Autobiography
Library
Links
Report about the search
Charming stories
Portal of master's degrees of DonNTU
DonNTU

ABSTRACT OF THESIS
The theme of a master's degree research: «The elaboration of theoretical fundamentals calculations of technological
gasses cleaning with ethanolamine solutions»
Author: Komissarova Olga Vladimirovna
Natural, coke and other technological gases contain sulfurous and other noxious contaminants precluding their
disposal as fuel or chemical raw stock without any preliminary cleaning. Being used both in everyday life and in
technological operations the gas is to contain the minimal amount of acid components. On one hand, sulfurous compounds
and their combustion products harmfully influence the man's health. On other hand, such compounds as hydrogen sulfide,
mercaptan, and other impurities, liberated from gases appear to be valuable raw materials for other segments of
industry and national economy in general.
Limited natural resources stipulate involvement into gas processing less qualitative raw stock with high hydrogen
sulfide and mercaptan content, the raw stock having unwanted correlation of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide and
other unfavorable raw material contaminants. As a result, there emerges the necessity in gas processing plants
working facilities modification. With facilities modernization all the accumulated experience of analogous equipment
maintenance (in our country and abroad) should be taken into account.
Recently the largest natural gas bowels containing considerable amount of acid components have been discovered.
That is why the new gas processing plants where the process of amic cleaning for acid components extraction out of
natural gas is used have been built and implemented.
Allowing for the prospect of sulfurous gas processing scope increase and the wide spread of amic cleaning in gas
industry, a great attention should be paid to the elaboration and the choice of a sure amic cleaning process design
procedure. For the working facilities operation analysis and the survey results processing and generalization it is
necessary to work out not only reliable but rather simple and easy-to-use design procedures.
Skill of process and apparatus quick and correct calculation has a huge importance in enhancing capacity of the
design of new and estimation of working gas processing plants.
As far as chemical recovery industry is concerned, the majority of chemical recovery plants in Ukraine employ
vacuum-carbonate process when hydrogen sulfide absorption is preformed with the help of soda solution or soda and kali
mixture to isolate coke-oven gas and hydrogen sulfide. This method is so wide spread due to low cost of reagents and
considerably low capital and operational expenses on gas processing. This technique's principle drawback is the low
percentage of hydrogen sulfide separation which makes up 80-85% depending on the operational
mode and device status.
One of the most effective absorptive methods of gases processing (dealing with acid components separation) is
ethanolamine treatments allowing to reduce the hydrogen sulfide component in gas up to 0,1 g/m3and even less
while undergo one-stage cleaning. These kinds of treatment obtain a wide spreading in natural and oil gases
technological processing.
Designing and building of workshops for monoethanol amine desulphurization is conducted on some chemical recovery
plants.
Designing of new and reconstruction of working gases processing facilities requires theoretically grounded methods
of technological operations calculations underlying the project. Meanwhile, theoretical grounds of ethanolamine gas
cleaning methods are scarcely devised that is why their design is done using simplified relationships and diagrams
based on real-life data of industrial facilities operation.
The main task of my master's degree research is the development of classical calculation method of absorption and
desorption processes; this method relies on the equation of mass transfer for continuous phase contact devices and on
the number of concentration change stages determination for nonbridging contact devices.
This task appears to be topical both for natural gases processing technology and for chemical recovery industry in
connection with coke-oven gas monoethanol amine desulphurization processes development in some
plants of Ukraine.
One of a few attempts of theoretically grounded method of calculation for hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide
removal (from natural gas) process which is performed with help of monoethanol amine aqueous solution is represented
in reference aid [2]. However, the analysis of stated in this research interpretations of chemical reactions
equilibrium constants taking the course in solution; as well as approaches to determination of equilibrium degrees
of gas and solution components transformation, and to making up mass and heat balance of absorption process is
indicative of theoretical inefficiency of the introduced calculation method. The following errors can be pointed out.
Calculation basis is stoichiometric equations of chemical consumption reactions of acid components with
monoethanol amine solution:
2RNH2+CO2+H2O ↔ (RNH3)2CO3
(1)
(RNH3)2CO3+CO2+H2O ↔ 2RNH3HCO3
(2)
2RNH2+H2S ↔ (RNH3)2S
(3)
(RNH3)2S+H2S ↔ 2RNH3HS
(4)
where R - group OHCH2CH2-.
To define the degree of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide transformation occurring during the consumption
reactions the values of equilibrium constant are used; these are represented as follows (taking into consideration
pressure inside the apparatus and the conditions of wet reaction behaviour):

