UKRAINE IN THE CONTEXT OF EUROINTEGRATION PROSPECTS
One of the vital topics for today is joining of Ukraine the European Union. Present president V. Yushchenko has stated precise intentions concerning integration of our country into Europe, carrying out on this way the maximum programme: to integrate into EU for 5 years. Let us try to estimate how purposeful is entry into EU and what consequences may expect Ukraine on this way.
Considering Ukraine in context of the European economic integration it is necessary to take into account peculiarities of its geopolitical position. Noted Ukrainian philosopher N.Mihalchenko in his book « Ukrainian society: transformation, modernization or limitrophe of Europe? » defines cultural position of Ukraine and its position concerning civilizations by the term "limitrophe" – boundary area between civilizations. He writes: « Presently Ukraine is not yet "bridge", "sanitary border", especially not "center" of any communities. Ukraine is limitrophe for Russia and Europe so far, it is intermediate space between the western and Russian -Eurasian civilizations. And limitrophe with double estimation. Europe regards eastern frontier of Ukraine as a line of a break between Europe and Russia. And Russia considers the western frontier of Ukraine to be a line of a break between the NATO and Commonwealth of Independent States space, identifying the last with zone of the personal interests » and further, that is essentially important, N.Mihalchenko marks: « Limitrophe position or condition is an intermediate position or condition. If people of " limitrophe" does not take roots in structure of the certain regional civilization then self-determination of this people as independent state remains problematic as creation of the local civilization is problematic » [1, 341-342]. Certainly, such condition of Ukraine is not accident, it is natural result centuries-old cultural and civilizational life of Ukrainian people on a break of civilizations.
Last decade in the Ukrainian foreign trade policy shows its orientation to the markets of the West-European countries, and especially to the countries included in the European Union.
It can be explained by intentions of Ukraine to enter this integration association, basically with the purpose of expansion of trading opportunities and improvement of conditions of trade.
At the present stage trade relations of Ukraine and EU are difficult enough and uncertain.
The markets of countries - candidates in particular Poland and Hungary are the major for foreign trade of Ukraine. In 2002 the Ukrainian commodity export into countries - candidates exceeded 2 $ billion, or 12,4 % of total exports whereas the share of export to the countries of EU was equal 19,7 %. At the same time export of to Ukraine makes rather small share, as such countries first of all are oriented to the markets of EU. (Tab. 3.2)
Table 1 – Countries - candidates (nowadays new members of EU) in the Ukrainian export (2002) % [8]
|
The country |
In general |
Hungary |
Poland |
Slovakia |
Czechia |
Latvia |
Lithuania |
Estonia |
Slovenia |
Cyprus |
|
Share in export |
12,4 |
2,9 |
2,8 |
1,6 |
1,0 |
1,3 |
1,1 |
0,5 |
0,1 |
1,1 |
The structure of the Ukrainian export in countries - candidates is similar to structure of export to EU. Thus the structure of export of countries - candidates for EU essentially differs from structure of export of Ukraine in this region: countries - candidates export to the European Union mainly production with the high added cost whereas in European export of Ukraine the goods with a low degree of processing prevail. It testifies about disbalance in structure of trade between EU and Ukraine which can go deeper without structural shifts in the Ukrainian economy.
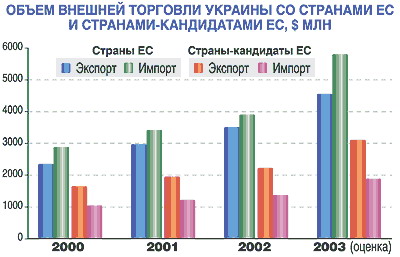
Figure 1 – Total amount of trade of Ukraine with the countries of EU and countries - candidates [8]
Countries - candidates use wider access on the commodity markets of EU due to the agreement in force on free trade (over 50 % of foreign trade of such countries falls at trade from EU). Moreover, countries - candidates actively work at creation of the customs union from EU: the common customs-tariff should be introduced from the time of countries entry into EU. Competition between Ukraine and countries - candidates, which is peculiar to trade in separate commodity groups may amplify because of introduction by countries - candidates and EU of the common customs-tariff.
