The summary:
In conditions of an intensification of technological processes, development
and development of the new technical equipment, essential value receive the
actions directed on maintenance of functional ability of constructive
elements, working in the field of high temperature and intensive thermal
loadings. The constructive elements working in such conditions, demand, as a
rule, effective means of thermal protection is cooling of protected elements.
Increase of efficiency coolings in comparison with only convection is
connected to phase transformation of the cooling environment into a cooling
contour which goes with the big absorption of heat and practically at the
constant temperature close to temperature of saturation. Calculation of
parameters coolings of constructive elements is connected to the whole
complex of the calculations including:
- Calculation of structure of
an atmosphere in working space of the unit;
- Calculation heat and
ðàäèàöèîííî-optical characteristics of an atmosphere;
- Calculation of
characteristics radiation-convection heat exchange of a cooling element;
- Calculation of a heat
transfer through working surfaces of a cooled element;
- Definition of a mode of phase
transition at cooling.
The decision of such complex
task is complicated nonlinearity of its{her} statement: "internal" and "external".
Internal nonlinearity of statement is defined{determined} by dependence heat
characteristics of a material of constructive elements from temperature. "External"
- presence as making radiating heat exchange.
In technological processes of metallurgy at
melt of steel, at processing ingots in heating, etc. there is an intensive
heat exchange between products of combustion and surfaces of firm bodies
which basic part falls at radiant heat exchange. The basic structure of
products of combustion is a carbonic gas, pairs water and nitrogen. From
these gases determining in heat exchange are three-nuclear-
![]() and
and
![]() ,
and
two-nuclear - practically dualheat and in calculations can not be taken into
account. In the literature cited the data on these gases basically as
nomogramm and at use of computer technologies they are not convenient, and
the analytical dependences received by various authors, have an error
achieving tens of percent, for example:
,
and
two-nuclear - practically dualheat and in calculations can not be taken into
account. In the literature cited the data on these gases basically as
nomogramm and at use of computer technologies they are not convenient, and
the analytical dependences received by various authors, have an error
achieving tens of percent, for example:
1. Kazantcev Å. I.
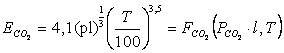 ,
Wò/ì2;
,
Wò/ì2;
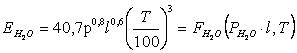 ,
Wò/ì2;
,
Wò/ì2;
2. Pomerancev À. À.
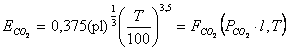 ,
Wò/ì2;
,
Wò/ì2;
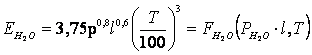 ,
Wò/ì2.
,
Wò/ì2.
New processing of diagrams which by means of
a method of the least squares approximates curves with a margin error 0,01 %
is offered. Analytical dependence is submitted as
![]() ,
where
,
where ![]() ,
,
![]() and
and
![]() –
the factors dependent from
pl,
and for carbonic gas
–
the factors dependent from
pl,
and for carbonic gas ![]() ,
,
![]() ;
for water pair
;
for water pair ![]() ,
,
![]() .
.
Definition of parameters of radiant heat
exchange is executed for temperatures of gas (Òã ) 500,
750, 1000, 1250, 1500 Ê Under Kazantsev E.I., Pomerantseva A.A.'s formulas
at use of diagrams and by an offered variant. The factor of heat exchange
was defined by radiation![]() for products of combustion of fuel
concerning horizontal heatchanger the steam boiler.
Diameter of a tube
D
= 45 ìì.
for products of combustion of fuel
concerning horizontal heatchanger the steam boiler.
Diameter of a tube
D
= 45 ìì.
![]() with
temperature of a surface
with
temperature of a surface ![]() .
Structure of gas 14%
.
Structure of gas 14% ![]() ,
4%
,
4% ![]() ,
the rest
,
the rest ![]() .
.
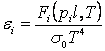 ,
,
where
![]() =
5,67·10-8 Âò/ì2Ê4
– Constant of Boltsman;
=
5,67·10-8 Âò/ì2Ê4
– Constant of Boltsman;
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
where
![]() -
degree of blackness of a mix of gases ÑÎ2
and Í2Î;
-
degree of blackness of a mix of gases ÑÎ2
and Í2Î;
 ,
,
where
![]() -
factor of heat exchange by radiation.
-
factor of heat exchange by radiation.
Results are resulted in table 1
Table 1 - Settlement values of factor of heat exchange by radiation
|
Òã, Ê |
500 |
750 |
1000 |
1250 |
1500 |
|
1. Kazantsev |
15,00 |
71,94 |
84,13 |
94,19 |
98,23 |
|
2. Pomerantsev |
1,20 |
22,15 |
43,20 |
161,40 |
189,30 |
|
3. Nomogram |
0,73 |
1,29 |
73,20 |
91,20 |
114,0 |
|
4. Calculate |
0,732 |
1,29 |
73,24 |
91,12 |
114,08 |
Results of the numerical
analysis have shown, that offered parities are closest to the exact decision
and in the best way suitable at use of computer technologies. Generalizing,
we shall receive for the mentioned task on various complexes ![]() ,
let's
receive
,
let's
receive
![]() ;
;
![]() ;
;
![]()
![]()
![]() ;
;
![]() .
.