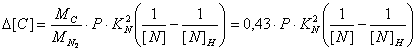The nitrogen concerns to harmful impurity in steel. The large contents of nitrogen in steel, which is made in electric arc furnaces (EAF), is explained to that melting in EAF conducts at the large meanings of temperatures (which both in open hearth furnaces, and in BOFs are not reached) at the expense of use of heat of electrical arches. Demand for steel recently has increased, in this connection the capacity EAF, hence, has increased contents of nitrogen in steel also has increased. Presently to steel the very rigid requirements are showed, as it is one of the most important materials of a modern industry. For this reason to removal of nitrogen from steel give a lot of attention, forces and time. All it is made to improve properties of steel. At the given stage of my master's work considered influence decarbonisation of steel upon the removal of nitrogen from metal. Speed of removal of nitrogen from melt at first was theoretically designed by it mass transfer in gas bubbles, which are formed as a result of oxidation of carbon contained in metal. This account was carried out with the help of the following equation:
where
The conditions, at which the given account was carried out, were the following: temperature - 1600 оС; pressure - 1 atm; the initial contents of nitrogen in metal - 0,01 %; speed of decarbonisation - from 0,01 up to 0,15 %/min. The received results of calculations are given in the table 1. The table 1 - Results of theoretical calculations
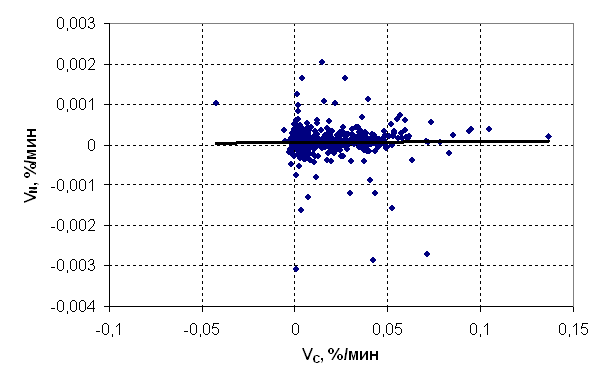
Then the analysis of the practical data was made which were taken on done melts in electric steelmaking shops on the Moldavian Metallurgical Plant (first half-year of 2000) and Byelorussian Metallurgical Plant (July, 2000). On this practical data the changes of concentration of carbon and nitrogen in metal, speed of removal of carbon and nitrogen from melt were calculated. The graphic dependence of speed denitrogation from speed of removal of carbon is represented in a fig. 1.
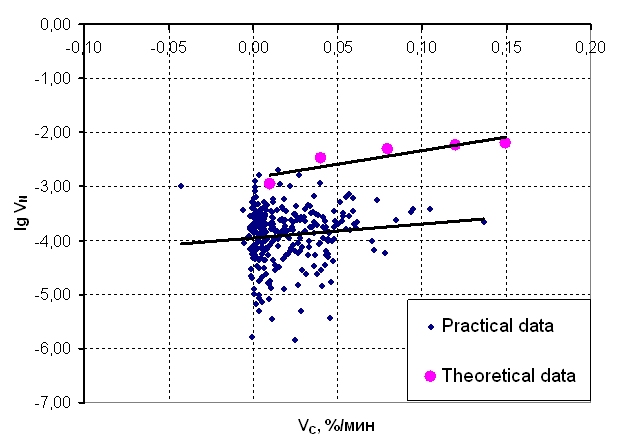
Fig. 1 - Dependence of speed of removal of nitrogen on change of speed of removal of carbon Visually to observe, as far as the theoretical accounts differ from the practical data, we shall construct graphic dependences of speeds of removal of nitrogen on change of speeds of removal of nitrogen of the fixed sizes and results of theoretical calculations.
Fig. 2 - Dependence of the decimal logarithm of speed of removal of nitrogen on speed of removal of carbon Having analysed results of calculations and given figures it is possible to make the following conclusions: 1. The change of concentration of carbon does not render essential influence on change of concentration of nitrogen; 2. The change of speed of decarbonisation does not render essential influence on changes of speed of denitrogation of metal; 3. Theoretical given, designed proceeding from the equation (1) on the order differ from practical. It is possible to explain a difference between theoretical and practical meanings by influence on the contents of nitrogen in metal of other factors, such for example, as: "pumping effect ", purge of melt by inert gas, low contents of nitrogen in raw materials, higher temperature of melting (in comparison with what took for theoretical accounts), lower partial pressure of nitrogen in an environmental atmosphere etc. As the result can be told, that the removal of nitrogen from steel with bubbles of oxid of carbon has shown low efficiency. But the given divergence between the theoretical and practical data causes of the further study of a question of efficiency of removal of nitrogen by taking away it with bubbles of gas.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
©
Луценко П.С.
2006 г.
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||