Modern Ukraine has made the choice it has chose the way of European integration.
However the European Union is divided into so-called "old" Europe and new members of the European Union. If "new" Europe, and in particular Poland will actively lobby interests of Ukraine on a way of the European integration on the contrary "old" Europe presented by Germany and France, most likely to say neither yes, or no, trying to postpone process of Ukrainian integration while the situation with Ukraine will not clear up. Not enough time has passed from the moment of orange revolution, and is not clear to Europe yet what «new Ukraine» is like. The USA also are interested in the prompt integration of Ukraine into EU, and it is not surprising, because recently joined members of the Union have rather good foreign policy contacts with the USA.
The European Union is a community of the states, incorporated in common to sustain global cut-throat competition. And they are not interested in presence of Ukrainian goods on the market. The illustration of this is annual growth of a share of the Ukrainian export under antidumping investigations. Scanty position of Ukraine in the foreign trade turnover of EU shows that today there are no places here for the basic export branches of our economy (metallurgy, light industry, the agroindustrial complex). Even economically important joint projects (such as transport plane An-70) are rejected by the countries of EU on political grounds.
It is obvious that European integration cannot be estimated unambiguously. Let us try to estimate what consequences for any country-candidate can be after becoming a member of EU.
Integration of the country into the European Community may have the following effects:
–Reduction of expenses on transaction in foreign trade with the countries of EU;
– Decrease in a level of borrowing rates in the countries Central and East Europe;
– Increase of competition level on the European market;
–Clarity of business operations in the national markets of new EU members.
Nevertheless, many countries of Central and East Europe which have joined the European Union, taking into account essential distinctions in economy, can face such problems as growth of poverty and social intensity, high inflation and weakness of a financial system, etc.
However, positive consequences from becoming a member of the European Union are huge:
– Increase in volumes of foreign trade of countries - candidates entered EU.
– Migration of labour, that will have a positive effect on the general level of economic development of EU.
– Increase in general level of economic development of countries - members of EU owing to favorable economic environment.
Considering advantages and disadvantages of countries from integration into EU in financial aspect it is necessary to note, that they depend first of all on economic policy and legal system of the countries, and also from ability of the enterprises to resist competitive pressure within the EU. It is impossible to determine all the "pluses" and "minuses", but all earnings can be divided into direct and indirect. Direct one are growth of opportunities of access to the market, capital forthcoming, direct transfers of financial resources from Europe, and indirect earnings are improvements of redistribution of factors of production, increase of efficiency of economic processes, economy of financial resources owing to release of barriers in operations with the countries of EU. [2]
Possible economic effects of EU expansion to the East are presented in the following table
Table 2 – Economic effects of EU expansion to the East [3]
|
Influence of expansion | |
|
Countries - candidates for members of EU |
– Reduction of expenses on transactions in foreign trade with the countries of EU; – Decrease in a level of borrowing rates in the countries Central and East Europe; – Increase of competition level on the European market; – Clarity of business operations in the national markets of new EU members |
|
Countries - members of EU |
– Fringe benefits to exporters; – Geographical expansion of economic space; – Expansion of the capital markets integration; – Reduction in expenses owing to accommodation of separate economic sectors in new countries - members of EU |
|
The European Union |
– Increase of aggregate demand and supply; – Increase in distribution of revenue –Deepening of a competition and specialization in the European market; – Redistribution of incomes among community |
|
The international economic relations |
– Change of geographical structure of EU foreign commerce; – Increase of a level of isolation of the European market for countries - members of community – Increase of the economic importance of EU in structure of the international economic relations |
|
Ukraine |
– Loss of traditional commodity markets in new members of EU; – Introduction by new members of EU of non-tariff restrictions, technical, sanitary and other kinds of the control concerning Ukrainian agricultural production; – Restriction of access of a labour from Ukraine on labour markets of new members of EU. |
Recently the European Community became the neighbour of Ukraine. On May 1 2004 10 new countries have joined EU, including Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, which has borders with Ukraine [4].
