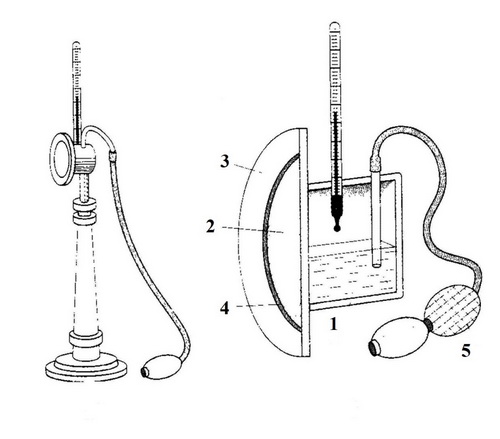
1 - metal box; 2-front wall; 3-ring; 4-thermal insulation pad; 5-rubber bulb; 6-thermometer
Figure 4-Condensation hygrometer
The temperature at which water vapor in the air becomes saturated is called the dew point.
At the moment of appearance of the first signs of dew (dimming of the surface), stop blowing air and quickly count the temperature t1 on the thermometer - the point of appearance of dew. After some time, the dimming begins to disappear from the surface 3 and at the moment of its disappearance, the temperature t2 of the disappearance of dew is counted. Usually the temperature t1 is slightly lower than t2. The dew point temperature is taken as the average of these two counts.
The dew point is determined at least 5 times and its average value is calculated. The absolute humidity is determined from the table of the dependence of the pressure and density of saturated water vapor on the dew point temperature (t cp). The maximum humidity is determined according to the same table, but at room temperature. Knowing the absolute and maximum humidity, we find the relative humidity by the formula.
The condensation hygrometer is an accurate instrument that is famous for its high measurement accuracy. Its use allows you to get accurate data about the microclimate in the room. Modern versions of the device are equipped with a display that displays the received readings. Due to the special principle of operation of the device, the result is quite accurate, and the error is minimal.
Ceramic hygrometer (Figure 5) is most often used to monitor humidity in residential areas. It is characterized by a fairly simple design, and the principle of its operation is based on mechanical actions. A solid or porous ceramic mass, which also includes metal elements, has an electrical resistance. Its level directly depends on the humidity in the room. For the proper functioning of a mechanical hygrometer, the ceramic mass must consist of some metal oxides. Moreover, clay, silicon and kaolin are used as the basis.
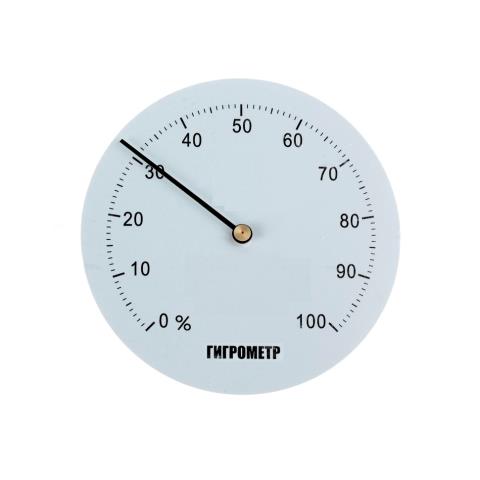

Figure 5-Ceramic hygrometer
3. Normalized microclimate parameters
There are certain requirements for the microclimate parameters for residential and public buildings. The parameters that characterize the microclimate in the premises:
- air temperature;
- air velocity;
- relative humidity.
According to GOST 30494-2011, the following classification of premises is accepted:
- category 1 rooms: rooms where people in the lying or sitting position are at rest and rest;
- category 2 premises: premises where people are engaged in intellectual work, study;
- category 3a premises: premises with a mass stay of people, in which people are mostly in a sitting position without street clothes;
- category 3b premises: premises with a mass stay of people, in which people are mostly in a sitting position in street clothes;
- rooms of category 3b: rooms with a mass stay of people, in which people are mostly in a standing position without street clothes;
- rooms of the 4th category: rooms for outdoor sports;
- category 5 rooms: rooms where people are half-naked (changing rooms, treatment rooms, doctors ' offices, etc.);
- rooms of the 6th category: rooms with temporary stay of people (lobbies, dressing rooms, corridors, stairs, bathrooms, smoking rooms, storerooms).
Optimal and permissible parameters of the microclimate in the serviced area of the residential premises (including hostels), kindergartens, public, administrative and residential buildings should be adopted for the corresponding period in the range of values of the parameters listed in table 1.
| Period of the year | Room name | Air temperature, °C | Relative humidity, % | Air speed, m / s | |||
| optimal | allowed | optimal | allowed | optimal | valid | ||
| Cold | Living room | 20-22 | 18-24 | 45-30 | 60 | 0,15 | 0,2 |
| Living room in areas with the coldest five-day temperature (security 0.92 minus 31 °C and below) | 21-23 | 20-24 | 45-30 | 60 | 0,15 | 0,2 | |
| Kitchen | 19-21 | 18-26 | Not normalized | Not normalized | 0,15 | 0,2 | |
| Toilet | 19-21 | 18-26 | Not normalized | Not normalized | 0,15 | 0,2 | |
| Bathroom, combined bathroom | 24-26 | 18-26 | Not normalized | Not normalized | 0,15 | 0,2 | |
| Recreation and training room | 20-22 | 18-24 | 45-30 | 60 | 0,15 | 0,2 | |
| Inter-apartment corridor | 18-20 | 16-22 | 45-30 | 60 | Not normalized | Not normalized | |
| Lobby, stairwell | 16-18 | 14-20 | Not normalized | Not normalized | Not normalized | Not normalized | |
| Storerooms | 16-18 | 12-22 | Not normalized | Not normalized | Not normalized | Not normalized | |
| Warm | Living room | 22-25 | 20-28 | 60-30 | 65 | 0,2 | 0,2 |
Conclusions
As a result of the analysis of two methods of obtaining water: the traditional method-obtaining water from rivers, and the condensation method - with the help of an installation that includes a Peltier module, both methods were analyzed, the features of each use, strengths and weaknesses were identified. The potential of using .... Method using the Peltier module. The norms of water consumption for one person were established, which amounted to 330 l / day, and the necessary costs of electric energy for obtaining water were determined for two cases: with the help of pumps and the Peltier module. Thus, the cost of electric energy for pumping 330 liters per day was 443.7 W, and for using the Peltier module, the cost was 224.125 kW, which is significant compared to the traditional one.
The obtained results make it possible to understand that the use of the Peltier module in this form is undesirable, it is necessary to improve by installing a more productive fan, increasing the air temperature before condensation, increasing the surface of the heat-removing system, as well as the surface on which water vapor condenses.
References
- Берлинер М. А. Измерения влажности. Изд. 2-е, перераб. и доп. М: «Энергия», 1973. - 400 с.
- Халиф А., Туревский Е.Н. Приборы для определения влажности М: «Энергия», 1995. — 44 с.
- Гигрометры [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://bboff.ru/gigrometr ....