(5)
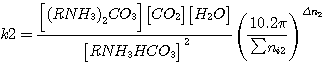
(6)
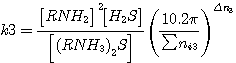
(7)
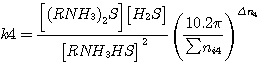
(8)
where  - pressure inside the apparatus;
- pressure inside the apparatus;
Σ ni - total number of moles in reaction mixture;
Δ n - difference in resultants and precursors number of moles
(1)-(4).
However, it should be noticed that these values are true only for gaseous phase reactions, and they are completely
incorrect for the reactions going on in solutions.
To define the degree of transformation in each reaction the base mixture composition is considered equal to
stoichiometric, whereas it is necessary to consider the actual feed composition. More than that, the transformation
degree of every reaction is defined independently from each other; the task has to be solved by means of joint
consideration of four equations. Besides, such solution is reasonable for the feedback system and also with the open
system uniflow phase movement. With the counterflow gas and liquids movement in absorbers the base mixture has a
different composition in every section, so such solution has no sense at all.
The incorrect calculation result grounded on the above mentioned formulas leads to the fact that the potion of
chemically combined carbon dioxide is 0,5% and the portion of hydrogen sulfide is 3% in a saturated solution. The rest
of the stock of these acid components is found in the unbound state. There emerges a question: Why ethanolamine should
be used if it doesn't combine the acid gases which have been absorbed?
The method of absorber heat balance composition is unreasonably complicated and contains a lot of grave errors.
For example, the gas mixture enthalpy is defined with empirical formulas for each component in relation to 0°K:

(9)
where A, B, C, D - coefficients, T - temperature.
And for solutions - in relation to 0°C according to conventional practice in thermodynamic calculations:
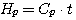
(10)
where Cp - specific heat capacity of solution, t - temperature.
Such approach to heat balance composition is prohibitive from the theoretical point of view, as during the
transformation of a substantial quantity of components from one phase into the other it will cause grave mistakes in
calculations.
From our point of view to make up the mass balance, the estimation of mass transfer motive force and absorber
dimensions determination; the equilibrium in gas - hydrogen sulfide - carbon dioxide - ethanolamine solution system
should be represented as the association of these components concentration in solution and their equilibrium pressure
in gaseous phase.
The actual form of these dependences or association could be estimated by means of joint solution of chemical
reactions equilibrium equations taking place in solutions, and absorption tie line equation worked out according to our
technique.
DESIGN PROCEDURE OF COKE-OVEN GAS ETHANOLOMINE DESULFURIZATION
The crux of the procedure is that using the set values of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in
absorbing solution the partial pressure values of these components in gas being processed are estimated at equilibrium
with the help of a joint solution of equilibrium equation of reaction taking place in the solution:
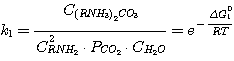
(11)
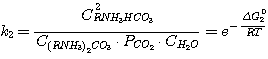
(12)
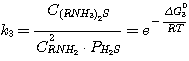
(13)

(14)
where C(RNH3)2CO3, CRNH3HCO3,
C(RNH3)2S, CRNH3HS, CRNH2 - mole
concentrations of correspondent compounds in solution at equilibrium, kmole/m3;
Δ G01, Δ G02,
Δ G03,
Δ G04 - standard isobaric potential alteration while the above mentioned reactions flow.
Disregarding free carbon dioxide concentration in solution, its general concentration in solution can be presented
as the concentrations sum of ethanolamine carbonate and hydrogen carbonate:
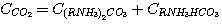
(15)
By analogy, the total hydrogen sulfide concentration in solution can be represented as follows:

(16)
To solve the set of equations (1), (2), (3), (4) let's express concentrations
C(RNH3)2CO3, CRNH3HCO3,
C(RNH3)2S and CRNH3HS via carbon dioxide and hydrogen
sulfide general concentrations in solution:

(17)
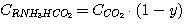
(18)

(19)
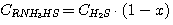
(20)
ãäå y - carbon dioxide fraction in solution combined and expressed as
C(RNH3)2CO3;
x - hydrogen sulfide fraction in solution combined and expressed as
C(RNH3)2S.
Free ethanolamine concentration in solution at equilibrium can be expressed as follows:
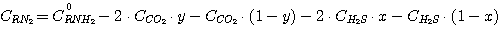
(21)
or