For Ukraine the given expansion in strategic attitude means the further promotion on a way to the European integration due to which new opportunities of widespread cooperation will appear. In the tactical attitude this process will have for Ukraine both positive and negative consequences practically in all spheres of activity.
However, full membership of Ukraine in the European Union is rather abstract concept. To integrate into the European Union Ukraine with its population of about 48 million person is not the same, that, for example, integration into EU of Estonia with its 1,2 million. Besides, Ukraine and the European Union are divided by an economic gap. So, for example, the gross national product (GNP) per capita in Ukraine in nominal calculation makes only about thousand dollars annually while the similar parameter in EU is equal to 20 thousand dollars, and in developed countries of EU it changes from 23 up to 32 thousand dollars. Predicted growth of gross national product is shown in figure 2.

Figure 2 – Growth of real gross national product, % [8]
In spite of the fact that Ukraine identifies itself as the European state, for western European people this state (despite all official statements) remains in practice a part of Eurasia. And integration of this state into EU may lead to undesirable for the European Union consequences. Therefore, joining of such countries as Ukraine or Russia to EU is not only a question of discrepancy in legal and economic system of the West-European standards and these countries, but also in civilization distinction.
Besides, it is necessary to take into account that fact that for the first time in the history, in EU entered such plenty of the countries, which standard of well-being and level of development of economy are much lower. Such active expansion can considerably aggravate position in EU both financially and functionally. Any deterioration of a condition of economic which is reflected in Europe will have influence on debate concerning expediency of the entry into EU and the conditions necessary for this entry. [5]
For Ukraine the pragmatism, real estimation of present situation and statement of the feasible purposes of integration policy are of great importance nowadays. However, it is necessary to remember, that organizational forms are not in a static condition, and constantly develop during changes of prospects of the European integration. [6]
Each new stage of expansion of the European Union may both to precipitate process of integration of Ukraine in EU and to slow down it. As G.Soros has noted « integration is dynamical process: if it does not move forward it is compelled to go in the opposite direction » [7]
At the present stage a priority task of the government of Ukraine acceleration of steady economic growth should be and as consequence European integration, instead of achievement at any cost criteria for the introduction into EU.
For use of potential opportunities and minimization of negative consequences from expansion of EU great value have the following factors:
— Performance of the Agreement on partnership and cooperation between EU and Ukraine, in particular acceleration of adaptation of the legislation of Ukraine to the legislation of EU;
— The joining of Ukraine the World trading organization;
— Granting to Ukraine on the part of EU of the status of the country with market economy. It will strengthen positions of Ukraine on foreign markets. For development of depressive boundary areas it is important to keep boundary trade, to stimulate cooperation and to enter the simplified visa mode for the Ukrainian businessmen.
Bibliography:
1. Михальченко Н.И. Украинское общество: трансформация, модернизация или лимитроф Европы? – К., 2001.
2 Наталія Гусинська Міжнародна економічна інтеграція як глобальна передумова світового економічного розвитку // Регіональна економіка №4, 2000, с.185-192;
3 Л.Г. Харсун Економічні наслідки розширення ЄС на Схід // Вісник Київського національного університету імені Тараса Шевченка, № 73, 2005, с.52-53
4 Lenta.ru, http://www.tribuna.com.ua; 28.04.2005
5 Ирина Бакаева Проблемы конвергенции стран Центральной и Восточной Европы с Европейским Союзом. // Економіст №2, 2003, с.36-38
6. Б.Губский Европейский вектор интеграционной политики Украины // Экономика Украины №5, 2004, с.19-27
7. Сорос Дж. Криза глобального капіталізму: (Відкрите суспільство під загрозою). К., „Основи”, 1999, с.242
8. Т. Щербакова, А. Блинов. Открытый шанс закрытого ЕС // Украинский деловой еженедельник «Контракты» № 47, 2003