(22)
where C0RNH2 - ethanolamine initial concentration in solution delivered into absorber.
In this case the equations take on the following form:
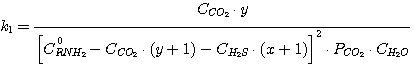
(23)
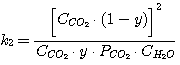
(24)
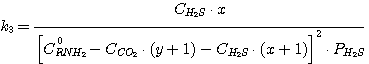
(25)

(26)
Solving the equations jointly (13), (14), (15), (16) and having the known K-values k1,
k2, k3, k4 as well as the set C0RNH2,
CCO2, CH2S values we obtain the x, y, PH2S and
PCO2 value.
Calculation results are represented in the form of diagrams PCO2 - CCO2 and
PH2S - CH2S and empirical dependences
PCO2 = f1(CCO2),
PH2S = f2(CH2S).
In taken values CCO2 and CH2S correlations can't be arbitrary as they
are defined by tie line equations of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide absorption processes as shown in Figure 1,
and these equations can be represented in this way:
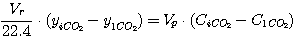
(27)
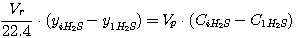
(28)
ãäå Vr - gas flow rate, nm3/hour;
yiCO2, yiH2S -
carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in gas, kmole/nm3 (gas);
Vp - solution consumption, m3/hour;
CiCO2, CiH2S - carbon dioxide and
hydrogen sulfide concentration in solution, kmole/nm3.
Intaking different values yiCO2 and yiH2S define the concentration
values of CiCO2 and CiH2S (various absorber sections are considered)
in concentration range starting with y1 up to yn. To obtain CiCO2
and CiH2S values carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide equilibrium pressure in gas which is in
process should be defined according to the considered method.

Figure 1 - The distribution of use rate concentration in gas and solution according to height of absorber.
© DonNTU Komissarova O.V. 2008
Author: Komissarova Olga Vladimirovna
2RNH2+CO2+H2O ↔ (RNH3)2CO3 |
(1) |
(RNH3)2CO3+CO2+H2O ↔ 2RNH3HCO3 |
(2) |
2RNH2+H2S ↔ (RNH3)2S |
(3) |
(RNH3)2S+H2S ↔ 2RNH3HS |
(4) |
where R - group OHCH2CH2-.
|
|
(5) |
|
|
(6) |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
(8) |
where  - pressure inside the apparatus;
- pressure inside the apparatus;
Σ ni - total number of moles in reaction mixture;
Δ n - difference in resultants and precursors number of moles
(1)-(4).
However, it should be noticed that these values are true only for gaseous phase reactions, and they are completely
incorrect for the reactions going on in solutions.
To define the degree of transformation in each reaction the base mixture composition is considered equal to
stoichiometric, whereas it is necessary to consider the actual feed composition. More than that, the transformation
degree of every reaction is defined independently from each other; the task has to be solved by means of joint
consideration of four equations. Besides, such solution is reasonable for the feedback system and also with the open
system uniflow phase movement. With the counterflow gas and liquids movement in absorbers the base mixture has a
different composition in every section, so such solution has no sense at all.
The incorrect calculation result grounded on the above mentioned formulas leads to the fact that the potion of
chemically combined carbon dioxide is 0,5% and the portion of hydrogen sulfide is 3% in a saturated solution. The rest
of the stock of these acid components is found in the unbound state. There emerges a question: Why ethanolamine should
be used if it doesn't combine the acid gases which have been absorbed?
The method of absorber heat balance composition is unreasonably complicated and contains a lot of grave errors.
For example, the gas mixture enthalpy is defined with empirical formulas for each component in relation to 0°K:

(9)
where A, B, C, D - coefficients, T - temperature.
And for solutions - in relation to 0°C according to conventional practice in thermodynamic calculations:
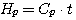
(10)
where Cp - specific heat capacity of solution, t - temperature.
Such approach to heat balance composition is prohibitive from the theoretical point of view, as during the
transformation of a substantial quantity of components from one phase into the other it will cause grave mistakes in
calculations.
From our point of view to make up the mass balance, the estimation of mass transfer motive force and absorber
dimensions determination; the equilibrium in gas - hydrogen sulfide - carbon dioxide - ethanolamine solution system
should be represented as the association of these components concentration in solution and their equilibrium pressure
in gaseous phase.
The actual form of these dependences or association could be estimated by means of joint solution of chemical
reactions equilibrium equations taking place in solutions, and absorption tie line equation worked out according to our
technique.
DESIGN PROCEDURE OF COKE-OVEN GAS ETHANOLOMINE DESULFURIZATION
The crux of the procedure is that using the set values of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in
absorbing solution the partial pressure values of these components in gas being processed are estimated at equilibrium
with the help of a joint solution of equilibrium equation of reaction taking place in the solution:
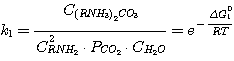
(11)
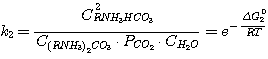
(12)
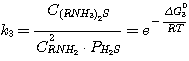
(13)

(14)
where C(RNH3)2CO3, CRNH3HCO3,
C(RNH3)2S, CRNH3HS, CRNH2 - mole
concentrations of correspondent compounds in solution at equilibrium, kmole/m3;
Δ G01, Δ G02,
Δ G03,
Δ G04 - standard isobaric potential alteration while the above mentioned reactions flow.
Disregarding free carbon dioxide concentration in solution, its general concentration in solution can be presented
as the concentrations sum of ethanolamine carbonate and hydrogen carbonate:
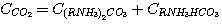
(15)
By analogy, the total hydrogen sulfide concentration in solution can be represented as follows:

(16)
To solve the set of equations (1), (2), (3), (4) let's express concentrations
C(RNH3)2CO3, CRNH3HCO3,
C(RNH3)2S and CRNH3HS via carbon dioxide and hydrogen
sulfide general concentrations in solution:

(17)
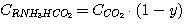
(18)

(19)
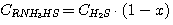
(20)
ãäå y - carbon dioxide fraction in solution combined and expressed as
C(RNH3)2CO3;
x - hydrogen sulfide fraction in solution combined and expressed as
C(RNH3)2S.
Free ethanolamine concentration in solution at equilibrium can be expressed as follows:
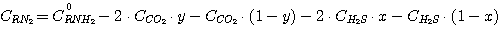
(21)
or

(22)
where C0RNH2 - ethanolamine initial concentration in solution delivered into absorber.
In this case the equations take on the following form:
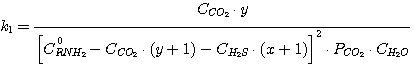
(23)
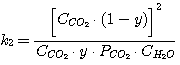
(24)
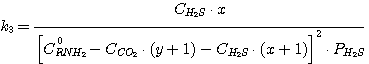
(25)

(26)
Solving the equations jointly (13), (14), (15), (16) and having the known K-values k1,
k2, k3, k4 as well as the set C0RNH2,
CCO2, CH2S values we obtain the x, y, PH2S and
PCO2 value.
Calculation results are represented in the form of diagrams PCO2 - CCO2 and
PH2S - CH2S and empirical dependences
PCO2 = f1(CCO2),
PH2S = f2(CH2S).
In taken values CCO2 and CH2S correlations can't be arbitrary as they
are defined by tie line equations of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide absorption processes as shown in Figure 1,
and these equations can be represented in this way:
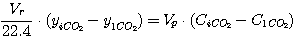
(27)
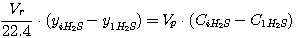
(28)
ãäå Vr - gas flow rate, nm3/hour;
yiCO2, yiH2S -
carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in gas, kmole/nm3 (gas);
Vp - solution consumption, m3/hour;
CiCO2, CiH2S - carbon dioxide and
hydrogen sulfide concentration in solution, kmole/nm3.
Intaking different values yiCO2 and yiH2S define the concentration
values of CiCO2 and CiH2S (various absorber sections are considered)
in concentration range starting with y1 up to yn. To obtain CiCO2
and CiH2S values carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide equilibrium pressure in gas which is in
process should be defined according to the considered method.

Figure 1 - The distribution of use rate concentration in gas and solution according to height of absorber.
© DonNTU Komissarova O.V. 2008
|
|
(9) |
where A, B, C, D - coefficients, T - temperature.
|
|
(10) |
where Cp - specific heat capacity of solution, t - temperature.
DESIGN PROCEDURE OF COKE-OVEN GAS ETHANOLOMINE DESULFURIZATION
The crux of the procedure is that using the set values of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in
absorbing solution the partial pressure values of these components in gas being processed are estimated at equilibrium
with the help of a joint solution of equilibrium equation of reaction taking place in the solution:
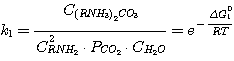
(11)
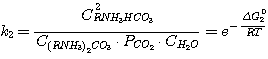
(12)
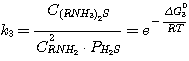
(13)

(14)
where C(RNH3)2CO3, CRNH3HCO3,
C(RNH3)2S, CRNH3HS, CRNH2 - mole
concentrations of correspondent compounds in solution at equilibrium, kmole/m3;
Δ G01, Δ G02,
Δ G03,
Δ G04 - standard isobaric potential alteration while the above mentioned reactions flow.
Disregarding free carbon dioxide concentration in solution, its general concentration in solution can be presented
as the concentrations sum of ethanolamine carbonate and hydrogen carbonate:
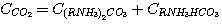
(15)
By analogy, the total hydrogen sulfide concentration in solution can be represented as follows:

(16)
To solve the set of equations (1), (2), (3), (4) let's express concentrations
C(RNH3)2CO3, CRNH3HCO3,
C(RNH3)2S and CRNH3HS via carbon dioxide and hydrogen
sulfide general concentrations in solution:

(17)
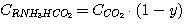
(18)

(19)
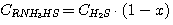
(20)
ãäå y - carbon dioxide fraction in solution combined and expressed as
C(RNH3)2CO3;
x - hydrogen sulfide fraction in solution combined and expressed as
C(RNH3)2S.
Free ethanolamine concentration in solution at equilibrium can be expressed as follows:
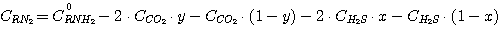
(21)
or

(22)
where C0RNH2 - ethanolamine initial concentration in solution delivered into absorber.
In this case the equations take on the following form:
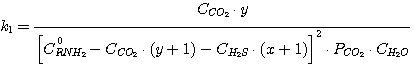
(23)
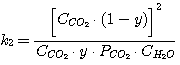
(24)
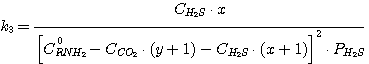
(25)

(26)
Solving the equations jointly (13), (14), (15), (16) and having the known K-values k1,
k2, k3, k4 as well as the set C0RNH2,
CCO2, CH2S values we obtain the x, y, PH2S and
PCO2 value.
Calculation results are represented in the form of diagrams PCO2 - CCO2 and
PH2S - CH2S and empirical dependences
PCO2 = f1(CCO2),
PH2S = f2(CH2S).
In taken values CCO2 and CH2S correlations can't be arbitrary as they
are defined by tie line equations of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide absorption processes as shown in Figure 1,
and these equations can be represented in this way:
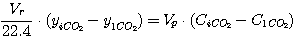
(27)
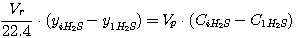
(28)
ãäå Vr - gas flow rate, nm3/hour;
yiCO2, yiH2S -
carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in gas, kmole/nm3 (gas);
Vp - solution consumption, m3/hour;
CiCO2, CiH2S - carbon dioxide and
hydrogen sulfide concentration in solution, kmole/nm3.
Intaking different values yiCO2 and yiH2S define the concentration
values of CiCO2 and CiH2S (various absorber sections are considered)
in concentration range starting with y1 up to yn. To obtain CiCO2
and CiH2S values carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide equilibrium pressure in gas which is in
process should be defined according to the considered method.

Figure 1 - The distribution of use rate concentration in gas and solution according to height of absorber.
© DonNTU Komissarova O.V. 2008
|
|
(11) |
|
|
(12) |
|
|
(13) |
|
|
(14) |
where C(RNH3)2CO3, CRNH3HCO3, C(RNH3)2S, CRNH3HS, CRNH2 - mole concentrations of correspondent compounds in solution at equilibrium, kmole/m3;
Δ G01, Δ G02, Δ G03, Δ G04 - standard isobaric potential alteration while the above mentioned reactions flow.
|
|
(15) |
|
|
(16) |
|
|
(17) |
|
|
(18) |
|
|
(19) |
|
|
(20) |
ãäå y - carbon dioxide fraction in solution combined and expressed as C(RNH3)2CO3;
x - hydrogen sulfide fraction in solution combined and expressed as C(RNH3)2S.
|
|
(21) |
or
|
|
(22) |
where C0RNH2 - ethanolamine initial concentration in solution delivered into absorber.
|
|
(23) |
|
|
(24) |
|
|
(25) |
|
|
(26) |
|
|
(27) |
|
|
(28) |
ãäå Vr - gas flow rate, nm3/hour;
yiCO2, yiH2S - carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in gas, kmole/nm3 (gas);
Vp - solution consumption, m3/hour;
CiCO2, CiH2S - carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide concentration in solution, kmole/nm3.
